* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Old Exam 3 Questions KEY
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
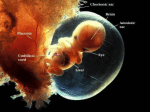
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
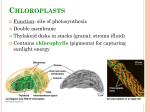
BIOL 212 SI, Molly Dr. Coffman and Dr. Peterson OLD EXAM 3 QUESTIONS 3/26/15 Cell Signaling Receptors are a. proteins that change conformation upon interaction with a stimulus b. genes that change expression in response to a stimulus c. phosphorylation cascades that control cellular responses d. specialized organelles that perceive environmental signals e. all of the above The process by which information from a cell’s environment is perceived and relayed to control a cellular response is known as a. signal transduction b. chemotaxis c. meiosis d. translation e. impulsive respondus Cell communication a. requires cytoplasmic connections. b. only occurs over short distances. c. controls mitotaxis. d. involves the exchange of genes. e. coordinates developmental processes in multicellular organisms. Your textbook defines three categories of cell surface receptors that respond to extracellular signals. They are: a. Ligand-gated ion channels, steroid receptors, G-protein coupled receptors b. Enzyme-linked receptors, G-protein coupled receptors, ligandgated ion channels c. Steroid receptors, enzyme-linked receptors, G-protein couple receptors d. Ligand-gated channels, exocrine receptors, G-protein couple receptors e. Exocrine receptors, enzyme-linked receptors, ligand-gated ion channels The likely mechanism by which a G-protein coupled receptor might transduce and amplify a signal intracellularly? a. By upregulating the expression of a transporter. b. By promoting the production of a second messenger. c. By degrading a repressor. What is the likely mechanism by which an enzyme-linked receptor might transduce and amplify a signal intracellularly? a. By activating a protein kinase cascade. b. By degrading a repressor. c. By upregulating the expression of a transporter. What benefits do hormone signaling provide for a multicellular organism? a. Long distance cellular communication. b. Amplification of weak signals. c. Coordination of bodily functions d. Protection from pathogen attack. e. None of the above f. All of the above From the graph above showing the amount of ligand bound to the receptor at different ligand concentrations, what do you estimate to be the Kd for ligand/receptor interaction as shown? a. About 1 pM b. About 5 pM c. About 15 pM d. About 30 pM e. About 60 pM If you did another experiment with the same ligand, only this time you add a fixed amount of a weak competitive inhibitor of the ligand along with the ligand, which of the following would be true? Note: You are still measuring the amount of ligand bound while increasing the ligand concentration. a. b. c. The Kd will decrease. The maximum binding will decrease. The Kd will increase. With reference to the above diagram from your textbook. Epinephrine acts …. (finish the sentence) a. By the GPCR transducing the signal across the plasma membrane. b. by promoting the dissociation of the G-protein β/γ dimer from the α subunit. c. by producing a second messenger (cyclic adenosine monophosphate). d. All of the above. e. None of the above. The figure above illustrates signaling through the EGF receptor. Which of the following would represent a gain-of-function situation for the EGF receptor? a. A mutation in the EGF receptor that binds ligand, but does not allow the receptor to dimerize. b. Deletion of the gene encoding Erk c. Increased cell division due to the inactivation of a tumor suppressor d. Deletion of the ligand binding domain of the EGF receptor so that it becomes ligand independent e. None of the above f. All of the above The figure above illustrates signaling through the EGF receptor. Which of the following would represent a loss-of-function situation for the EGF receptor? a. A constitutively active from of the Ras protein. b. Deletion of the ligand binding domain of the EGF receptor so that it becomes ligand independent c. A mutation of the EGF receptor so that it can no longer be phosphorylated. d. All of the above e. None of the above You want to test the hypothesis that EGF receptor activation is sufficient for stimulate cell division in cultured epithelial cells. Which of the following would potentially test your hypothesis? a. Forcing expression of the Her2 protein in the cultured cells. The Her2 form of the EGF receptor is constitutively active. b. Add epidermal growth factor to the cell culture medium. c. Add GDP to the cell culture medium d. All of the above e. A and B above Multicellularity/specialization Which a. b. c. d. e. of the following is an example of