* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Changes to Earth`s Surface
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
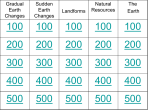
Changes to Earth’s Surface Chapter C1 Changing Landforms Earth’s ________ is always changing due to _______, ________, _________, ________, and _________ Earth’s ________, physical features on its surface always ________ over time Most changes to Earth’s surface happen so ________ that you cannot _______ them directly Water The shaping of landforms starts when _______ wears away rock Weathering is the process of breaking rock into _____, sand and other tiny pieces, or particles, called __________ Water is an important agent, or _______, of weathering Fast-flowing ________, ________ waves, and ________ weather rocks After weathering has broken rock into sediment, _________ and __________ move the sediment around and leave it in new places __________ moves the sediment from one place to another and __________ is the process of dropping sediment in a new location Water is also the chief agent of ________ in the form of ________, _________, and __________ Most rivers deposit _________ in flat areas along their banks and they an become rich _____________ areas Wind Wind is another form of _________ and _________ Wind can carry bits of _______ and ______ that weather rock surfaces Wind can also move _________ from place to place, helping to ________ it Wind erodes ______ sediment more easily than it erodes soil or _______ rock Wind erosion can blow sand into large mounds called ________ and beach dunes can help ________ the land behind them during storms Ice Ice in the form of _______, which are thick sheets of ice, can also change landforms Glaciers are ________ sheets of ice and because of their great size and weight they _______ everything underneath them Glaciers erode _________ from one place and _______ it in another The two kinds of glaciers are ________ and _____________ Valley glaciers flow slowly down _______________, eroding the mountain under them and forming U-shaped __________ ____________ glaciers are ice sheets that cover large areas of Earth and cover almost all of Greenland and ____________ Mass Movement A ________ is one type of mass movement Mass movement is the _________ movement of rock and soil because of _______ and can change landforms ________ ________ move wet soil and ________ move dry soil Landslides occur when _________ becomes stronger than the _________ that holds soil in place on a hill, causing soil to fall suddenly to the bottom of a hill A mass movement that occurs slowly is called ________ and occurs when soil moves ________ downhill because of gravity Creep may move the land only a few centimeters each _______ but over time can move fences, roads and utility poles A sinkhole is a large _______ in the ground that opens __________ and form after _______ under the surface has dissolved or become weak Sinkholes often appear in areas of _________ rock since it dissolves easily and can cause the land to collapse New Landforms Erosion and deposition can _______ landforms or ______ new ones Rivers can deposit _________ that builds _______ _________ are major forces for forming new landforms When the glaciers melted, they left behind at their lower ends long ridges of rock and soil, called _________ __________ New islands can be formed by _________ eruptions __________ volcanoes increase their height by depositing melted rock and ash and eventually break through the sea surface as __________ Earth’s Interior Earth is not a solid ball of rock, but has ________ distinct layers and we live on Earth’s _______ The ________ is the outer layer, and it is made of _______ The ________ is the layer of solid ______ just beneath the Earth’s crust The mantle is however _______ in texture due to its ______ temperature The only way we can observe parts of the __________ are when it reaches the Earth’s surface through ___________ The _________ is the center layer of Earth and it can be divided into two parts: outer core of liquid, or molten, _______ and an inner core of solid _______ Even though the core is very hot, great __________ at the center of the Earth keeps the inner core _________ Earth’s Crust Moves (#1) Earth’s surface is not a single layer of ________ but is made up of many ________ Plates are rigid blocks of _______ and upper ________ rock There are ______ major plates make up Earth’s surface Earth’s plates fit together like pieces of a ________ _______ The plates ________ on the soft rock of the __________ _________ and ________ within the Earth produce __________ in the soft rock of the mantle As the mantle moves, the _________ floating on it move slowly, too Because plates are close to one another, the _________ of one plate affects another Some plates _______ together, some ______ apart, some ________ past each other all causing changes in Earth’s _________ Earth’s Crust Moves (#2) When plates collide, _______ is released and new _______ are produced On land, ________ rise and ________ erupt and on the ________ floor deep trenches form As plates pull apart, ________ dotted with ________ develop and forms new sea floor at the ridges The ______, or crack will one day result in the separation of parts of continents When plates scrape and slide past each other, they ________ Earth’s surface causing ____________ Mountain Formation (#1) _________ are Earth’s highest landforms and form as the crust ______, ________ and _______ upward because of movement of Earth’s plates Most of the highest mountains form where ________ ________ collide As the plates push together, their edges _______ and ______ into mountains, and the _________, Earth’s highest mountain range located in Asia, formed this way At some places, continental and _______ plates collide and the lighter ________ plate moves up and over the oceanic plate, forming mountains Some mountains form away from edges of plates, where _______ from movement at the boundaries _______ a block of rock upward seeming to rise from flat land around them Mountain Formation (#2) Plates that pull apart leaves _______ between them and ________ can bubble up between the plates Magma is a hot, soft ______ from Earth’s ________ Magma builds up along the _______, forming long chains of ________ under the ocean and are called ____-_______ ridges The Mid-Atlantic Ridge separates North American and ________ plates in the north and South American and _______ plates in the south Volcanoes Most volcanoes form at ________ boundaries and are mountains formed by ______ and _____ _______ is magma that reaches Earth’s ________ and ______ is small pieces of hardened lava Chains of volcanoes form where a __________ plate and an _________ plate collide The edge of the _______ plate pushes under the _______ plate and the leading edge of the oceanic plate ________ as it sinks deep into the _________ The melted rock becomes ________ that forces its way up between the _______ Sometimes, volcanoes form in the _______ of plates, over unusually hot columns of _______ as the magma melts a hole in the plate and causes volcanic _________ Earthquakes An earthquake is a shaking of the ground caused by the sudden release of _______ in Earth’s ________ The energy released as _______ crush together, scrape past each other, or bend along jagged ________ can cause great damage More than one ________ earthquakes occur each year and many earthquakes occur along the boundaries of the ________ plate Earthquakes also occur along _________ in the crust Faults occur in the middle of a _________ where the forces pressing on the Earth’s _________ have bent or broken it An earthquake sends out _________ in the form of seismic waves, which are like ________ that form on a pond when a stone is tossed in