* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is Nanotechnology?
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
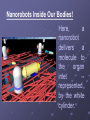
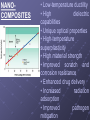
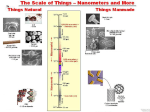
NANOTECHNOLOGY BASIC DEFINITION • Engineering of functional systems at the molecular scale. • In its original sense, 'nanotechnology’ refers to the projected ability to construct items from the bottom up, using techniques and tools Meaning of Nanotechnology • Nanotechnology is the science and engineering of nanometer scale objects. • Nanotechnology involves the manufacture and manipulation of molecules from 1-100 nanometers in size. BIFURCATION OF NANOTECHNOLOGY • NANO-SCIENCE • NANO-ROBOTS • NANO-SENSORS • NANO-FABRICATION • NANO-COMPOSITES • NANO-ENCAPSULATION • NANO-ENGINEERED MATERIALS NANO-SCIENCE • Nano science is the study of atoms, molecules, and objects whose size is on the nanometer scale. • The word itself is a combination of nano, from the Greek “nanos” (or Latin “nanus”), meaning “Dwarf”, and science. NANO-SCIENCE • Nanoscience and nanotechnology are an extension of the field of materials science, and materials science departments at universities around the world in conjunction with physics, mechanical engineering, bioengineering, and chemical engineering departments are leading the breakthroughs in nanotechnology. Nano Devices • Nano-devices have a size of only a few nanometres. The interaction of "spin waves" emitted by two nano-oscillators that generate microwave signals. • Research has been carried out into very small components, many of which depend on quantum effects and may involve movement of a very small number of electrons in their action. • Such devices would act faster than larger components. Nano-particles • Nanoparticles are small lipid vesicles in the range of nanometers (10-9m). • The best way to characterize them is to compare them with liposomes and emulsions. • Liposomes and nanoparticles are of comparable size. Both occur in the range from 20 to 1000 nm in diameter. Whereas liposomes are composed of one or more bilayer membranes, nanoparticles are formed by a single layered shell. Activity of Nanoparticles • Nanoparticles are small lipid vesicles formed by a monolayer of phospholipids. Whereas liposomes are typical carriers for water substances, nanoparticles are the ideal delivery system to transport and protect organic agents. • Nanoparticles are very stable and have a high affinity to the skin. Therefore, an enhanced bioavailability of the encapsulated material to the skin is achieved. Nano-robots • Nanorobots are miniature machines that function on the scale of individual atoms and molecules. • They can work together in response to environment stimuli and programmed principles to produce macroscale results. • Nano-Robots can respond with cells in the human body at a molecular level for more targeted diagnosis and targeted curing of diseases. Nanorobots Inside Our Bodies! Here, a nanorobot delivers a molecule to the organ inlet -represented by the white cylinder. Nano-Robots This screenshot shows the molecular identification by collisions contact. In this diagram, you can see the workflow of a nanorobot gathering information and biomolecules. NANO-SENSORS • Miniaturized radiofrequency devices • Flexible circuits and hybrid fluid/electronic circuits using polymer and elastomer lithography • Integrated chemical and biological sensors • Nano-Raman spectrometer in a chip NANO-SENSORS • Ultra-thin carbon foils are key components of numerous science instruments currently in space and proposed for future space missions. • These foils are approximately 0.5 µg cm2, equivalent to approximately 3 nm or approximately 20 atoms thick NANO-ENGINEERED MATERIALS • Multilayered optical thin films • Solid electrolytes • High-temperature alloys and ceramics The figure shows a diamond like carbon (DLC) thin film. • Molecular clusters for catalysis NANO-ENGINEERED MATERIALS • Metal-containing carbon nanotubes • Molecularly imprinted polymers for sensor development • Biologically functional coatings for medical implants • Enhanced heattransfer fluids NANOCOMPOSITES • Low-temperature ductility • High dielectric capabilities • Unique optical properties • High-temperature superplasticity • High material strength • Improved scratch and corrosion resistance • Enhanced drug delivery • Increased radiation adsorption • Improved pathogen mitigation APPLICATION OF NANOTECHNOLOGY Fuel Cells Concentration on Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFC) and are developing new fuel cell components and designs using nano sized oxide materials . These will be used in various components in the fuel cell and new construction techniques to use them more effectively. APPLICATION OF NANOTECHNOLOGY Ignitors • By using nanomaterial precursors, a new line of energetic materials with enhanced performance can be developed. • This incorporates high safety features. APPLICATION OF NANOTECHNOLOGY Nanoscale devices Many micro-devices that involve building features at the nanoscale, including switched, RF comms, guidance systems and sensors (biomedical, pressure, acoustic) are developed. APPLICATION OF NANOTECHNOLOGY Modelling Structure • This shows a molecular model of the polymeric component of bone. • These link the mineral platelets and are ~1.5nm in diameter and the helix has a pitch of 10nm. DISADVANTAGES OF NANOTECHNOLOGY POISON / TOXICITY: It could adversely affect the stability of cell membranes or disturb the immune system when inhaled or digested. WEAPONS: The nano-weapons may be compared to weapon concepts such as genetically engineered bacteria or viruses though their terrorism applications are clear. Reference •www.help2engg.com