extracellular matrix Collagen Fibronectin Chitin All of the above None of the above Which of the following is a function of the extracellular matrix (ECM)? a. Strengthening cell-cell and tissue-tissue contacts b. Providing support. Tissues such as bone are largely ECM. c. Mediating cell signaling d. All of the above e. None of the above Which of the following is true of the plant cell wall? a. It forms a barrier making plant cells resistant to osmotic lysis. b. A major component is cellulose. c. A major component is glucose. d. It is composed of a primary and a secondary cell wall, each with distinctive properties. e. All of the above f. None of the above Which a. b. c. d. e. of the following is true of the plant cell wall? It strengthens cell-cell and tissue-tissue contacts. A major component is cellulose. A major component is glucose. All of the above None of the above Given the information in the table above, which of the following is a reasonable conclusion? a. b. c. d. All collagens have similar physical characteristics. Collagens only form long fibers. Collagens are not found throughout the body. Collagens are found in the extracellular matrix of cells. Given the information in the table above, which of the following is a reasonable conclusion? a. All collagens have similar physical characteristics. b. Collagens form fibers that can be rigid, flexible, elastic, or form meshworks. c. Collagens are not found throughout the body. d. Collagen fibers are found within cells. Why would it be important to have epithelial layers lining compartments such as the intestine? a. For cellular communication via gap junctions b. To strictly control what substances cross the barrier c. To create a smooth surface d. To secrete ECM molecules onto the surface e. A and C Which of the following statements about the extracellular matrix is most correct? a. It is composed of living cells. b. It is a site of electron transport. c. It is composed of lipopolysaccharides. d. It is a static, rigid structure. e. Its components are produced and secreted by the cell. Tight junctions a. connect the cytoplasm of one cell to another. b. are composed of pectin. c. connect cells to the extracellular matrix. d. form seals that prevent solutes from diffusing in between cells. e. pair chromosomes during meiosis. All but which of the following are involved in physically holding cells together? a. Extracellular matrix b. anchoring junctions c. paracrine ligands d. middle lamella e. cell adhesion molecules Which of the following processes are important for normal development? a. cell division b. cell migration c. cell differentiation d. programmed cell death e. A,B,C f. all of the above Cellulose is a. found in the plant extracellular matrix b. a component of the cytoskeleton c. associated with DNA to form chromosomes d. produced in chloroplasts e. a type of proteoglycan What is the purpose of cell-cell junctions a. To keep the extracellular matrix from breaking b. To link cells together in various ways c. To facilitate the movement of cells d. To make sure that cells will obtain food Which types of cell-cell junctions allow form a seal between intestinal epithelial cells? a. Tight junctions b. Anchoring junctions c. Gap junctions Which types of cell-cell junctions allow for the passing of small molecules between cells? a. Tight junctions b. Anchoring junctions c. Gap junctions Which types of cell-cell junctions have close assocations with the cytoskeleton? a. Tight junctions b. Anchoring junctions c. Gap junctions The figure above is from your textbook. It shows an electron micrograph of two intestinal epithelial cells from an experiment where lanthanum, an electron dense element, was injected into the bloodstream of a mouse. What outcome would you predict if the mouse was fed lanthanum rather than injected with it? a. The lanthanum would be observed on both sides of the tight junction. b. The lanthanum would be observed on the apical side of the tight junction. c. The lanthanum would be observed on the basal side of the tight junction. d. The lanthanum would not be seen as it would be degraded in the digestive tract. Most multicellular organisms have which of the following? a. An outer cell layer that separates the organism from the environment. b. Cell-cell communication c. A transport system that allows fluids to move within the organism. d. All of the above e. None of the above What is a function of the extracellular matrix? a. To support the organism b. To help arrange cells in space c. To help cells sense and respond to environmental changes d. All of the above e. None of the above Pattern formation involves which of the following? a. Axis information provided by the mother b. Cell-cell communication c. Gradients of morphogens d. The influence