* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Skeletal System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
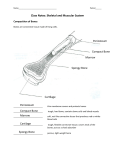
Skeletal System Chapter 11 Bone Basics Osseous tissue Mainly Ca & P 206 bones Classified by shape and composition Skeletal system Function Support Protection Aid in movement Blood formation (hematopoiesis) Mineral storage Types of Bone Tissue Spongy (cancellous bone) porous found in the interior of bones contains many blood vessels inside short / irregular bones most of epiphysis (red marrow) More Spongy Bone Compact Bone cortical or dense bone hard material…solid bone very few cells, solid matrix Bone types Long(a): length > width Short (c) length= width Flat: (b) thin & flat Irregular( d): complex shapes Sesamoid: round like patella Bone Structure Proximal Epiphysis (end) Diaphysis (shaft) Distal Epiphysis (end) Bone Structure Articular Cartilage End of all bone surfaces where joints form (hyaline cartilage) Periosteum outer layer initiates bone growth, repair, and development contains vessels and nerves Endosteum -inner layer -lines medullary cavity Medullary Cavity -”hollow” portion of the diaphysis -contains bone marrow Yellow Marrow found in most bones contains fat cells, blood vessels, and nerves Red Marrow located in spongy gone -site of red and white blood cell formation Compact Bone Yellow Marrow Bone composition Ca3(PO4)2 & CaCO3 Cartilage Dense connective tissue Collagen Osteocytes Osteoblasts/osteocyte: produce matrix Osteoclasts: dissolve bone Microscopic structures Dense bone Osteocytes: located in bony chambers called lacunae Form concentric circles around central canals Transport nourishment & waste through caniculi. Intercellular material Collagen Inorganic salts - Ca3(PO4)2 & CaCO3 Osteon Central canal, caniculi, & lacunae Cemented together by compact bone Orientation & arrangement of units help bone resists compressive forces Microscopic structure Central canal Blood vessels & nerves Nourishment Volkman’s canal’s Communication between surface of the bone and medullary cavity. Spongy bone Osteocytes: Located in lacuna separated by trabeculae Nourished through caniculi by diffusion Histology Spaces for bone cells Bone system Sheets of matrix Osteocyte communication Thin plates Longitudinal Blood vessel passage membrane Transverse Blood vessel passage Bone development & Growth 1st 2 months of life Develop 2 ways embrionic membrane – intramembranous bones ~week 5 Include skulls flat bones, clavicle & mandible From from osteoblasts hyaline cartilage- endochondral bones All other bones Form from chondroblasts Bone growth & development Growth Interstitial growth: length Appositional growth: width Bone remodeling & repair New matrix and bone re-absorption continue through life. Bones under the greatest stress more frequently Maintains homeostasis by continually adding minerals to system Repair Bleeding & inflammation lead to a procallus Fibroblasts secrete dense connective tissue to replace procallus Chondroblasts & osteoblasts then gradually building an osseous callus Osseous callus then goes through remodeling until it is healed. Organization of the skeleton 206 bones (adult) Axial= 80 bones 28 skull 26 vertebrae 25 thorax 1 hyoid Appendicular = 126 4 shoulder 60 upper limb/60 lower limb 2 pelvis Surface features of bones Condyle Knuckle, large smooth rounded surface Occipital condyle, femoral condyle Facet Smooth articular surface Between vertebral bones Fissure Narrow opening or cleft Orbital fissure of sphenoid Foramen Opening or hole Foramen magnum Fossa Depression or groove Glenoid cavity of scapula Process Any projection from the surface Styloid process Spine A narrow or pointed projection Spine of scapulas, spinous process Trochanter A large blunt process Greater trochanter femur Tubercle Small rounded process Greater tubercle humerus Tuberosity Rounded , elevated area of bone that is usually roughened Deltoid tuberosity, tibial tuberosity Other features Meatus Tubelike passageway External auditory meatus Crest Narrow, ridgelike projection Iliac crest Fovea Small pit or depression On head of humerus Fontanel Soft region between bones Fontanel of infant skull Sutures (wormian