* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Suggestion from clinicians
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Prescription drug prices in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacognosy wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of beta-blockers wikipedia , lookup
Prescription costs wikipedia , lookup
Pharmaceutical industry wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Drug interaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
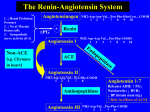
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
Losartan vs Candasartan vs Valsartan Replacement to the List Peer Feedback: “candasartan or valsartan - losartan has flat dose response curve, other effective ARB are available” Literature Review Question: What is the most effective ARB of Losartan, Candasartan, and Valsartan? Literature Search: eCPS – Hypertension; Cochrane Pubmed – “angiotensin receptor blockers AND losartan AND (candesartan OR valsartan) AND (effect OR efficacy) AND meta-analysis/review” Candesartan and losartan in essential hypertension (2011) In this systematic review and meta-analysis, we reviewed 12 studies that compared the effects and safety of candesartan versus losartan. Comparing the common therapeutic dose of the two agents, candesartan showed a superior lowering of SBP and DBP compared with losartan at trough after a 24 h dose. When comparing double dosage or titration to double dosage of the two agents, similar results were found at trough and peak after administration. Nevertheless, the response and blood pressure-controlling efficacy of candesartan in follow-up was superior to that of losartan. The results of this meta-analysis indicate that candesartan is more effective than losartan in reducing blood pressure. There was no evident difference in their common adverse events profiles. Candesartan seems to cause fewer serious adverse events than losartan. Zheng, Zhenfeng, et al. "A systematic review and meta-analysis of candesartan and losartan in the management of essential hypertension."Journal of Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (2011): 1470320310391503. Candesartan compared to other ARBs (2011) Clinical trials have demonstrated that candesartan cilexetil is an effective agent in reducing the risk of cardiovascular mortality, stroke, heart failure, arterial stiffness, renal failure, retinopathy, and migraine in different populations of adult patients including patients with coexisting type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, or kidney impairment. Clinical evidence confirmed that candesartan cilexetil provides better antihypertensive efficacy than losartan and is at least as effective as telmisartan and valsartan. Candesartan cilexetil, one of the current market leaders in BP treatment, is a highly selective compound with high potency, a long duration of action, and a tolerability profile similar to placebo. Cernes, Relu, Margarita Mashavi, and Reuven Zimlichman. "Differential clinical profile of candesartan compared to other angiotensin receptor blockers."Vascular health and risk management 7 (2011): 749. Valsartan Meta-analysis (2009) In all, 31 RCTs (n = 13,110 patients) were included in the analysis. This meta-analysis demonstrates that valsartan at doses of 160 and 320 mg is more effective in reducing BP than losartan at the 100 mg dose. At comparable doses, valsartan achieves comparable antihypertensive efficacy to the other ARBs. Findings confirm that valsartan has a strong dose– response relationship when increasing from 80 to 160 mg and 320 mg and that further head-tohead trial are warranted. The clinical application of these results should take into consideration the limitations discussed in this analysis Nixon, R. M., et al. "Valsartan vs. other angiotensin II receptor blockers in the treatment of hypertension: a meta‐analytical approach." International journal of clinical practice 63.5 (2009): 766-775. ARBs Cochrane (2008) Is there a difference in the magnitude of BP lowering effect between individual drugs in the ARB class? This review provides a reasonable amount of data to assess the trough BP lowering effect of 9 different ARBs. When the different ARBs are compared, there is a similarity in their BP lowering effects at trough. When the best estimate of the near maximal BP lowering efficacy of these 9 drugs is compared, they range from -6/-3 mm Hg to -10/-7 mm Hg. For many of the drugs, there are insufficient data for a full range of doses. Therefore it remains possible that there could be differences between some of the drugs. However, the data are most consistent with the near maximum BP lowering effect of each of the drugs being the same. It would require head-to-head trials of different ARBs at equivalent BP lowering doses to assess whether or not there are differences in the BP lowering efficacy between different drugs. This review provides useful doseresponse information for estimating equivalent doses and thus designing trials to compare different ARBs. Heran, Balraj S., et al. "Blood pressure lowering efficacy of angiotensin receptor blockers for primary hypertension." The Cochrane Library (2008). eCPS (2015) Table 6: Drugs Used for Hypertension Class Drug Dosage Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARB) candesartan Initial: 8 mg/day Usual: 8–16 mg/day Once daily po Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARB) losartan Angiotensin Receptor Blockers Atacand, gen erics Cozaar, gener ics valsartan Diovan, gener Initial: 50 mg/day Usual: 25–100 mg/day Maximum:100 mg/day Once daily or divided BID po Initial: 80 mg/day Usual: 80–320 mg/day Adverse Effects Drug Interactions Comments Costa $ Hyperkalemia. Can precipitate renal failure in susceptible patients (bilateral renovascular disease, those with volume depletion or with concurrent NSAID use). Angioedema has been reported, but a causal association has not been established. Marked increase in serum K+ in patients receiving K+supplements and/or K+-sparing diuretics. May elevate Li+levels (monitor Li+levels, adjust dose). Contraindicated in pregnancy—caution when prescribing to women of child-bearing potential.7 $ Use lower initial doses in patients who are volume depleted or on diuretics (increased risk of hypotension in hypovolemia). Hyperkalemia usually occurs only in those on K+ supplements or drugs that cause K+retention, those with renal impairment or diabetics with high serum K+ levels. Assess SCr and K+ after a few days, then regularly. $ Class (ARB) Drug Dosage ics Once daily po Legend: $<$20 Adverse Effects $-$$ <20–40 Drug Interactions $$ 20–40 Costa Comments $$$ 40–60 $$$$ 60–80 Cardiovascular Disorders: Hypertension; Norm R.C. R. C. Campbell, MD, FRCPC, Paul Gibson, MD, FRCPC, and Ross T. Tsuyuki, PharmD, MSc, FCSHP, FACC; Date of Revision: March 2015 Medication losartan Uses hypertension, delay diabetic nephropathy Contraindications (CI), drug interactions (DI) or cautions CI: bilateral artery stenosis or kidney stenosis if only 1 kidney), angioedema, pregnancy(T2 and T3) DI: increases lithium and potassium, fluconazole, rifampin (decrease efficacy) Adverse Effects (common and severe) hypotension, cough, headache, dizziness, fatigue, angioedema, hyperkalemia Initial dose; typical dose 25mg; 25100mg one time a day Monitoring electrolytes, renal function (SCr, BUN, electrolytes)