of gravity e. All of the above f. None of the above Pattern formation involves which of the following? a. The expression of homeotic genes b. Differential gene expression c. Communication of anterior-posterior and dorsal-ventral axis information d. The influence of gravity e. All of the above f. None of the above Which of the following statements is true? a. A finger muscle cell and a finger skincell express similar pattern formation genes, but the muscle expresses mesoderm genes and the skin cell expresses endoderm genes. b. An arm neuron and a leg skin cell express different pattern formation genes, but both expressed common endoderm genes before diverging into neuronal and epidermal lineages. c. Morphogens function in a concentration-dependent manner. d. Once cells occupy a specific region in the embryo, they differentiate only based on their history or lineage. Which of the following statements illustrate the principle of differential gene regulation? a. Neurons have a different mRNA profile than muscle cells. b. Only a subset of cells will respond to the presence of a hormone. c. Many cells express the same set of actin proteins, but at different levels. d. All of the above e. None of the above In extracellular cellular matrix (ECM), Elastin protein: a. provides tensile strength b. provides elasticity c. provides both strength and elasticity d. none of the above In extracellular cellular matrix (ECM), collagen protein: a. provides tensile strength b. provides elasticity c. provides both strength and elasticity d. none of the above What is the major component in plant cell wall: a. Collagen b. Elastin c. Cellulose d. Chlorophyll In animal cells, the cell junctions can be: a. Anchoring junctions b. Tight junctions c. Gap junctions d. All of the above In anchoring junctions, there are two kinds of cell adhesion molecules (CAMs), cadherin and integrin. The function of integrin is: a. to create cell-to-cell junctions b. to create connections between cells and ECM (extracellular matrix) c. to mediate both cell-to-cell and cell-to-ECM interactions d. None of the above Gap junctions function to: a. Connect cells to the extracellular matrix b. Permit the passage of molecules from the cytoplasm of one cell to another c. Form tight seals that prevent extracellular fluids from leaking between cells d. None of the above Tight junctions function to: a. Connect cells to the extracellular matrix b. Permit the passage of molecules from the cytoplasm of one cell to another c. Form tight seals that prevent extracellular fluids from leaking between cells d. None of the above Development During limb formation, which is NOT true: a. Cell division promotes the growth of the limb b. Cell migration causes cells to reach to their correct location c. Cell differentiation produces specialized cells d. Apoptosis eliminates cells in between the fingers e. Cells undergo meiosis Pattern formation during development can be determined/influenced by: a. Morphogens b. Cell contacts c. Cell signaling d. All of the above Drosophila embryos have 15 segments, the identity of which is determined by: a. Bicoid b. Gap genes c. Pair-rule genes d. Segment-identify genes e. A transcriptional hierarchy of Bicoid/Gap genes/Pair-rule genes/Segment identity genes If the homeotic gene Antennapedia is ectopically expressed in embryonic segment that gives rise to antenna, the fly will have: a. legs form in the place for antenna b. legs everywhere c. legs in abdomen d. None of the above Above is a model for flower patterning in Arabidopsis. If you mutate C function gene (AG), the four whorls will be: a. Sepal-Petal-Stamen-Carpel b. Sepal-Sepal-Petal-Petal c. Sepal-Petal-Sepal-Petal d. Sepal-Petal-Petal-Sepal The figure shown above represents the chromosome locations and expression patterns of homeotic genes (Hox or Hom genes) in Drosophila and mice. Which of the following statements is consistent with the information shown? a. Mice have more Hox genes than Drosophila. b. The anterior to posterior expression patterns of Hox gene expression is conserved. c. The Abdominal B genes were likely duplicated multiple times over the course of evolution. d. All of the above e. None of the above The figure shown above illustrates the expression domains of homeotic genes (Hox genes) in chickens and mice. Which of the following statements is consistent with the information shown? a. Chickens and mice express similar sets of Hox genes in the same anterior to posterior order. b. The different body morphologies between mice and chickens is due in part to changing the domains of the expression of Hox genes. c. The locations of forelimbs and hindlimbs is governed by conserved mechanisms in vertebrates. d. All of the above e. None of the above The figure shown above