* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolution = descent with modification
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
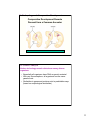
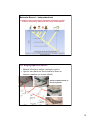
Chapter 21: Evidence for Evolution I. Evolution & Darwin II. Artificial Selection III. Fossil Record IV. Comparative Anatomy V. Embryology VI. Genetic Analysis VII. Biogeographical Evidence VIII. Conclusions “Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution” --Theodosius Dobzhansky I. Evolution & Darwin Evolution = descent with modification ! Macroevolution = large changes ! Microevolution = small changes Both rely on same mechanisms! Primarily natural selection Charles Darwin: On the Origin of Species (mid-1800’s) • Traveled extensively • Galapagos Islands – off the coast of Ecuador • One area of focus: finches 1 I. Evolution & Darwin • Finches of the Galapagos • 14 species • Difference between them: – Beak shape • • • • Seed crackers Cactus eaters “Tool users” Vampire • Darwin’s idea: – One original species has adapted to different food sources II. Artificial Selection CAN selection produce major evolutionary change? ! Darwin found convincing evidence for his ideas in the results of artificial selection Artificial selection: • organisms may be modified by controlled breeding • and change drastically in short time periods! • 3 examples… A) Plants !Broccoli, brussel sprouts, kale, cabbage, & cauliflower ! All artificially selected from Brassica oleracea 2 II. Artificial Selection (cont.) B) Insects: Pesticide resistance (Florida) Agent of Natural Selection: Pesticide called "Combat®" – Cockroaches who like bait: continuously killed – Those who didn’t like bait: survived • Had rare, glucose disliking mutation – Bait now is ineffective>> populations are resistant II. Artificial Selection (cont.) C) Mammals: Dogs Change can happened over a very short geological period if the selection pressure is strong! READ 420-421 SILVER FOX 3 III. The Fossil Record Fossils: Preserved remains of ancient organisms III. The Fossil Record How to make a fossil: ! Burial in sediment ! Mineralization of organic material ! Hardening of sediment 4 III. The Fossil Record Darwin and his contemporaries saw and knew of fossils: ! Local fossils looked like local organisms ! Progressive changes in layers • Fossil Record – Remains or evidence of past life – Dating fossils • Relative dating – old layers under new • Absolute dating – radioactive decay – Fossilization chancy • Right kind of organism, in right place • Gaps unavoidable – Many excellent series though • Horses, titanotheres, whales, humans Organization of fossils: a) Fossils are found in distinct layers 5 Organization of fossils: a) Fossils are found in distinct layers b) Resemblance to modern forms of life gradually increases with younger fossils c) Many fossils are of species now extinct Conclusions: ! Many different types of organisms in the past (some extinct) ! Change in lineages over time III. The Fossil Record Facts – Geology and Fossils • Fossils are found in sedimentary rocks • Many fossils represent extinct organisms • Oldest sedimentary rocks contain no fossils, or fossils of extremely simple organisms – Prokaryotes (stromatolites) • Fossil prokaryotes appear prior to fossil eukaryotes • Colonial eukaryotes appear prior to multicellular eukaryotes (invertebrates and plants) • Invertebrates appear prior to vertebrates –Fish, amphibians, reptiles, mammals, and birds appear in order • Seedless vascular plants, seeds, gymnosperms, and angiosperms appear in order 6 Unstable isotopes decay at a constant and predictable rate READ 422 Allows setting of absolute age on rock strata. One conclusion: the Earth is very old ! ~4.5 billion years How Do We Know That Evolution Has Occurred? Fossil record evidence of evolutionary change over time Ancient primitive organisms ! Several intermediary stages !Modern forms READ 423-425 7 Whale Evolution: Fossil Record of Evolution Modern toothed whales Rodhocetus kasrani reduced hind limbs could not walk; swam with up-down motion like modern whales Ambulocetus natans walked on land …like sea lions Pakicetus attocki lived on land; skull had whale characteristics swam by flexing & paddling … like otters READ 422-423 Copyright © 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Benjamin Cummings III. The Fossil Record: Evidence for Mass Extinctions Number of families Diversity over the Last 600 Million Years 800 600 400 200 0 600 Cambrian (545-490) 500 400 Silurian (438-408) Ordovician (490-438) 300 200 100 Carboniferous Triassic Cretaceous (360-280) (248-213) (144-65) Devonian (408-360) Permian Jurassic (280-248) (213-144) 0 Tertiary (65-2) Millions of years ago 8 IV. Comparative Anatomy • Organisms can be grouped (classified) by unique anatomical characteristics • Similar anatomy is found in organisms with greatly divergent functions Similar anatomy is found in organisms with greatly divergent functions Homologous structures ! structures that may have different appearances and functions, yet all derived from a common ancestor Evolution helps us understand patterns in the diversity of life 9 Vestigial structures are Evolutionary relicts. They present a strong argument for common ancestry. Vestigial structures ! No apparent purpose ! Resemble similar functional structures in other, closely related species ! also human appendix V. Embryology and Comparative Development Embryological stages pig cow rabbit human ! All vertebrate embryos look similar early in their development ! evidence of common ancestry ! similar developmental “instructions” in DNA 10 V. Embryology and Comparative Development Comparative Development Reveals Descent from a Common Ancestor VI. Genetic Analysis Modern technology reveals relatedness among diverse organisms • Essentially all organisms have DNA as genetic material • With very few exceptions, all organisms use the same genetic code • Similarities in genes and proteins exist in predictable ways (based on morphological similarities) 11 Molecular Record – Independent test ! Distantly related organisms are expected to accumulate a greater number of evolutionary differences than closely related species. VII. Biogeographical Evidence • Islands often have unique (endemic) species • Species on islands are most similar to those on nearest continent (or nearest island) Species of Gallotia lizards on the Canary Islands 12 VII. Biogeographical Evidence • Different continents have different species • Modern species on any continent are most similar to fossils on that continent VIII. Conclusions Evolution in Action • Darwin’s Finches – beak size – Grant and Grant – 1970s • Showed beak size heritable and responsive to environmental change • Guppies – with and without predators • Pesticide and Antibiotic resistance • Peppered Moths/Industrialized Melanism! 13 VIII. Conclusions READ 416-417 VIII. Conclusions Evolution – Supported by Many Independent Lines of Evidence ! Evolution requires that all of these facts are true and congruent with each other. – Fossils, Order of Appearance, Relative and Absolute Dates – Anatomical Classification, Vestigial Structures, Homologies – Embryology – Biogeography – Genetic Analysis 14 VIII. Conclusions Evolution – Both a Fact and a Theory • That evolution has occurred (and is currently occurring) is NOT in scientific debate now; it has been settled. • FACT – The biodiversity on Earth is a result of evolution from a common ancestor. • FACT – Evolution continues today. • THEORY – The intricacies of evolutionary change and mechanisms driving evolution. VIII. Conclusions Myths ! Evolution is “only a theory”. – Misuse of word “theory” – Theory of Gravity, Relativity, Cell theory, Germ theory of disease etc. – “Theory” in science means most certain 15 End Evolution 16