* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pediatric infectious diseases Vaccination programs
Ebola virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Poliomyelitis wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Influenza A virus wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
Orthohantavirus wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Antiviral drug wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis wikipedia , lookup
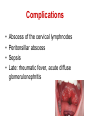
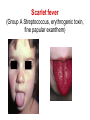
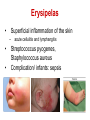
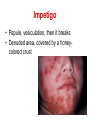
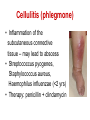
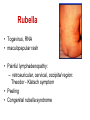
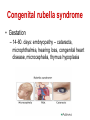
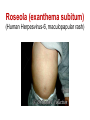
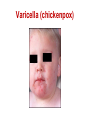
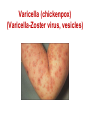
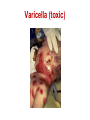
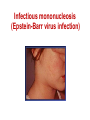
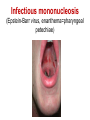
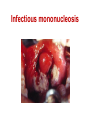
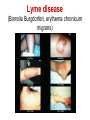
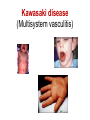
Pediatric infectious diseases Vaccination programs Sallai Ágnes MD, Ph.D. Localizing symptoms • • • • • • • • • Skin Upper respiratory Lower respiratory Genitourinary Gastrointestinal CNS Skeletal Cardiovascular Hepatic Characteristics in infants and children • Neonates, infants: non-specific initial symptoms (irritability, lethargy, poor feeding) • Specific rashes • Sites of infection • Prevention: vaccination/ immunization Group A Streptococcal infections • • • • • • • • Acute pharyngitis Impetigo Cellulitis Scarlat fever Pneumonia Septic arthritis Osteomyelitis Meningitis Tonsillopharyngitis streptococcica • Treatment: Penicillin for 10 days • Other bacteria: S. aureus, H. influenzae positive in throat microbiological cultures are not pathogenic. - Antibiotic treatment is not necessary! • Aminopenicillin antibiotics are not recommended – possible infectious mononucleosis Complications • • • • Abscess of the cervical lymphnodes Peritonsillar abscess Sepsis Late: rheumatic fever, acute diffuse glomerulonephritis Scarlet fever (Group A Streptococcus, erythrogenic toxin, fine papular exanthem) Scarlet fever • Skin: diffusely erythematous („sandpaper rash) • Petechiae on the soft palate, on the upper abdomen and trunk • Circumoral pallor • Desquamation on the face: end of the first week, then generalized • Strawberry tongue Erysipelas • Superficial inflammation of the skin – • • acute cellulitis and lymphangitis Streptococcus pyogenes, Staphylococcus aureus Complication/ infants: sepsis Impetigo • Papule, vesiculation, then it breaks • Denuded area, covered by a honeycolored crust Cellulitis (phlegmone) • Inflammation of the subcutaneous connective tissue – may lead to abscess • Streptococcus pyogenes, Staphylococcus aureus, Haemophilus influenzae (<2 yrs) • Therapy: penicillin + clindamycin Infectious diseases with rash • Stadium incubationis: in general no symptom • Stadium prodromum: non-specific symptoms • Stadium floritionis Measles (Rubeola) • Paramyxovirus, RNA virus • Rash: retroauricular, temporal region, then on the face, spreads over most of the body in 24 hours - maculo-papulous exanthemes (Koplik spots on the buccal mucosa opposite the lower molars) • Complications: otitis media, interstitial pneumonia, encephalitis, cerebellitis, subacute sclerotizing panencephalitis Rubella • Togavirus, RNA • maculopapular rash • Painful lymphadenopathy: – retroauricular, cervical, occipital region: Theodor - Klatsch symptom • Peeling • Congenital rubella syndrome Congenital rubella syndrome • Infection of seronegative mother during pregnancy • Risk of fetal infection – – – – I. trimenon: 