illustrates the expression domains of homeotic genes in Arabidopsis. What would the pattern of structures be (Whorl 1 to Whorl 4) for a loss of-function mutant in B? a. Sepals, Petals, Stamens, Carpels b. Sepals, Sepals, Stamens, Stamens c. Sepals, Sepals, Carpels, Carpels d. Carpels, Stamens, Stamens, Carpels The figure shown above illustrates the expression domains of homeotic genes in Arabidopsis. What would the pattern of structures be (Whorl 1 to Whorl 4) for a loss of-function mutant in C? C limits the domain of expression of A. a. Sepals, Petals, Petals, Sepals b. Sepals, Sepals, Stamens, Stamens c. Sepals, Sepals, Carpels, Carpels d. Carpels, Stamens, Stamens, Carpels The figure shown above illustrates the expression domains of homeotic genes in Arabidopsis. What would the pattern of structures be (Whorl 1 to Whorl 4) for a loss of-function mutant in A? A limits the domain of expression of C. a. Sepals, Petals, Stamens, Carpels b. Sepals, Sepals, Stamens, Stamens c. Sepals, Sepals, Carpels, Carpels d. Carpels, Stamens, Stamens, Carpels Shoot a. b. c. d. e. f. lateral meristems are……(Finish the sentence) totipotent stem cells pluripotent stem cells bipotent stem cells determined cells All of the above None of the above Root meristems are……(Finish the sentence) a. totipotent stem cells b. pluripotent stem cells c. bipotent stem cells d. determined cells e. All of the above f. None of the above A loss-of-function mutation in a Drosophila melanogaster gene called dorsal causes a pattern defect in the fly embryo. Mutant embryos are completely dorsalized; that is, dorsal structures form where there should be ventral structures. What does this tell us about the normal function of the dorsal+ gene? a. That it is required for producing dorsal structures. b. That it is not required for producing dorsal structures. c. That it is required for making ventral structures. d. That it is not required for making ventral structures. e. None of the above. A molecule that during development provides positional information via a concentration gradient is known as a a. transcription factor b. exon c. endocrine signal d. plastochron e. morphogen Zebrafish is used as a model organism to study development because a. their embryos are almost identical to humans b. they live longer than other fish c. they have synchronous cell division cycles d. they reproduce apomictically e. they have rapid generation times In plant development, the following is NOT true of shoot apical meristems a. they only occur in embryos b. they involve pattern formation, morphogens, transcriptional hierarchies, progressive restriction of cell fate c. they occur at the tips of shoots and roots d. they are a self-renewing cell population (like animal stem cells) e. Continually produce organs, tissues, ect. Which of the following is NOT true of homeotic genes that control the identity of flower organs? a. Mutants show changes in organ identity b. They encode transcription factors c. They function in a transcriptional hierarchy d. They function combinatorially e. All these statements are true. In plant development, what makes flower organs (petals, stamens, etc.) different from each other? a. Each inherits different genes b. Each expresses different genes c. Each discards different genes d. Each gene codes different proteins in different organs e. Each organ inherits different morphogens. Which of the following DOES NOT contribute to the differentiation of stem cell daughters? a. transcriptional hierarchy b. cell signaling c. progressive restriction of cell fate d. altered genetic content e. altered gene expression Loss-of-function mutations in a gene called Pax6 cause mammal or fish embryos to not form eyes. What is the normal function of the Pax6 gene? a. It is required for eye formation b. It blocks eye formation c. It is a morphogen d. It signals formation of an R8 cell. e. The function cannot be determined from the information given. In bone marrow, there are hematopoietic stem cells (cells that generate blood) and other cells called stromal cells. Stromal cells express a protein called ”kit”. Injecting mice bone marrow with anti-kit antibodies causes inactivation of the kit protein and results in a dramatic decrease in the number of hematopoietic stem cells. The most likely function for the kit protein is a. a ribosome b. an ion channel c. a membrane receptor d. a secreted signaling ligand e. a cell adhesion molecule The Hox gene complex is a cluster of genes that a. Controls parasympathetic neural signaling b. Controls alternation of generations in plants c. Encode a signal transduction pathway that promotes oogenesis d. Controls anterior-posterior body segment identities in vertebrates and insects e. Controls stem cell proliferation and differentiation