* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download energy levels
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Molecular Hamiltonian wikipedia , lookup
Mössbauer spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Electron scattering wikipedia , lookup
Auger electron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
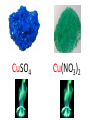
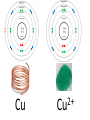
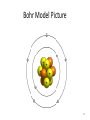
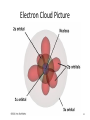
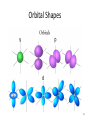
Tuesday Oct 14 Objective: Describe different models of the atom. Checkpoint: • Draw a picture of a copper atom, including electrons in the correct energy levels. • Does copper want to gain or lose electrons to be come stable? What ion will it form when it does this to become stable? HW: • Study for Nuclear Chem re-take exam on Wednesday (after school), 12:30 PM • Read pp 104-108 in book (Section 4.2) Answer questions 8-14 on pp 108. Due Friday. Copper 29 p 35 n Copper 29 p 35 n Cu 2+ Nuclear Chem make-up exam Wednesday 12:30 PM • • • • • • • • Ba(NO3)2 Ca(NO3)2 Cu(NO3)2 Pb(NO3)2 LiNO3 KNO3 NaNO3 Sr(NO3)2 • • • • • • • • Yellow/Green Orange Green/Blue Light blue Red Pink/Purple Bright yellow Orange/Red CuSO4 Cu(NO3)2 Cu 2+ Cu Thomson Model • Created the “Plum-pudding model” • Electrons are surrounded by a sea of evenly distributed positive charge 9 Rutherford Model • Small, dense, positive nucleus surrounded by cloud of electrons 10 Bohr Model • Proposed that electrons orbit the nucleus in a fixed, circular path • Orbit path has specific energy that prevents electrons from falling into the nucleus • Quantum of energy is the amount of energy needed to move an electron between energy levels 11 Bohr Model Picture 12 Erwin Schrödinger • Quantum Mechanical Model – Modern model – Estimates the probability of finding an electron within a certain volume of space surrounding the nucleus – Where you find the electron 90% of the time 13 Electron Cloud Picture 14 Energy Levels - 1 • Electrons exist within energy levels or shells – General location around the nucleus where the electron is moving – Energy levels are not equally spaced apart, they become more tightly packed the farther you get from the nucleus 15 Energy Levels - 2 • Principal quantum numbers (n) identify the energy levels in an atom – Tells you how far away the electron is from the nucleus – There are 1-7 energy levels, correlates with period numbers – Each level has same n number of sublevels – Maximum number of 2n2 electrons per level 16 Atomic Orbitals - 1 • Atomic orbitals are more specific regions within each energy level where electrons are found – Highest probability of finding an electron – Also called sublevels, subshells, azimuthal quantum number, or angular momentum quantum number (l) • Number of orbitals for each energy level equals n2 17 Atomic Orbitals - 2 • Sublevels are designated by letters – s,p,d,f • Each sublevel has a unique shape and number of orbitals related to different spatial orientations • Each sublevel orbital can hold a maximum of 2 electrons 18 Orbital Shapes 19 Orbital Shapes cont. Summary • Each principal energy level consists of one or more sublevels and each sublevel consists of one or more orbitals • Orbitals Sublevels Energy Level 21 Thought of the Week The joy of life comes from our encounters with new experiences, and hence there is no greater joy than to have an endlessly changing horizon, for each day to have a new and different sun. Christopher McCandless