Force
... To find the sum of the two forces, graph the vectors and use the “head-totail” method. Follow these five steps: Step 1: Draw the 40-lb force. Draw a horizontal line on a sheet of notebook paper, or use a horizontal grid line on a sheet of graph paper. See Figure 1.12. Choose a convenient scale, such ...
... To find the sum of the two forces, graph the vectors and use the “head-totail” method. Follow these five steps: Step 1: Draw the 40-lb force. Draw a horizontal line on a sheet of notebook paper, or use a horizontal grid line on a sheet of graph paper. See Figure 1.12. Choose a convenient scale, such ...
Chapter 18 Static Equilibrium
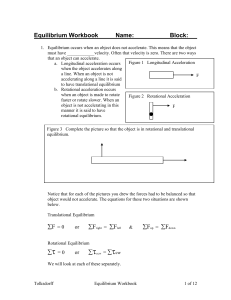
... Figure 18.3 Free-body force diagrams for each body. The condition that the forces sum to zero is not sufficient to completely predict the motion of the beam. All we can deduce is that the center of mass of the system is at rest (or moving with a uniform velocity). In order for the beam not to rotate ...
... Figure 18.3 Free-body force diagrams for each body. The condition that the forces sum to zero is not sufficient to completely predict the motion of the beam. All we can deduce is that the center of mass of the system is at rest (or moving with a uniform velocity). In order for the beam not to rotate ...
Rotational Dynamics SL and Honors 2016 2017
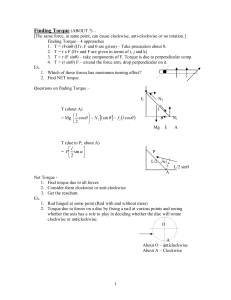
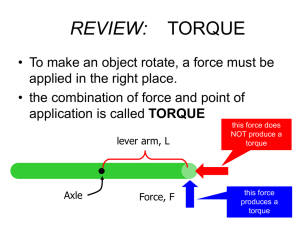
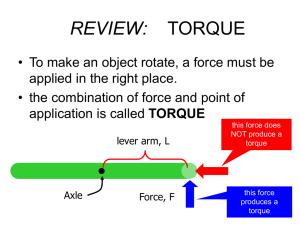
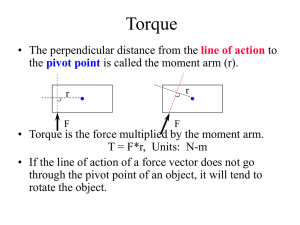
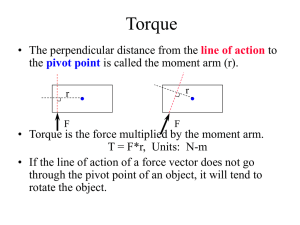
... has been broken up into its’ perpendicular and parallel components as shown. • This second method (which I like better) is to let the lever arm be the distance from the axis to the force, shown here as “r” and then just use the perpendicular component of the force, shown by F ...
... has been broken up into its’ perpendicular and parallel components as shown. • This second method (which I like better) is to let the lever arm be the distance from the axis to the force, shown here as “r” and then just use the perpendicular component of the force, shown by F ...
Angular Kinetics
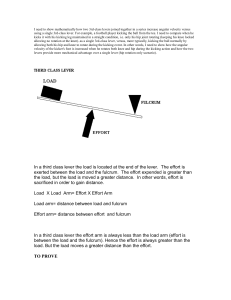
... • A lever consists of two forces (motive and resistance forces) acting around a pivot point (axis or fulcrum). • The perpendicular distance from the line of action of the effort force to the fulcrum is called the motive arm. • The perpendicular distance from the line of action of the resistance forc ...
... • A lever consists of two forces (motive and resistance forces) acting around a pivot point (axis or fulcrum). • The perpendicular distance from the line of action of the effort force to the fulcrum is called the motive arm. • The perpendicular distance from the line of action of the resistance forc ...
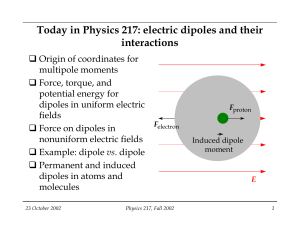
Today in Physics 217: electric dipoles and their interactions
... and the electrical properties of materials made with these components are decisively influenced by the behaviour of these dipoles in each others’ fields. Some materials are of course made up of neutral, non-polar components, but even these can have dipole moments induced by external fields. Consider ...
... and the electrical properties of materials made with these components are decisively influenced by the behaviour of these dipoles in each others’ fields. Some materials are of course made up of neutral, non-polar components, but even these can have dipole moments induced by external fields. Consider ...
Ch13 Powerpoint
... In the body, weight of a segment cannot be altered instantaneously. Therefore, torque of a segment due to gravitational force can be changed only by changing the length of the moment arm. ...
... In the body, weight of a segment cannot be altered instantaneously. Therefore, torque of a segment due to gravitational force can be changed only by changing the length of the moment arm. ...
Lecture 07: Equilibrium I: Statics, Center of Gravity
... A seesaw consisting of a uniform board of mass mpl and length L supports at rest a father and daughter with masses M and m, respectively. The support is under the center of gravity of the board, the father is a distance d from the center, and the daughter is a distance 2.00 m from the center. A) Fin ...
... A seesaw consisting of a uniform board of mass mpl and length L supports at rest a father and daughter with masses M and m, respectively. The support is under the center of gravity of the board, the father is a distance d from the center, and the daughter is a distance 2.00 m from the center. A) Fin ...