* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Wolfson Inner Solar System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
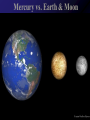
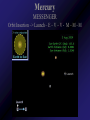
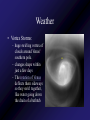
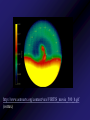
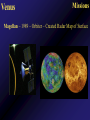
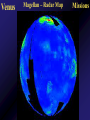
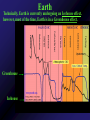
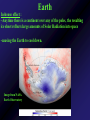
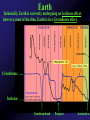
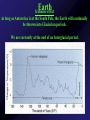
Mercury Mythology - Hermes – The messenger god) 1st ever color photo of Mercury by MESSENGER probe; 2008 Mercury Transit across Sun 1st ever color photo of Mercury by MESSENGER probe; 2008 Mercury Mapped by Mariner 10 Mercury vs. Earth & Moon 1/6 size of Earth Mercury Images by Mariner 10 Mercury Statistics: * .4 A.U. From Sun * 1/3 Size of Earth * Orbital Period = 3 Months *Rotation Period = 88 Days * Surface Gravity = 1/6 of Earths * The planet is too small to hold an atmosphere Atmosphere: •There is no atmosphere •heat is not trapped on the planet. • it is VERY HOT during the day, and VERY COLD during the night Mercury is NOT the hottest or coldest planet. core 1. Very Large 2. Solid 3. Iron Mercury has a disproportionately large Iron core. It should be cooled and solid. However, MESSENGER flyby data indicates the core is partially molten. This contradicts current theories. Lobate scarps Definition – curved cliffs Cause =When the core cooled,it shrunk, causing the crust to collapse. Mercury Missions to Mercury Mariner 10 Launched Nov 1973 Flyby March 1974 MESSENGER Launched Aug 2004 Orbit insertion March 2011 Mercury MESSENGER Orbit Insertion –> Launch – E – V – V - M – M - M Mercury MESSENGER Orbit Insertion –> Launch – E – V – V - M – M - M Venus Aphrodite – The goddess of Love The Morning/Evening Star/Sister Planet Venus Statistics • Distance - .73 A.U. From Sun • Size – Same Diameter as Earth More Statistics • Orbital Period – .6 Years • Rotation Period – 243 days • Surface Gravity – .9 of Earths Venus Atmosphere • Runaway Greenhouse Effect – Visible light from sun hits the surface – Surface reradiates the energy in the form of infrared – Clouds block some of the IR from escaping – Surface gets hotter Runaway Greenhouse Effect Results • CO2 Atmosphere • NO WATER! CO2 Atmosphere No Water! Atmospheric Conditions 1. Pressure 90x that of Earths 2. Very dry, no surface water 3. Sulfuric Acid in Clouds Atmosphere 4. Temperature 900 F 5. Wind Speed up to 250 Miles per Hour. Venus Weather Twin cyclones: two storms with lowpressure centers that causes a circular Images/Video from pattern of winds to form. Venus Express Orbiter Weather • Vortex Storms: – huge swirling vortex of clouds around Venus' southern pole. – changes shape within just a few days – The rotation of Venus deflects them sideways so they swirl together, like water going down the drain of a bathtub. http://www.astroarts.org/content/vex/VIRTIS_movie_500_b.gif (vortex) Venus Solar Storms i. Venus does not have a magnetic field. ii. Solar Wind erodes away the atmosphere. Venus Missions Venera 9-14 –1978 - 1982 – Landers (First & only images of Surface) Venus Images from Venera 13 probe Surface Venus Missions Magellan – 1989 – Orbiter – Created Radar Map of Surface Venus Magellan – Radar Map ~8 min Missions magellan_mapping_venus.wmv Venus Magellan – Radar Map Missions Venus Missions Pioneer Venus 1 & 2 - 1978 – Orbiters & Descent Probes Venus Missions Venus Express – 2005 to present – Orbiter Animation of Venus Express Studying Venus Venus Venus Express Missions ~5 min Venus Although Venus is often called Earth’s Twin or Sister planet. The only similarities is the size. Almost every other feature makes Venus very different from Earth. Earth MESSENGER animation Leaving earth. Earth Earth Atmosphere -78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen Distance -1 au from sun (93,000,000 miles) Contains water in all 3 phases Surface Gravity – 9.8 m/s Rotation – 1 day Orbit – 1 year Earth Greenhouse Effect -Has Liquid Water (Some Water Vapor in Atmosphere) -Water vapor keeps planet warm (main greenhouse gas) -Ozone Layer prevents water from Disassociating Earth Technically, Earth is currently undergoing an Icehouse effect. however, most of the time, Earth is in a Greenhouse effect. Greenhouse Icehouse Earth Icehouse effect : - Anytime there is a continent over any of the poles, the resulting ice sheet reflects large amounts of Solar Radiation into space -causing the Earth to cool down. Image from NASA Earth Observatory Earth Technically, Earth is currently undergoing an Icehouse effect. however, most of the time, Earth is in a Greenhouse effect. Greenhouse Icehouse Gondwanaland Pangaea Antarctica Earth Icehouse effect As long as Antarctica is at the South Pole, the Earth will continually be thrown into Glaciation periods. We are currently at the end of an Interglacial period. Earth 70 Atmospheres of CO2 is trapped in Earths Rocks. If all of this CO2 were released, which planet would we look like? Only place we know of that supports life - 4 reasons: 1. 2. 3. 4. Correct distance from sun Natural/Stable greenhouse effect Ozone Layer & Magnetic Field Presence of Liquid Water Planet Guidelines • The IAU therefore resolves that planets and other bodies in our Solar System be defined into three distinct categories in the following way: • (1) A planet1 is a celestial body that (a) is in orbit around the Sun, (b) has sufficient mass for its selfgravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape, and (c) has cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit. • (2) A dwarf planet is a celestial body that (a) is in orbit around the Sun, (b) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that Planet Guidelines • (1) A planet is a celestial body that – (a) is in orbit around the Sun, – (b) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape, and – (c) has cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit. Planet Guidelines • (2) A dwarf planet is a celestial body that – (a) is in orbit around the Sun, – (b) has sufficient mass for its self-gravity to overcome rigid body forces so that it assumes a hydrostatic equilibrium (nearly round) shape2, ( – c) has not cleared the neighbourhood around its orbit, and – (d) is not a satellite. Planet Guidelines • (3) All other objects3 orbiting the Sun shall be referred to collectively as "Small Solar System Bodies". Video Links • Earth from Spaceshuttle – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wHyonFhWp6w • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9ddEjVwpX9I • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=F5d6cd7XXiA &feature=related • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Mj52CgKHzH Q • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lwwioJhQzeg& feature=PlayList&p=0D959158C1FC558F&playn ext=1&index=21 Mars Go to inner_mars.ppt