* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Simulating Mantle Convection and Seismic Anisotropy with Data
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Seismic inversion wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Seismic anisotropy wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
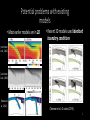
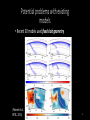
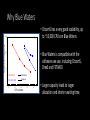
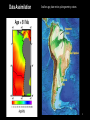
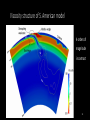
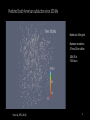
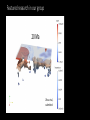
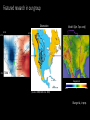
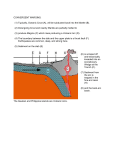
Simulating Mantle Convection and Seismic Anisotropy with Data Assimilation Project PI: Lijun Liu, UIUC Presenter: Jiashun Hu Collaborator: Manuele Faccenda, University of Padua, Italy Group members: Quan Zhou, Ching Chang NCSA team: Ryan Mokos, Bill Gropp, Darren Adams, Yifeng Cui Geologist’s view on plate subduction CourtesytoandinmemoryofProf.PaulHeller Whyitmatters– tomodelmantleconvection • Howtheearthworks • Naturalhazards Fromthefilm SanAndreas (Braun2010) TherealEarthismuch morecomplex. fromUSGS Keychallenges • Cleanupboundaryconditions • Earth’shistoryisverycomplex.Wehavelimitedconstraints onthemotionsandtheagesoftheplates. • Largeviscositycontrast • Significantlyslowdowntheconvergenceofthesolver • Requireshigherresolutiontoresolve • Unknownpropertiesandprocesses • Suchasthegenerationandbehaviorofmagmainthe mantlewedge,andthepropertiesofthesuperplumesin deepmantle Potentialproblemswithexisting models • Mostearliermodelsarein2D A • Recent3Dmodelsusedidealized boundaryconditions [vanHunen etal.,2002] B [vanHunen etal.,2000] C [Manea et al.,2012] (Taramon et al., G-cubed, 2015) 5 Potentialproblemswithexisting models • Recent3Dmodelsusedfixedslabgeometry (Flament et al., EPSL, 2015) 6 ModelingS.Americansubduction history Wetrytodevelopamodelthatisconsistentwithallavailable geophysicalandtectonicconstraints: • Theknownsubductionhistory(platemotion&seafloorage) • Dynamicallyevolvinginsteadofprescribedslabs • GoverningEquations • Assumethemantleis an incompressible fluid, which satisfies theBoussinesq approximation 7 WhyBlueWaters • CitcomS hasaverygoodscalability,up to~10,000CPUsonBlueWaters. Machine time (second) 1000 • BlueWatersiscompatiblewiththe softwares weuse,includingCitcomS, DrexS andFSTRACK 100 10 129×257×257 Blue Waters 513×1025×1025 Stampede 1 0 10 1 10 2 10 CPU number 3 10 4 10 • Largercapacityleadstolarger allocationandshorterwaitingtime. Data Assimilation Seafloor age, plate motion, plate geometry,cratons 9 ViscositystructureofS.Americanmodel 4ordersof magnitude incontrast (Huetal.,EPSL, 2016) 10 PredictedSouthAmericansubduction since 100 Ma Modelsize:8.6mgrids Maximumresolution: 27kmx20kmx8km 1024CPUs ~150hours (Huetal.,EPSL, 2016) 11 Accomplishments Thepowerofdataassimilation: Fittinguppermantleslab geometry 12 Fittinglowermantletomography Themodelfitstothetomographyimages wellto1000kmdepth,especiallyinthe northernpartofSouthAmericathathas abetterseismiccoveragethanthe southernpart. 13 Slabtearvs.intra-slabseismicity (Hu&Liu,EPSL,2016) Newinterpretationofflatslabsubduction (Hu&Liu,EPSL,2016) Late Cenozoic Andean Flare-up ThecentralAndesareunusualfortheabundanceoffelsicignimbritesand theirdistributionisshownseparatelyfromtheintermediatetomafic volcaniccenters. Volcaniczoneissignificantlybroadenedsince~30Ma. Thrumbull etal.,2006 Haschke etal.,2002 16 Geologicimplication:Slabdynamics&Andeanevolution N The30-Maslabtear correlateswiththe Andeanignimbriteflareupbothinspaceandin time. Newimplicationson Andeanshortening& upliftaswell? 33Ma N 5Ma 40Ma 15Ma 30Ma N 17 Predictingseismicanisotropy • Calculateseismicanisotropy(LPO)byintegratingthe mantle flowfield • Integrating the anisotropy in the upper mantle to generate synthetic SWS Conclusions • Supercomputers,suchasBlueWaters,makeitfeasibletorun mantle-convectionmodelsin3Dwithatimescaleofhundredsof millionyears. • Theimplementationofdataassimilationmethodisnecessaryin ordertodirectlycompareobservationwithprediction. • Challengesremaininfastsolvingfluiddynamicswithcomplex rheology,suchasnon-Newtonianrheologyandextremelyvarying rheology. 19 Publications • Hu,J.,Liu,L.,Hermosillo,A.andZhou,Q.,2016.SimulationoflateCenozoic SouthAmericanflat-slabsubductionusinggeodynamicmodelswithdata assimilation. EarthandPlanetaryScienceLetters, 438,pp.1-13. • Hu,J.andLiu,L.,2016.Abnormalseismologicalandmagmaticprocesses controlledbythetearingSouthAmericanflatslabs. EarthandPlanetary ScienceLetters, 450,pp.40-51. • Hu,J.,Faccenda,M.andLiu,L.,2017.Subduction-controlledmantleflow andseismicanisotropyinSouthAmerica. EarthandPlanetaryScience Letters, 470,pp.13-24. Modelsize:51.5mgrids On-goingResearch Maximumresolution: 27kmx27kmx8km ~10,000CPUs ~200hours Featuredresearchinourgroup Zhouetal., submitted Featuredresearchinourgroup Observation 125˚W 60˚N 20˚N 70Ma ModelI(Dyn.Topo.only) 65˚W subsidence Topography(m) (Liuetal.2008;Smithetal.1994) -2000 0 2000 Changetal.,inprep.