* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Psychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of direct thrombin inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
MTOR inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of HIV-protease inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of direct Xa inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of integrase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of neuraminidase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotease inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of ACE inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
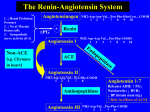
From Snake Venom to SAVE : The Benefits of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and AT2 receptor blockade by John Hakim, M.D. 08/99 1 Outline on ACE talk Renin-Angiotensin-Bradykinin System Brief History of ACE inhibitors and AT2 Blockers Mechanism of Action Clinical Indications Hypertension CHF and LV dysfunction LV Dysfunction after MI Diabetic Nephropathy Side Effects Conclusions 08/99 2 Renin-Angiotensin-Bradykinin System Renin is secreted by kidneys by JG apparatus Angiotensinogen made by liver Renin cleaves of the decapeptide angiotensin 1 from angiotensinogen ACE splits angiotensin 1 into angiotensin II during passage through the lungs. Angiotensin II has blood pressure increasing effects ACE catalyzes breakdown of bradykinin to inactive peptides 08/99 3 Angiotensin Converting Enzyme: What is it? Kinase 2 - a bivalent dipeptidyl carboxyl metalopeptidase Two Forms: 08/99 Endothelial ( on blood vessels and in brain) Soluble form in blood and body fluids 4 Yin and Yang of ACE Bradykinin (via B2 receptor) Promotes vasodilatation by stimulating production of arachodonic acid metabolites, NO, and endothelium derived hyperpolarizing factor Promotes renal naturesis via direct tubular effects Increases vascular permeability, augments mucus secretion Angiotensin 2 08/99 Potent vasoconstrictor, acting directly on vascular smooth muscle cells. AT2 interacts with sympathetic nervous system both peripherally and centrally Causes Sodium and fluid retention via aldosterone and ADH Promotes cellular migration, proliferation and hypertrophy Promotes growth of smooth muscle cells and hypertrophy of blood vessels and the heart. 5 History ACE inhibitors 1st ACE inhibitor was teprotide, an IV nonapepetide from venom of Bothrops jararaca isolated, elucidated, and synthesized 1971 Captopril was 1st oral ACE inhibitor (1978) rapid onset of action with maximum activity in 15 to 30 minutes, but plasma T1/2 only 2 hours. 08/99 6 History ACE inhibitors Newer ACE inhibitors Longer T1/2, more potent. Currently 9 oral ACE inhibitors approved by FDABenazepril, Captopril, Enalapril, Fosinopril, Lisinopril, Moexipril, Ramapril, Quinapril, and Trandolapril AT1 receptor antagonists (ARB) – Losartan, Valsartan, Irbesartan 08/99 7 ACE Pharmacology Differences: Active Moieties – sulfhydryl -Captopril – phosphinyl -Fosinopril – carboxyl -Enalapril,lisinopril, Benzapril, Quinapril, Ramapril, Trandilopril, Moexipril Potency & Plasma half life Distribution and affinity for tissue bound ACE Cardiac affinity – quniapril=benazapril>lisinopril>fosinopril>captopril 08/99 Excretion- all renal (fosinopril and trandolapril also metab by liver) 8 Angiotensin Receptors Angiotensin receptors of AT1 subtype are the target of the new drugs Signal transduction by G Protien (Gq/11) which activates phospholipase C to generate diacylglcerol and inositol triphosphate inositol triphosphate causes release of calcium from intracellular stores Ca=2 and diacylglycerol activate protein kinases to phosphorolate proteins and effect cell function gene is on Chromosome 3 AT2 receptor gene is on X chromosome 08/99 9 ACE Inhibitors: Clinical Indications Hypertension Congestive Heart Failure LV dysfunction after Myocardial Infarction Atherosclerotic Vascular Disease Diabetic Nephropathy 08/99 10 Clinical Indications: Hypertension ACE inhibitors decrease Systemic Vascular resistance but cause little change in heart rate With chronic ACE inhibition, AT II and aldosterone levels tend to return to pretreatment levels (AJC 1982;49:1561-1563) JNC VI has beta blockers and duretics as first line therapy for uncomplicated HTN – ACE inhibitors are indicated for HTN with coexisting conditions such as CHF and DM Nephropathy 08/99 11 Clinical Indications: Hypertension Racial Differences In VA Cooperative Study Group Trial, captopril reduced BP more in White patients with mild to moderate HTN than Black patients at 7 weeks. These racial differences were abolished by the addition of HCTZ (BR J Clin Pharm 1982;14:97S-101S) Racial Differences have not yet been noted with the AT2 Receptor Blockers 08/99 12 Congestive Heart Failure and LV Dysfunction ACE Inhibitors have been shown to cause regression in LV Hypertrophy improve LV dysfunction decrease mortality in patients with CHF Clinical trials 08/99 CONSENSUS SOLVD-TREATMENT V-HEFT II SOLVD-Prevention 13 High Cardiac affinity ACE Quinipril - a high cardiac affinity ACE 08/99 Has been shown to be superior to enalapril in preventing LVH in animals Circulation 1995;91;1 16-19 Relavance of Blockade of Cardiac and Circulatory ACE for the prevention of Volume Overload induced Cardiac Hypertrophy 14 ATB’s may be as effective as ACE in CHF ELITE Study- “Evaluation of Losartan in the Elderly” Reported equivalent effects of Losartan and Captopril in on the progression of CHF in elderly patients. There was an unexpected reduction in the incidence of sudden death in the Losartan group. Lancet 1997;349:747-752 Randomized trial of Losartan vs Captopril in patients over 65 with heart failure. 