75-90% II. trimenon: 20-40% III.trimenon: 25-50% Fetal lesion • 1-8. gest. week: 80% • 9-12. gest. week: 30% • 13-20. gest. week: 10% Rubella vaccination is prohibited during pregnancy! Congenital rubella syndrome • Gestation – 14-60. days: embryopathy – cataracta, microphthalmia, hearing loss, congenital heart disease, microcephalia, thymus hypoplasia Roseola (exanthema subitum) (Human Herpesvirus-6, maculopapular rash) Varicella (chickenpox) Varicella (chickenpox) (Varicella-Zoster virus, vesicles) Varicella (toxic) Infectious mononucleosis (Epstein-Barr virus infection) Infectious mononucleosis (Epstein-Barr virus, enanthema=pharyngeal petechiae) Infectious mononucleosis Lyme disease (Borrelia Burgdorferi, erythema chronicum migrans) Immunization schedule Hungary - 2016 • • • • • • • • • • • BCG DTPa+IPV+Hib+PCV DTPa+IPV+Hib DTPa+IPV+Hib+PCV PCV MMR DTPa+IPV+Hib DTPa+IPV MMR dTap Hepatitis B Birth to 4 week 2 mo 3 mo 4 mo 12 mo 15 mo 18 mo 6 yr 11 yr (6. school yr) 11 yr (6. school yr) 12 yr (7. school yr) PCV: pneumococcal conjugate vaccine , a: acellular, i: inactivated Types of vaccines • Live attenuated viruses (measles, mumps, rubella, varicella, polio) • Inactivated viruses (polio, hepatitis B, influenza) • Inactivated bacteria (pertussis, diphtheria, tetanus, H. influenzae type b, pneumococcus) Non-mandatory vaccines (but recommended) • Polysaccharid vaccines – Meningococcus A, B, C, W-135, Y serotypes • • • • • • • Hepatitis A, A+B Human papillomavirus (HPV) – 12 yr (girls: 7. school yr) Influenza Tick - borne encephalitis Rotavirus (from 6 weeks till 6-8 mo) Chickenpox (varicella) - > 1 yr RSV (premature babies) Antibiotic prophylaxis to prevent endocarditis I. • For all patients with significant cong. heart defect (unoperated, palliated or repaired) • Rheumatic valve lesions • Prosthetic heart valves • Mitral heart prolapse • Subaortic stenosis • Transvenous pacemaker leads • Previous endocarditis • NOT indicated: isolated secundum ASD, repaired sec. ASD and VSD 6 mo after patch placement, ligated PDA 6 mo after repair Antibiotic prophylaxis to prevent endocarditis II. • During dental / respiratory procedures : oral amoxicillin, 50 mg/kg 1 hr before • During gastrointestinal / genitourinary procedures: oral amoxicillin or parenteral ampicillin + gentamicin, iv. 30 min before • For patients allergic to penicillin: clindamycin, 20 mg/kg Oral-dental procedures requiring endocarditis prophylaxis • • • • • Extractions Periodontal procedures Dental implant placement Root canal surgery beyond the apex Subgingival placement of orthodontic bands but not brackets • Prophylactic cleaning of teeth / bleeding is anticipated • Intraligamentary local anesthetic injections Kawasaki disease (Multisystem vasculitis) Tetanus (Clostridium tetani exotoxins) AIDS • Occurrence is rare in children • 80% intrauterine, intra partum, breast feeding, 10-15% blood and blood products, 5% unknown origin • Risk of children of HIV infected mother: 20-40% AIDS / clinical forms • Rapidly progressing: intrauterine infection • Repeated, severe infections with classical and opportunistic pathogens (Pneumocystis carinii, Cryptosporidium, Candida, HSV, EBV, CMV) • Failure to thrive, enlargement of parotid gland, lymphadenopathy, cortical atropy, demyelinisation of the brain, death at the age of 3 yrs • BCG sepsis! AIDS / clinical forms • Slowly progressing form: intra partum, post partum infection • Frequent and severe infections after latency (1-2 yrs) • Lymphoid interstitial pneumonitis, hypergammaglobulinemia • Death before the age of 6 yrs in 60% AIDS / prevention • Antiviral treatment of infected mother during pregnancy • Isolation of newborn baby from infected mother • No breast feeding • BCG vaccination is prohibited!