F g - mrbernabo
... An object will only change its Rotational speed if a Net Torque is applied. No net Torque = keeps rotating at the same speed ...
... An object will only change its Rotational speed if a Net Torque is applied. No net Torque = keeps rotating at the same speed ...
Torque, Energy, Rolling
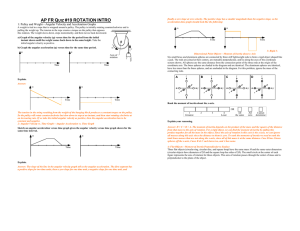
... When the force is at some angle, the perpendicular component causes the rotation ...
... When the force is at some angle, the perpendicular component causes the rotation ...
Midterm I Physics 231
... can write the tension in terms of the angular velocity: T=m2R. This means that for a fixed radius, if we double the angular speed, then the tension is 22=4 quadrupled. The correct answer is 6x4=24N. ...
... can write the tension in terms of the angular velocity: T=m2R. This means that for a fixed radius, if we double the angular speed, then the tension is 22=4 quadrupled. The correct answer is 6x4=24N. ...
2AngDyn - TuHS Physics
... use = rFsin, r = .24 m, F = 16 N But is not 56o. You want to use the angle between r and F which is 90 – 56 = 34o Finally, = (.24 m)(16 N)sin(34o) = 2.1 Nm TOC ...
... use = rFsin, r = .24 m, F = 16 N But is not 56o. You want to use the angle between r and F which is 90 – 56 = 34o Finally, = (.24 m)(16 N)sin(34o) = 2.1 Nm TOC ...
Circular Motion and Torque
... Uniform Circular Motion • Motion in a perfect circle (so the radius is always the same) at a constant speed. ...
... Uniform Circular Motion • Motion in a perfect circle (so the radius is always the same) at a constant speed. ...
Rotational Motion
... torque on the object. • The magnitude of the torque due to a given force is the product of the perpendicular distance from the axis to the line of application of the force (the lever arm) and the magnitude of the force. • The rate of change of the rotational motion is most simply expressed by defini ...
... torque on the object. • The magnitude of the torque due to a given force is the product of the perpendicular distance from the axis to the line of application of the force (the lever arm) and the magnitude of the force. • The rate of change of the rotational motion is most simply expressed by defini ...
force
... Diagram B The force is resolved into components and the perpendicular component is used with the original moment arm. τ = rFsinθ Either method for calculating torque is acceptable ...
... Diagram B The force is resolved into components and the perpendicular component is used with the original moment arm. τ = rFsinθ Either method for calculating torque is acceptable ...
Chapter 8
... The lever arm, d, is the perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation to a line drawn along the direction of the force d = r sin q ...
... The lever arm, d, is the perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation to a line drawn along the direction of the force d = r sin q ...
(CON)CircularMotion
... 1. The amount of force exerted 2. The distance between the force and the axis of rotation Lever Arm – the distance between the applied force and the axis; measured in meters. Example: Using a wrench. Hold close to bolt, it’s harder to turn than when you hold farther away. Greater lever arm, greater ...
... 1. The amount of force exerted 2. The distance between the force and the axis of rotation Lever Arm – the distance between the applied force and the axis; measured in meters. Example: Using a wrench. Hold close to bolt, it’s harder to turn than when you hold farther away. Greater lever arm, greater ...