08/99 15 ACE Inhibitor Studies in LV Dysfunction post MI SAVE NEJM 1992:327:669-667. CONSENSUS II NEJM 1992;327:678-684 AIRE Lancet 1993;342:821-828 ISIS-4 Circulation 1993 Supplement I GISSI 3 Lancet 1994;343:1115-1122 TRACE NEJM 1995;333:1670-1676 SMILE NEJM 1995;332:80-85 08/99 16 ACE Inhibitors Post MI Subgroup analysis of SAVE (Uniformity of Captopril in SAVE Study) and TRACE (Trandolapril Cardiac Evaluation Study- ACE post MI) document beneficial effect of long term use of ACE inhibitors post MI Beneficial effects in preventing LVH and Heart failure persist even when analysis were limited to diabetics. 08/99 17 ACE Inhibitors and Acute MI GISSI-3 analysis* ACE inhibitor (lisinopril) reduced both six week (30%) and six month (20%) mortality (vs. placebo) in diabetics given drug within 24hours of admission. Survival benefit was maintained for six months despite the fact that patients got drug for only six weeks. Advantage was present in both IDDM and NIDDM. Patients with Cr>2.0, SBP<100mmHg, and Killip class 4 excluded. *Circulation 1997;96:4239-4245. Zuanetti et al, Effect on Ace Inhibitor Lisinopril on mortality in diabetic patients with AMI. 08/99 18 ACE Inhibitors and Acute MI Current guidelines in the treatment of AMI consider aspirin and fibrinolytics mandatory for all eligible patients. Acute ACE inhibition appears to be particularly beneficial to Diabetics with MI. (Circulation 1997;96:4239-4245. Zuanetti et al, Effect on Ace Inhibitor Lisinopril on mortality in diabetic patients with AMI) 08/99 19 ACE Inhibitors and Ischemia ACE inhibitors reduced recurrent MI by 25% in the SAVE Trial. (Circulation 1994; 90:17311738. Effects of Captopril on ischemia after myocardial infarction.) ACE inhibition was associated with 37% fewer ischemic events in the CATS trial JACC 1997;30:400-405. Long term anti ischemic effects of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors in patients after myocardial infarction. 08/99 20 ACE Inhibitors and Ischemia ACE inhibitors increases parasympathetic tone and helps restore the autonomic balance in CHF. JACC 1993; 21:655-661. Sustained augmentation of parasympathetic tone with angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition in patients with CHF. ACE inhibitors may decrease central sympathetic outflow. ACE inhibitors blunt sympathetic coronary vasoconstriction by decreasing angiotensin 2. Circulation 1997;96:148-153 Intracoronary Angiotensin 2 potentiates coronary artery sympathetic vasoconstriction in Humans. 08/99 21 ACE Inhibitors and Remodeling Remodeling of the LV post MI can be seen within 3 hours, with increased end-diastolic and end-systolic volumes. Early Ramapril in Anterior Infarct was associated with substantial recovery of wall motion within 14 days post MI.* *Circulation 1997; 95:2643-2651. Healing and Early Afterload Reducing Therapy (HEART) Trial Investigators. 08/99 22 Atherosclerotic Vascular Disease Studies in LV dysfunction suggest ACE inhibitors decrease the frequency of ischemic events Several trials are underway to show ACE prevent ischemic events in high risk patients without LV dysfunction ACE inhibitors reverse endothelial dysfunction in hypertensive pts and pts with NIDDM ACE Inhibitors improved endothelial function by enhancing bradykinin induced endothelial NO production 08/99 23 Diabetic Nephropathy ACE inhibitors prevent progression of microalbuninuria to overt proteinuria. A large, prospective placebo controlled study in IDDM has shown that captopril slows the progression of nephropathy to dialysis, transplant and death NEJM 1993;329:1456-1462 Effect is by selectively dilating efferent arterioles and decreasing glomerular filtration pressure. 08/99 24 ACE: SIDE EFFECTS Class Effects – Hypotension, – Cough (10% Whites, up to 40% Asians) – Hyperkalemia, Renal Failure, Fetal anomalies, – Angioedema (2/1000 in whites higher in blacks) – Dysgeusia Sulfhydryl-related effects (Captopril) – Neutropenia, Rash, Nephrotic -range proteinuria 08/99 25 AT2 receptor Blockers: Adverse Effects Hypotension Impaired Renal Function Fetal/Neonatal Morbidity and Mortality Please Note ATB are only indicated for Hypertension at Present 08/99 26 Conclusion ACE Hypertension Congestive Heart Failure LV dysfunction after Myocardial Infarction Atherosclerotic Vascular Disease Diabetic Nephropathy ATB Indicated for HTN Elderly (>65) with CHF benefit (less sudden death and less CHF) 08/99 27 ATLAS Study Compared low Dose to High Dose lisinopril vs. high Dose lisinopril 3000 pts, Class II, III, IV CHF All pts who could tolerate 12.5 mg lisinopril randomized to 2.5-5mg vs 35mg lisinopril 08/99 28 ATLAS Results High dose arm lower risk of death or hospitalization (12% reduction in all cause mortality and hospitalization) Low Dose gives you 50% of the benefit of an ACE inhibitor 08/99 29