* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circular Motion and Gravity Jeopardy
Pioneer anomaly wikipedia , lookup
Torque wrench wikipedia , lookup
Roche limit wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Equivalence principle wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gravity wikipedia , lookup
Newton's law of universal gravitation wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to general relativity wikipedia , lookup
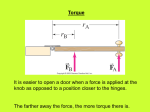
THIS IS Enjoy Your Circular Motion & Gravitaion Going in Circles Centripetal Force Torque Law of Gravitation Vocabulary Assorted 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Spinning motion of a body A 100 What is rotational motion? A 100 The type of motion experienced by someone in a Ferris wheel car. A 200 What is circular motion? A 200 The velocity of an object moving around in a circular path. A 300 What is tangential velocity (circular velocity)? A 300 The direction of the tangential velocity vector with respect to the circular path in which an object moves (or with respect to centripetal force acting on the object). A 400 What is tangent to the circle? (or perpendicular to the centripetal force acting on the object) A 400 Angular motion is measured in these units. (There are 2π of these in a full circle.) A 500 What are radians (rad)? A 500 The units of centripetal force. B 100 What are Newtons (N)? B 100 Centripetal force is directed here. B 200 What is towards the center of the circle? B 200 Racetrack designers make sure the curves are produced in this manner to generate centripetal force needed to help the cars stay on the path. B 300 What is banked? B 300 Acceleration of an object directed toward the center of the circular path in which it moves. . B 400 What is centripetal acceleration? B 400 The centripetal force needed to keep the moon orbiting the Earth is equivalent to this force. B 500 What is gravitational force? B 500 Torque is a force that does this. C 100 What is twist, turn or rotate an object? C 100 The tool used to apply torque to a bolt. C 200 What is a wrench ? C 200 Torque depends on two things: a force, and a ______arm. C 300 What is the lever arm? C 300 DAILY DOUBLE C 400 The torque lever arm is the perpendicular distance from this axis to the direction of the force applied. C 400 What is the rotational axis? C 400 The units of torque. C 500 What are Newton-meters or Foot-pounds? C 500 Scientist developed a Universal Law of Gravitation. D 100 Who is Sir Isaac Newton? D 100 These are two factors of objects related to their gravitational attraction for one another. D 200 What are mass and distance from each other? D 200 The force of gravitational attraction between two objects is directly proportional to this. D 300 What is mass? D 300 This is how much the gravitational force of attraction decreases as the distance between two objects doubles. D 400 What is by a factor of four? D 400 6.67259 x 10-11 N m2/kg2 is the value of this number associated with calculations of the force of gravitational attraction. D 500 What is G, the Universal Gravitational constant (constant of proportionality)? D 500 The average position of an object’s mass. E 100 What is the center of mass? E 100 Constant tangential speed. E 200 What is uniform circular motion? E 200 The average location of the weight of an object. E 300 What is the center of gravity? E 300 This quantity measures the resistance to a change in rotational motion. E 400 What is the moment of inertia? E 400 This adjective describes the motion of a body as it shifts from one point in space to another. It normally takes place in straight line. (Non physics definition: related to a job of converting speech from one language to another.) E 500 What is translational? E 500 This helps cause the tides. F 100 What are the gravitational forces exerted by the Earth and its moon? F 100 This scientist used a torsional balance to calculation the Universal gravitational constant. F 200 Who is Lord Henry Cavendish? F 200 If you swing a ball attached to a string in a circle above your head, and the string breaks, this causes the ball to fly off ’s in a straight line path. F 300 What is the ball’s inertia? F 300 This is said of satellites that are in orbit around the Earth. (and causes astronauts on the ISS to be weightless). F 400 What is they are in a continual state of free fall? F 400 Einstein didn’t believe that gravity was a force at all, but a curve or distortion in this. F 500 What is the shape of spacetime (“fabric of space”)? F 500 The Final Jeopardy Category is: Einstein’s Gravity Please record your wager. Click on screen to begin Einstein’s theory that describes gravity as a distortion of the shape of space-time. Click on screen to continue What is The General Theory of Relativity? Click on screen to continue Thank You for Playing Jeopardy Please do well on your test! Game Designed By C. Harr-MAIT