* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plants
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
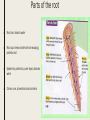
PLANTS Chapter 1 Review Questions ■ What types of plants do not have flowers? ■ Name one example of a plant that is vascular ■ Name one example of a plant with leaves that are needles. Roots ■Absorb water and minerals ■Store food ■Holds the plant to the soil/ground Parts of the root ■ Root hair: absorb water ■ Root cap: keeps nutrients from escaping, protects root ■ Epidermis: protection, outer layer, absorbs water ■ Cortex: core, stores food and nutrients Types of Roots ■ Aerial: never touch the ground, get water from rain ■ Fibrous: very thin, branch out to get water ■ Taproots: start from ground, build up ■ Prop: support the plant’s stem Stems ■ Support the plant – Soft Stems and Woody Stems – Examples: ■ Transport system for nutrients ■ Xylem: moves water and minerals ■ Phloem: moves sugar from leaves to other parts In groups, create a diagram showing the process of how plants use sunlight to gain energy. ■ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cQUk X9S06qw Photosynthesis vs. Respiration ■ Photosynthesis: ■ Respiration: ■ NEED: carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight. ■ NEED: oxygen. ■ Sunlight -> sugar & oxygen ■ Oxygen & sugars are inhaled, carbon dioxide is exhaled ■ Oxygen leaves plant as “Waste” Exit Questions ■ Why do you think that people who own plants talk to them? Will this help the plants grow? Why/why not? ■ Can plants survive without absorbing the carbon dioxide we breathe in? Explain why/why not. CLASSIFYING ANIMALS Intro Questions ■ What groups of animals do you think you belong in? Why? ■ What are some things that humans can do but animals cannot? Simple Invertebrates ■ Sponges: do not have real tissues or organs. They are asymmetrical ■ Cnidarians: soft-bodied creatures that have radial symmetry to divide in parts ■ Worms: soft-bodied creatures with bilateral symmetry to divide into 2 parts only – Nematodes – https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X1YiIiPUQR 8 Tell what type of symmetry these two shapes have Complex Invertebrates ■ Mollusks: Have a shell, and tissues that make up tentacles. Have bilateral symmetry – Examples: snails, squids, clams. • Echinoderms: skeleton is located inside the body. Have radial symmetry • Examples: sea urchins, starfish • Arthropods: skeleton is located outside the body. Have bilateral symmetry • Examples: most insects, crabs Vertebrates ■ Fish: 3 types (Bony, Cartilage, Jawless) Cold-blooded – Bony have bones & nerve cord – Jawless suck in food whole, have nerve cord – Cartilage have nerve cord made of cartilage ■ Amphibians: can live in both land & water, cold-blooded – Start with gills, develop lungs later ■ Reptiles: cold blooded, scaly skin – Need warmth from sun/light, shed skin ■ Birds: 2 legs, warm-blooded, feathers, hollow bones Quick Check ■ What 3 characteristics do vertebrates have in common? ■ What are the 3 classes of fish? ■ Why do reptiles have to stay in the sun? Mammals ■ Have large brains, have hair (fur) and feed their own young Warm blooded: generate body temperature by burning food for energy ■ Monotreme: lays eggs (platypus, spiny anteater) ■ Marsupial: Partially developed newborns stay in pouch – Kangaroos, Koala bears ■ Placental: Fully developed newborns – Humans, elephants, tigers Quick Check ■ Why are humans considered mammals? ■ What does it mean to say that birds and mammals are warm-blooded? ■ Why do mammals need to eat more than reptiles? Animal Systems ■ What is the purpose of your digestive system? ■ What is the purpose of your respitory system? ■ Is there any system you cannot live without? Explain Systems ■ Respiratory: helps breathe, filters air – Removes CO2 from blood, gets oxygen ■ Digestive: helps break down food, separates nutrients – Stomach acid = good bacteria ■ Excretory System: filters toxins (kidneys, intestines, liver) – Removes salt, water, carbon dioxide Systems (Cont’d) ■ Circulatory: Heart and blood vessels transfer nutrients – Heart gives blood oxygen, picks up nutrients in intestines ■ Nervous: Series of messages between brain and body – Instincts, involuntary muscles, regular movements ■ Endocrine: Releases hormones (Adrenaline) Heart Rate Exercise ■ Check how many times your heart beats in 30 seconds while sitting down ■ 45 seconds of dancing/stretching/moving NOT RUNNING ■ Check to see how many times you feel a beat in 30 seconds after ■ What could be another time when your heart rate would dramatically increase? Explain