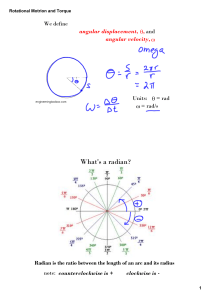
Rotational Dynamics and Static Equilibrium
... Conservation of angular momentum means that the total angular momentum around any axis must be constant. This is why gyroscopes are so stable. ...
... Conservation of angular momentum means that the total angular momentum around any axis must be constant. This is why gyroscopes are so stable. ...
Rotational Work
... legs are separated by a distance d, with one foot uphill and one downhill. The center of mass of the person is at a distance h above the ground, perpendicular to the hillside, midway between the person’s feet. Assume that the coefficient of static friction between the person’s feet and the hill is s ...
... legs are separated by a distance d, with one foot uphill and one downhill. The center of mass of the person is at a distance h above the ground, perpendicular to the hillside, midway between the person’s feet. Assume that the coefficient of static friction between the person’s feet and the hill is s ...
Solution
... A choice of coordinate system is essential. There are many ways to do this problem, and several ways to select a coordinate system. The solution presented here refers to vertical and horizontal forces. Any way the problem is done, it must be recognized that there are ...
... A choice of coordinate system is essential. There are many ways to do this problem, and several ways to select a coordinate system. The solution presented here refers to vertical and horizontal forces. Any way the problem is done, it must be recognized that there are ...
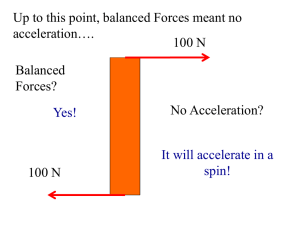
Equilibrium is not just translational, is is also rotational. While a set
... Achilles tendon is attached to the heel. If the tendon exerts a force of F = 720 N at a n angle of 55° to the lever arm, find the torque of this force about the ankle joint, which is 3.6 x 10-2 m from the point of attachment. ...
... Achilles tendon is attached to the heel. If the tendon exerts a force of F = 720 N at a n angle of 55° to the lever arm, find the torque of this force about the ankle joint, which is 3.6 x 10-2 m from the point of attachment. ...
13 torque problems w/Key File
... The net torque on the branch is the sum of the torques exerted by the children. Each individual torque is given by F , where F is the magnitude of the force exerted on the branch by a child, and is the lever arm (see the diagram). The branch supports each child’s weight, so, by Newton’s third ...
... The net torque on the branch is the sum of the torques exerted by the children. Each individual torque is given by F , where F is the magnitude of the force exerted on the branch by a child, and is the lever arm (see the diagram). The branch supports each child’s weight, so, by Newton’s third ...
Document
... The dimensions of moment of inertia are ML2 and its SI units are kg.m2 We can calculate the moment of inertia of an object more easily by assuming it is divided into many small volume elements, each of mass Dmi ...
... The dimensions of moment of inertia are ML2 and its SI units are kg.m2 We can calculate the moment of inertia of an object more easily by assuming it is divided into many small volume elements, each of mass Dmi ...
Torque - curtehrenstrom.com
... Forces that are not concurrent (same point) are called Parallel Forces. Parallel Forces exert Torque on an object. Torque is the product of the Parallel Force and the torque arm (lever arm) the force acts through. τ=rxF ...
... Forces that are not concurrent (same point) are called Parallel Forces. Parallel Forces exert Torque on an object. Torque is the product of the Parallel Force and the torque arm (lever arm) the force acts through. τ=rxF ...