* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Features suggestive of a neurally - mediated cause
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Heart arrhythmia wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
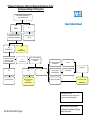
Pathway for Diagnosis / Referral of Adults with Dizziness and/or Syncope presenting in Primary Care Did the patient have a spontaneous loss of consciousness and/or dizziness? YES or UNCERTAIN NO Is there a family history of Sudden Cardiac Death under 40yrs, Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy or Channelopathies? NO Still Requires ECG Is there a history of brain injury or feature strongly suggestive of epilepsy and normal ECG? Consider falls, TIA, CVA, drug misuse etc YES ECG & REFER CARDIOLOGY Is there evidence of significant structural heart disease or abnormal ECG NO Cardiac exam / CXR Features strongly suggestive of vasovagal syncope Reassure Recurrent Events YES YES Suggest Neurology Referral Open access memo or tape* and / or Echo REFER CARDIOLOGY NO Features suggestive of orthostatic hypotension Neither vagal, nor orthostatic Review medications Open access memo or tape * REFER CARDIOLOGY * Open access memo or tape If available locally, an aid to the correct device Is given in the accompanying guidelines ECN DS FINAL 090907 6 pages Note: Recurrent worrying symptoms unexplained by this pathway: Cardiology 1 advice can be sought Management of Adults with Dizziness and/or Syncope presenting in Primary Care 1. Initial Evaluation History 3 Key Questions to answer during initial evaluation: A. Is loss of consciousness due to syncope? Features that suggest a non-syncopal attack: Confusion after the attack for more than 5 minutes (seizure) - some caution in elderly patients where recovery may be more protracted Prolonged (>15 sec) tonic-clonic movement starting at the onset of the attack (seizure) Associated with vertigo, dysarthria, diplopia (TIA) TIAs in general do not cause drop attacks and syncope B. Are there clinical features suggestive of diagnosis? See Aids to Diagnosis below C. Is heart disease present or absent? Aortic Stenosis Left Ventricular systolic dysfunction Examination Supine and Erect BP ECG ECN DS FINAL 090907 6 pages 2 2. Aids in Diagnosis: Syncope Is a sudden but brief loss of consciousness that is caused by inadequate blood supply to the brain. Recovery is spontaneous and rapidly complete. Syncope is common, disabling and possibly associated with sudden cardiac death. Vasovagal Syncope Precipitating event such as fear, severe pain, emotional stress, instrumentation or prolonged standing are associated with typical prodromal symptoms (although prodrome is not always present, the precipitating factors still have diagnostic significance) Situational Syncope If syncope occurs during or immediately after urination, defecation, cough or swallowing Orthostatic Syncope If there is documentation of orthostatic hypotension (decrease of SBP=20mmHg or to <90mmHg) associated with syncope or presyncope Features strongly suggestive of Reflex Syncope Occurs when standing, extreme pallor, random limb jerks, always collapse to floor, quick recovery Syncope due to Cardiac Ischaemia If symptoms present with ECG evidence of acute ischaemia with or without myocardial infarction Syncope due to Cardiac Arrhythmia If ECG changes showing : Sinus bradycardia <40bpm or repetitive sinoatrial blocks or sinus pause >3 seconds Atrioventricular block (2nd degree, Mobitz 11, or 3rd degree atrioventricular block ) Alternating left and right bundle branch Pacemaker malfunction with cardiac pauses Rapid paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia or ventricular tachycardia ECN DS FINAL 090907 6 pages 3 Vertigo Is a hallucination of movement of the environment about the patient, or of the patient with respect to the environment. It is not synonymous with dizziness. It may be central - due to a disorder of the brainstem or the cerebellum - or peripheral - due to a disorder in the inner ear or the Vlllth cranial nerve. Always would suggest ENT review prior to cardiac review unless associated with palpitations or chest pain Significant Structural Damage This includes Previous Myocardial Infarction, Heart Failure, Cardiomyopathy, Valvular Heart Disease Features suggestive of heart rhythm abnormality This includes sudden unexplained syncope during exercise/exertion, excitement, stress or startle. Features suggestive of a cardiac cause Symptoms when supine During exertion Preceded by palpitations Presence of severe heart disease ECG abnormalities: o Wide QRS (>0.12 sec) o AV conduction abnormalities o Sinus bradycardia less than 50 bpm or pause of greater than 2 seconds during the day, or 3 seconds at night o Long QT interval Features suggestive of Epilepsy Tonic/Clonic Movement, cyanosis, incontinence, lateral tongue biting, prolonged post ictal confusion Features suggestive of a neurally - mediated cause After sudden unexpected unpleasant sight, sound or smell Prolonged standing at attention or crowded warm place Nausea, vomiting associated with syncope Within one hour of a meal After exertion Temporal relationship with start of medication or changes of dosage ECN DS FINAL 090907 6 pages 4 Electrocardiograms that require urgent attention Bradycardia: <40bpm) or pauses >3secs Mobitz 11, 2nd, 3rd degree AV block Altemating RBBB LBBB Rapid Supraventricular Tachycardia Ventricular Tachycardia Cardiac ischaemia Myocardial Infarction WPW Long QT Brugada Prognostic Stratification Poor prognosis: o structural heart disease:- This is the most important predictor of total mortality and sudden death in patients with syncope, independent of the cause of the syncope Excellent prognosis: o young, healthy, normal ECG o neurally mediated syncope o orthostatic hypotension o unexplained syncope ECN DS FINAL 090907 6 pages 5 Cardiomemo or 24 hour tape? A cardiomemo is a patient activated event recording device that is generally provided for 5 to 7 days. It is helpful for infrequent symptoms and is recommended for patients who have symptoms less than once a day but more frequent than once a fortnight A 24 hours tape allows continuous heart rhythm monitoring for 24 hours. It is indicated where there are symptoms on a daily, or near daily, basis ECN DS FINAL 090907 6 pages 6