bones) Interlocking line of union Small bones found in suture Sutures of cranium sinus Air-filled cavity with in a bone Frontal sinus Axial Skeleton Skull Bones( 22 together) 8 cranial 13 facial & the mandible Cranium Protects and houses the brain Contains sinuses Drain fluids Reduce weight of bones Give resonance to your voice Bones of cranium Frontal bone-1 Parietal-2 Occipital-1 Temporal-2 Sphenoid-1 Ethmoid-1 Sutures: immovable joints between skull bones Coronal suture Between frontal bone and both parietal bones Between right & left parietal bones Lambdoidal suture coronal Sagittal suture squamosal Between parietal bones & occipital lobe Squamosal suture Between temporal and parietal bones Sagittal suture lambdoidal Skull: cranium Frontal bone Forehead Forms Superior orbit Supraorbital foramen Frontal sinus cranium Parietal bones(2) Meet at sagittal suture Temporal bones(2) Squamosal suture 1 External auditory meatus 2 Madibular fossa 3 Zygomatic process 4 Styloid process 5 Mastoid process 6 1 4 3 2 5 6 Occipital bone Posterior & floor of head Lambdoidal suture Foramen magnum Permits passage of spinal cord Occipital condyles Articulates with atlas(C1) for head movement Sphenoid bone Single butterfly shaped bone Foramen Optic rotundum Superior and inferior orbital fissures Sella turcica Sinuses(2) Ethmoid Cribiform plate Crista galli Perpendicular plate Nasal conchae sinuses Facial Bones Maxillary bones (2) Form Attachment for teeth Palatine process Drain into nasal cavity Alveolar process foramen Sinuses face & upper jaw Floor of orbit Roof of mouth Walls of nasal cavity Hard palate Cleft palate/cleft lip Anterior nasal spine Infraorbital foramen Nasal spine Patients with clefts: (A) incomplete unilateral cleft of the lip, (B) unilateral cleft of the lip, alveolus, and palate, (C) bilateral cleft of the lip, alveolus, and palate, (D) isolated (median) cleft palate. Stoll et al. BMC Medical Genetics 2004 5:15 doi:10.1186/1471-2350-5-15 Facial bones Palatine bones (2) L-shaped posterior to maxillary Form Roof of mouth Floor of nasal cavity Lateral walls of nasal cavity Membrane attachment is soft palate Facial bones Zygomatic bones (2) Form Cheek Lateral orbit Temporal process Zygomatic arch Facial bones Nasal bones (2) Rectangular bones meet at the midline of the bridge of the nose. End of nose is all cartilage Facial bones Lacrimal bones(2) Posterior lateral to nasal bones Anterior to sphenoid Form medial wall of orbit Vomer(1) w/ perpendicular plate of ethmoid form nasal septum Forms the Midline of nasal cavity Facial bones Mandible (1) Lower jaw Body Ramus Coronoid process Mandibular condyle articulates with fossa in temporal bone to form TMJ. Alveolar process Hold lower teeth Foramen Mental mandibular Axial Hyoid Does not articulate with any other bone Suspended from the styloid process or temporal bone Supports tongue Vertebral column 1. Description extends from skull to pelvis 26 bones (adult) 33 child/young adult intervetebral disks fibrocartilage disk 2.Function Support head & neck Movement rotation & bending Vertebral column 3. Curvatures Primary( fetal ) Concave anteriorly thoracic, pelvic or sacral Secondary (weight bearing) convex posteriorly Cervical Hold head up lumbar Support upright posture/walking Vertebral column 4. Structure a. body, thick b. pedicles c. Laminae vertebral arch d. spinous process e. transverse process f. vertebral foramen a b f e c d Vertebral column 5.Cervical Vertebrae ( 7 ) a. transverse foramina b. Bifurcated (forked) spinous process c. Atlas- C1 articulates w/ occipital bone no spinous process rotates on dens of axis d. Axis- C2 ondontoid process (dens) first spinous process e. C-7 large process at bottom of neck Vertebral column 6.Thoracic vertebrae:(12) a. Spinous process sloped downward b. rib articulations c. forward flexion of trunk Vertebral column 7. Lumbar vertebrae (5) a. largest support body weight b. transverse process sharp posterior angle c. spinous process thick & horizontal Vertebral column 8. Sacrum ( 1 ) a. fused spinous process 1 adult, 5 infant bones Fuse ~10-25 years of age b. foramina for vessel/nerves 9. Coccyx ( 1 ) a. 4 bones fuse ~ age 25 b. shock absorber for sitting Thoracic cage 1.Costals ( ribs ) - 12 pair -True ribs – 7 pair Attach directly to sternum - False ribs- 5 pair 1st 3 Attach via cartilage last 2 float w/ no anterior attachment 2.Sternum ( breast bone) - Manubrium Clavicle & 1st rib attachment - Middle body Ribs 2-7 - Xiphoid process Inferior tip points posteriorly False rib attachment Appendicular skeleton 1. Pectoral(shoulder) girdle A. Function Support of upper limb muscle attachment B.Structures 1. clavicle( 2 ) a. only bony attachment of arm to axial skeleton -sternum medially -acromion process of scapula laterally b. braces freely moving scapula c. weak structure -easily fractured -joints easily sprained B. Structures 2. Scapula( 2 ) a. acromion process ( end of scapular spine ) -forms acromioclavicular joint (ac jt.) -only bony attachment of scapula to axium b. glenoid fossa articulates with head of humerus -glenohumeral joint (gh jt.) -fossa deepened by labrum (cartilage) c. muscle attachment to thorax posteriorly 2. Upper Limb A. Structures 1.Humerus Aka: upper arm a. fractures at neck 2.Radius Aka: forearm a. shorter of 2 forearm bones thumb or lateral side b. rotates over ulna to pronate hand 3. ulna aka: forearm a. olecranon process makes elbow prominence b.styloid process bump on wrist 4. Carpals (8) are short bones Aka : wrist bones or carpus a. concave anteriorly= makes carpal tunnel -passage for nerves and tendons b. (lateral >medial, proximal > distal rows) -scaphoid, lunate, triquitrum, pisiform -trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, hamate Palmer surface 3 4 5. Metacarpals (5) are long bones Aka: hand bones 2 5 a. framework of palm b. connect carpals to phalanges c. numbered 1-5, thumb to pinky 1 6. Phalanges ( 14 ) are long bones Aka: digits or fingers a. proximal- closest to mc b. middle digits 2-5 c. distal- end or tip d. Thumb or Pollux -only proximal & distal e. polydactyly –extra digits Lower Limb & pelvis 3. Pelvic Girdle A. Function Support of trunk Attachment of lower limb Muscle attachment Protection of pelvic organs -bladder, intestine, internal reproductive organs B. Structures 1. Coxae( 2 ) or Coxa a. Ilium-largest most superior iliac crest ASIS (anterior superior iliac spine) SI joint posteriorly b. Ishium- lowest portion, L shaped tuberosity, supports weight while sitting c. Pubis- lower anterior portion -anteriorly form symphysis pubis - pubic arch < 90˚ =male > 90˚ = female 2. Pelvis : Coxae, sacrum & coccyx a. . Greater or False pelvis -above linea terminalis -lumbar vertebrae, iliac crests & abdominal wall b. Lesser or True pelvis -below linea terminalis -sacrum, coccyx, lower ilium, ishium & pubis bones -child passes through cavity during birth Linea terminalis II. Lower Limb Structures Femur (long bone) Aka: thigh bone longest bone in the body Head articulates with acetabulum to form Hip joint -fovea capitus (pit in the head) Trochanter (greater & lesser) large process for muscle attachment Condyles- medial & lateral ligament attachment form knee -hyaline cartilage Epicondyle-medial & lateral -attachment for ligament & muscle Patella (sesamoid bone) aka: kneecap Function as a lever for low leg Enbedded in quadraceps/patellar tendon Osgood schlatters Tibia aka: shin bone larger of 2 low leg bones proximal- lateral & medial condyles Form knee joint Menisci ( meniscus) deepens articulation & cushions hyaline cartilage tibial tuberosity attachment for patellar ligament distal-medial malleolus -aka ankle bone -1/2 of ankle joint with talus Fibula Non-weight bearing bone lateral malleolus -completes ankle joint with talus& tibia Interosseous membrane connects to tibia & fibula -length of shafts -surface for muscle attachment Tarsals (7) Aka: ankle bones framework of foot & arch cuniform 1 cuniform 2 cuniform 3 Cuboid distal row medial to lateral navicular talus (ankle) -only free moving bone calcaneous (heel) distal row medial to lateral -largest Metatarasals (5) Aka: foot bones a. numbered 1-5 like hand b. distal end (heads) forms ball of foot longitudinal (medial) arch transverse arch (across ball of foot) Phalanges or Phalanx (14) a. proximal- closest to metatarsals b. middle c. distal- end or tip Great toe or Hallux -only proximal & distal digits 2-5 only Longitudinal arch