* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Antidepressants
Metalloprotease inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Atypical antipsychotic wikipedia , lookup
Toxicodynamics wikipedia , lookup
5-HT3 antagonist wikipedia , lookup
5-HT2C receptor agonist wikipedia , lookup
Serotonin syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
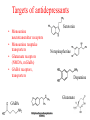
Julie Kennedy Symptoms •Anhedonia- loss of interest in everyday activites •Despondent mood •Altered sleep patterns •Changes in weight/appetite •Persistent feelings of guilt •Morbid thoughts •Agitation •Inability to concentrate •Loss of executive memory •Indecisiveness Physiological effects •Depleted monoamine neurotransmitters: serotonin, norepinepherine, dopamine •Degeneration of neurons and synaptic connectivity •Decreased GABA levels •Imbalanced HPT (hypothalamic-pituitarythyroid) axis •Increased cytokine levels Systems of diagnosis DSM-IV • Major depressive disorder: 2 weeks depressed mood or loss of interest accompanied by 4 additional symptoms • Dysthymic disorder: 2 yrs depressed mood for more days than not ICD-10 • Mild to moderate depression: common symptoms + functional impairment • Severe depression: physical symptoms Treatments available • Antidepressant drugs (SSRIs, TCAs, MAOIs) • Counseling (Cognitive therapy, interpersonal psychotherapy, non-directive counseling, befriending, exercise, problem solving therapy) • Natural supplements (St Johns Wort) • Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) Electric shock • Anaesthetisia,treatment muscle relaxant administered • 10% inpatients receive to avoid self-injury • Electrical current passed through brain to induce seizure • Unknown method of action (thought to involve NTs) • Mainly for drug resistant depressed patients ECT • 70% of all patients receiving ECT are women • Older patients more common • More common in Asia, S. America, Africa-may be used without anaesthesia & muscle relaxants Targets of antidepressants • Monoamine neurotransmitter receptors • Monoamine reuptake transporters • Glutamate receptors (NMDA, mGluRs) • GABA receptors, transporters Serotonin Norepinepherine Dopamine Glutamate GABA Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors • 1st antidepressants introduced (iproniazid, antitubercular agent) • Inhibit degradation of catecholamine to aldehydes • Mechanis of MAOI action not well understood • More likely to have side effects • Used more commonly for atypical depression • Interaction with tyramine (cheese)-MAOIs enable its systemic circulation Tricyclic antidepressants • Three fused rings (6,7,6 carbons) • Inhibit serotonin and norepinepherine reuptake • Developed from antihistamines • Common side effects: dry mouth, constipation, dizziness Desipramie Imipramine Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors •Similar efficacy with Tricyclic’s, but lower side effects •Introduced in the 1980s90s •Block serotonin uptake @ presynaptic 5-HT transporter •Act on 4-TM ion channel receptors and 7-TM GCPRs •Mode of action remains largely inconclusive •Direct-to-consumer marketing •Sales exceed $17 billion worldwide in 2003 •Interference with MDMA, cocaine, TCAs •May intitially increase suicide risk Theories for 2-3 week delay in effectivness • Quickly increase serotonin concentraion, which inhibits 5-HT firing, autorecptors become desensitized after prolonged SSRI exposure • Feedback regulation at 5-HT receptors requiring chronic administration to sustain therapeutic sertonin levels • Need for alterations in genetic ∂ and ß-adrenergic receptor expression • Changes in nerve connectivity and neurotrophic factors Common SSRIs • Fluoxetine (Prozac): best selling antidepressant, 1st SSRI to have real success • Sertraline (Zoloft): 6th best-selling overall med. In the US in 2004 ( >$3 bill.) • Paroxetine (Paxil)” short half-life, controlled release available Serotonin-Norepinepherine reuptake inhibitors • Even newer, less selective • Faster onset • Venlafaxine (Effexor): 1993, generic 2006 • Duloxetine (Cymbalta): lower risk of relapse • Common side effects: sweating, weightloss, nausea, diarrhea, constipation, vomiting, dry mouth Norepinepherine reuptake inhibitors • Introduced in 1970s to increase selectivity • Reboxetine: most effective at improving social functioning • Side effects: blurred vision, hypotension tremors, headache, urinary hesitancy Dopamine agonists • Bupropion (Wellbutrin): blocks reuptake of norepinepherine and dopamine, less risk of side effects, used as an aide to quit smoking (Dopamine) Lithium • Lithium bicarbonate (Li2CO3) • Most commonly used for bipolar disorder • Mode of action poorly understood, thought to reduce the action of the HPT system • Dosed by augmentation (increasing until desired effects acheived) Antidepressant Discontinuation Syndrome • Occurs within 3 days of cessation, only occurs after taking antidepressants for at lease 6 weeks • Also occurs when switching antidepressants or switching to generic “equivalent” (may be up to 20% different) • Flu-like symptoms, insomnia, nausea, imbalance, sensory disturbances, hyperarousal • Generally resolves itself after 2 weeks • Misleadingly termed “withdraw,” since antidepressant are not habit-forming Future of anitdepressants • Many aspects of both depression and action of antidepressants remain not well understood • Much room for development: increased specificity, decreased side effects, decreased time for onset of action