* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Homeostasis
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
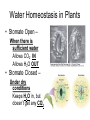
Plant Homeostasis NOTES Structure and Function • FLOWERS • Organs of sexual reproduction in plants Roots • Function – Provide support – Absorb water – Osmosis occurs at the root tip. – May contain sugars that help the plant get energy Leaf Function Contain photosynthetic cells that produce the plant’s food (Glucose) Stomates – small pores in the leaf’s surface Guard Cells – control the opening and closing of the stomates. Water Homeostasis in Plants • Stomate Open – When there is sufficient water Allows CO2 IN Allows H2O OUT • Stomate Closed – Under dry conditions Keeps H2O in, but doesn’t get any CO2 Stem Function • Support the plant • Xylem – Long thin tubes that transport water • Phloem – Long thin tubes that transport sugars (sap) Water Movement of Food and water • Transport moves water from • Roots through the Xylem • To all parts of the plant. • Mainly Leaves. Food Transport moves sugar From the Leaves through the Phloem To all parts of the plant Mainly Roots(storage) Water Movement Transpiration -Water moves into roots by diffusion (osmosis). Water evaporates from the stomates creating a suction Water flows from the roots to the leaves to replace the lost water Capillary Action – movement of water into small spaces Root Pressure – diffusion of water into roots creates a pressure Sugar Transport • Pressure flow model Transport moves sugar from the leaves through the stem to all parts of the plant, mainly the roots (storage) Regulation of Plant Growth • Photoperiodism- the response a plant has to the light and dark hours • Hormones- chemical messengers that regulate plant function • Auxins- hormones that stimulate plant growth. Located at root tips and stems. • Tropism- Plant growth towards a stimulus • Phototropism- growth towards sun(leaves) • Geotropism- growth towards earth(roots) Plant Nutrition • Photosynthesis- Capturing of sunlight to make food (glucose) • Photosynthesis is the source of most of the oxygen in the air. • Occurs within the Chloroplasts Which contains Chlorophyll (green pigment) It absorbs light energy from the sun to make glucose • Chorophyll absorbs red & blue and reflects Green light Chemical Equations for Photosynthesis and Respiration • Inorganic molecules -------------------- Organic Molecules Comparison Chart of Photosynthesis and Respiration Photosynthesis Energy-Storage Storage Occurs in Chloroplast Uses Sunlight, CO2, H2o Makes Glucose,O2 They are Reverse reactions of each other RESPIRATION Formula Respiration Energy Mitochondria O2, glucose CO2, H2o, ATP