* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hydrochloric acid
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
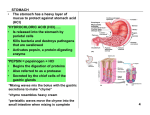
ANTACIDS Selin Palabıyıkoğlu 12-D What is antacid? Antacids are medicines that neutralize stomach acidity. The stomach secretes: • Hydrochloric acid: the hydrogen ion concentration of the HCl normally cause pH to be between 1.5-2.5 • Bicarbonate: helps buffer acidic properties of HCl • Pepsinogen: a precursor for the enzyme pepsin that breaks down proteins into peptides. • Mucus: protective barrier against HCl These are known collectively as gastric juice. Factors Affecting the Balance in the Stomach Mucosa Aggressive Factors Protective Factors Stomach Acidity Pepsin Alcohol, nicotine Anxiety Helicobacter pylori sytotoxine (bacteria usually affecting the ulcer) Drugs ( Aspirin and other analgesics) Mucus production Mucosal blood circulation Cell repairing Bicarbonate production Acid related diseases can arise if the stomach lining is damaged or when too much acid is produced. Acid Related Diseases 1) Indigestion 2) Peptic Ulcer 3) Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) Indigestion The discomfort caused by excess acid is known as indigestion and may result from overeating, alcohol, smoking, anxiety or in some people from eating certain types of food. Peptic Ulcer • Peptic ulcers are localized wounds in the stomach, duodenum and lower esophagus mucosa with tissue destruction. • “Peptic” reflects a belief (probably misplaced) that peptic activity is related with pepsin. • The common symptom is pain occurring before meals or overnight, relieved by antacids, milk and food. GERD • It is defined as present in an individual who experiences typical symptoms of GERD (heartburn, acid regurgitation to mouth, belching, globus sensation, chronic cough and hoarsenes), due to reflux of stomach contents into esophagus. • Mucosal injury may present or not. • It is a very common disorder affecting between 1030% of western population. • Especially common in pregnant women and obese people. Antacids • Antacids work by neutralizing the acid, preventing inflammation, relieving pain and discomfort, allowing the mucus layer and stomach lining to mend. • When used in the treatment of ulcers, they prevent acid from attacking the damaged stomach lining and so allow the ulcer to heal. • They are most affective if taken between one and three hours after eating, as food typically remains in the stomach for up to four hours after a meal. • Antacids are intended to treat digestive upset by raising the pH level of the stomach from a highly acidic 2 to between 3 and 4. This can neutralise up to 99% of the excess acid in the stomach, leading to substantial relief from symptoms for most people. • Raising gastric pH from 1.3 to 1.6 neutralizes 50% of the gastric acid. • Raising gastric pH 1 point (1.3 to 2.3) neutralizes 90% of the gastric acid. • Antacids are bases, usually, metal oxides, hydroxides, carbonates or hydrogen carbonates (bicarbonates) to neutralize excess acidity. • They begin to work within a minute and can provide a relief that ranges from 10 minutes to more than 90 minutes. Action of Antacids • Magnesium Oxide: MgO(s)+ 2HCl(aq) MgCl2(aq) + H2O(l) • Magnesium Hydroxide: Mg(OH)2(aq)+2HCl(aq) MgCl2(aq)+ 2H2O(l) • Aluminum Hydroxide: Al(OH)3(s)+3HCl(aq) AlCl3(aq)+ 3H2O(l) • Calcium Carbonate: CaCO3(s) + 3HCl (aq) CaCl2(aq)+H2O(l)+CO2(g) • Sodium Bicarbonate: NaHCO3(aq)+HCl(aq)NaCl2(aq)+H2O(l)+CO2(g) • Magnesium Trisilicate: Mg2Si3O8(s)+4HCl(aq)3SiO2(s)+2H2O(l) +2MgCl2(aq) • Antacids are combined with chemicals called alginates that produce a neutralising layer that prevents acid reflux. They prevent acid in the stomach from rising into the esophagus and causing “heartburn”. • Similarly, anti-foaming agents, such as dimethicone or simethicone are added to reduce the surface tension of gas bubbles, causing them to come together, producing a defoaming action. BRAND NAME INGREDIENTS Tums® CaCO3, MgCO3, MgSi3O8 (magnesium trisilicate) Rennie® CaCO3, MgCO3, NaC6H7O (sodium alginate) Rotaids® AlNa(OH)2CO3 (dihidroxylaluminum sodium carbonate Dank®, Kompensan® AlNa(OH)2CO3 Maalox® Asidal®, Mucaine®, Simeco® Mg(OH)2, Al(OH)3 , simethicone Di-Gel® CaCO3 Alca-Seltzer® NaHCO3, citric acid, aspirin Milk of Magnesia® Mg(OH)2 Amphogel® Al(OH)3 Side Effects Side effects are very rare. They are more likely when the medicine is taken large doses or over a long time. Aluminum Compounds constipation or irregularity prevent uptake of phosphate ions causing possible bone damage if taken in high doses over a long period Magnesium Compounds diarrhea Calcium Carbonate excessive amount of calcium ions being absorbed into the body kidney stones Sodium Ions hypertension Excessive use of Sodium Bicarbonate alkalosis ( alkaline stomach causes discomfort and is often mistaken as being due to an acidic stomach so one takes more antacid, making the stomach still more alkaline, causing more indigestion) fluid retention ( bloating) Precautions • Antacids should not be given to children under 6 years old. • Before combining antacids with extra calcium ( dairy products or calcium supplements) ask for assistance. • Be careful in low-sodium diet( hypertension cases) • Occasional use of antacids in small amounts is safe during pregnancy. • Magnesium containing antacids should be avoided in patients with chronic kidney failure. • Absorbtion of some antibiotics and iron inhibited by antacids. Acid “Rebound” Antacids show the most rapid action but may cause acid “rebound”: a condition in which the gastric acid return in greater concentrations after the drug effect has stopped. • Remember that; Antacids DO NOT prevent the overproduction of acid. Antacids DO neutralize the acid once it’s in the stomach. Questions 1) Which would be the most effective in combating indigestion- a spoonful of liquid containing 1.00 g of magnesium hydroxide, or a spoonful of liquid containing 1.00 g of aluminum hydroxide? 2) One common type of drug taken orally is antacid. Antacids such as sodium hydrogencarbonate are taken to reduce stomach acidity. (i) State the names of two metals, other than sodium, whose compounds are often used in antacids. (ii)Give an equation for the neutralization of HCl in the stomach by sodium hydrogencarbonate. (iii) Explain how heartburn is caused. (iv)Explain why dimethicone is added to some antacids.