* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Imamah (Shia) wikipedia , lookup
Muslim world wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Islamofascism wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
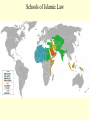
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Afghanistan wikipedia , lookup
Censorship in Islamic societies wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Islamic Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
Islamic ethics wikipedia , lookup
Medieval Muslim Algeria wikipedia , lookup
Historicity of Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Origin of Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
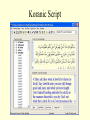
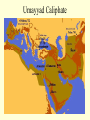
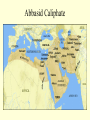
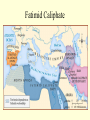
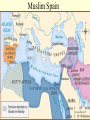
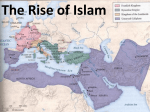
Islam Islam Third of the Abrahamic Faiths Why Study Islam ? • > 1.2 billion followers worldwide • > major impacts on world history • > key factor in regional, world politics Islam is ... Islam is a monotheistic religion begun by Muhammad around 600 CE in Arabia. The word means “surrender”...to the will of god. Islam united Arab tribes, and was the basis for an empire from Spain to India. MUHAMMAD Muhammad was an Arab merchant who interacted with Jews, Christians and others as he traveled in S.W. Asia. He founded a new religion (Islam), based on revelations and his teachings, converting poly-theistic tribes to belief in one god, Allah. He died in 632CE . Muhammad’s home region: the Arabian Peninsula Abu Bakr • Abu Bakr • lived until 630 CE • was key advisor to Muhammad • became the 1st caliph • consolidated control of Arabian tribes • began Islam’s expansion outside Arabia Umar was 2nd caliph, ca. 640 CE led expansion to Egypt, Mesopotamia, and Persia Uthman was 3rd caliph, ca. 650 CE Quaran was written under his direction Ali Ali was Muhammad’s cousin, son-in-law (married to Fatima), and closest male heir. He was the 4th caliph and 1st Shi’a imam, until he was killed in 661 Hasan and Hussein Ali’s sons, the 2nd and 3rd imams. killed by Umayyad forces in Iraq. Islamic Beliefs and Practices THE FIVE PILLARS -- Creed --- Prayer --- Charity --- Fasting --- Pilgrimage -- Creed There is no god but Allah, and Muhammad is his prophet . Prayer Five times daily, facing Mecca . Charity Annual giving to the poor. Fasting Dawn-to-dusk during Ramadan . Pilgrimage To Mecca, once in a lifetime . The Sunni - Shi’a Split in Islam ~ The Problem ~ Muhammad died without a son. Who will be the new leader of the faith? ~ The Sunni Solution ~ A council of Muhammad’s confidant’s elects a senior advisor (Abu Bakr) as the first caliph. ~ The Shi’a Solution ~ Find the nearest male relative (Ali), and continue Muhammad’s bloodline through imams. Sunnis and Shi’ites Clash. ... today, 80% of Muslims are Sunni. ... Iran and Iraq are the only Shi’a-run countries . Shi’a Islam Shi’at Ali ... “Party of Ali” 12 Imams ... most are martyred. ...the 12th [Mahdi] will reappear on the Day of Judgement Shi’ite pilgrimage sites include Karbala and Najaf in Iraq. Islamic Holy Books Koran [Quran] -- “The Recitation” ... a record of Muhammad’s revelations from god through Gabriel. Begun around 610 CE; written around 650 CE. Similar accounts as the Old Testament . The Koran Hadith Sayings of Muhammad. Basis of Sharia, along with the Koran . Shari’a Shari’a is the Islamic legal code, based mainly on the Koran and Hadith, and as compiled by Muslim scholars (ulama). Schools of Islamic Law Islamic Holy Sites Islam’s Three Holiest Cities ... Mecca ... Medina ... Jerusalem The Ka’aba • located in Mecca, Saudi Arabia • sacred cube at center of the universe • ancient Arab tribal pilgrimage site • dedicated to Allah by Muhammad Medina • “City of the Prophet” • Formerly Yathrib • Muhammad found sanctuary here after the Hejira (622 CE) • Islam’s 2nd holiest site The Dome of the Rock Dome of the Rock 3rd holiest site in Islamic world located in Jerusalem rock where Abraham took Ismail Muhammad ascended to heaven here Inside the Dome of the Rock Islamic Art and Literature Islamic Art Islamic religious artists avoid “graven images” of people -especially the Prophet- and other persons. Arabic writing was developed into the art form of calligraphy. The most popular text is Koranic scripture. Arabesques are repeated geometric or floral designs. Similar to tessellations. Koranic Script The Koran as Sculpted Design Mosque Art Art and Literature of the Abbasid Period Omar Khayyam Persian astronomer and poet lived during Abbasid period, ca.1100 CE wrote the “Rubaiyat”…quatrain poetry of love and transience of life Omar Khayyam "The Moving Finger writes: and, having writ, Moves on: nor all thy Piety nor Wit Shall lure it back to cancel half a Line, Nor all thy Tears wash out a Word of it.” Muslim Empires Umayyad Caliphate Umayyad Caliphate • 661 - 750 CE, begun by Mu’awiyah • Arab control grows to greatest extent ... Spain to Persia • Capital at Damascus (Syria) Mu’awiyah • lived 661 to 680 CE • 1st Umayyad caliph • established hereditary rule Tariq > general who took Muslim forces into Spain in 711 CE ... beginning 700 years of Islamic rule in Spain Gibralter = Jabar al-Tariq (Rock of Tariq) Abbasid Caliphate Abbasid Caliphate > > > > 750 - 1258 CE founded by Persian (non-Arab) rebels capital at Baghdad weakened by Turks; ended by Mongols Harun al-Rashid • Abbasid caliph • ruled during “Golden Age” of Islam: translations of Greek works, progress in astronomy, navigation Fatimid Caliphate Fatimid Caliphate • 909 - 1171 CE • Ismaili Shi’ite dynasty • begun in Tunisia, expanded east to Cairo (Egypt) Saladin • Kurdish general who served as Fatimid vizier, then staged a coup • Recaptured Jerusalem from European Crusaders in 1187 CE Muslim Spain Muslim Spain • 711 - 1492 CE • Islamic control of diminishing Spanish territory until the Reconquest by Ferdinand and Isabella. • unique Islamic art and architecture • rallied Christian (esp. Catholic) Iberian forces to wage holy war against Islam Examples of Art and Architecture from Islamic Spain (Andalusia) Alhambra in Granada Mosque at Cordoba Muslim trading network (Dar al-Islam) Merchants could trade from Spain across North Africa, southwest-central-south-southeast Asia using one language, writing, and set of rules..Arabic and Islam. Islamic Contributions Medicine: Avicenna Chronicles of Diseases: Symptoms and Treatments Arabic numerals Algebra Astrolabe