* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Role of People in Security
Cyberwarfare wikipedia , lookup
Multilevel security wikipedia , lookup
Information security wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Next-Generation Secure Computing Base wikipedia , lookup
Post-quantum cryptography wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Security printing wikipedia , lookup
Airport security wikipedia , lookup
Computer and network surveillance wikipedia , lookup
Unix security wikipedia , lookup
Mobile security wikipedia , lookup
Cyber-security regulation wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
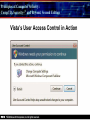
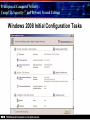
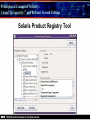
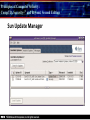
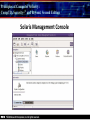
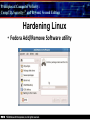
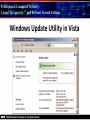
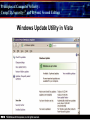
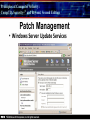
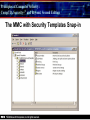
Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Baselines Chapter 14 © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Objectives • Harden operating systems and network operating systems. • Harden applications. • Establish group policies. © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Key Terms • • • • • • • • • • © 2010 Application hardening Baseline Baselining Firmware update Globally unique identifier (GUID) Group policy Group policy object (GPO) Hardening Hotfix Network operating system (NOS) Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Key Terms (continued) • • • • • • • • • • © 2010 Operating system (OS) Patch Patch management Pluggable Authentication Modules (PAM) Process identifier (PID) Run levels Security template Service pack Shadow file TCP wrappers Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Overview of Baselines • The process of establishing a system’s security state is called baselining. • The resulting product is a security baseline that allows the system to run safely and securely. • Once the process has been completed, any similar systems can be configured with the same baseline to achieve the same level of security and protection. • Uniform baselines are critical in large-scale operations. © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Password Selection • The heart of the problem is that most systems today are protected only by a simple user ID and password. • Selecting a good password for all user accounts is critical to protecting information systems. • This is especially true for servers. • Compromise of a server can mean access to multiple user passwords. © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Operating System and Network Operating System Hardening • Common hardening tasks: ‐ ‐ ‐ ‐ ‐ ‐ © 2010 Disabling unnecessary services Restricting permissions on files and directories Removing unnecessary software Applying patches Removing unnecessary users Applying password guidelines Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Hardening Windows Server 2003 • IIS 6 isolates individual web applications. • 19 services running under Windows 2000 by default were disabled under Server 2003. • Two new service accounts with lower privilege levels introduced. • Security Configuration Wizard (SCW). • Software Restriction Policy (SRP). • Enhanced audit capabilities were provided. • Network Access Quarantine Control was introduced. © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Hardening Windows Vista • User Account Control allows users to operate the system without requiring administrative privileges. • An outbound filtering capability was added to Windows Firewall. • BitLocker allows encryption of all data on a server, including any data volumes. • Vista clients work with Network Access Protection (NAP). • Windows Defender is a built-in malware detection and removal tool. • A new, more-secure version of Internet Explorer. © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Vista’s User Access Control in Action © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Hardening Windows Server 2008 • BitLocker allows encryption of all data on server. • Role-based installation of functions and capabilities minimizes server footprint. • Network Access Protection (NAP). • Read-only domain controllers. • More granular password policies. • IIS 7 administration of web sites and web applications. © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Windows 2008 Initial Configuration Tasks © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Hardening UNIX- or Linux-based Operating Systems • General UNIX hardening is the same as hardening for Windows OS © 2010 Disable unnecessary services Restrict permissions on files and directories Remove unnecessary software Apply patches etc. Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Hardening UNIX- or Linux-based Operating Systems (continued) • ps command run on a Fedora 10 system © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Hardening UNIX- or Linux-based Operating Systems (continued) • Service configuration utility from a Fedora 10 system © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Hardening Solaris • Define the system’s purpose. • Install the operating system. • Install the software. – pkgadd – pkgrm • Patch the system. – – – – © 2010 patchadd patchrm smpatch pkgparam Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Solaris Product Registry Tool © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Sun Update Manager © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Solaris Management Console © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Hardening Solaris • TCP wrappers are filters that compare incoming connection requests to lists of authorized and unauthorized connections. • Controlled by two files: – hosts.allow – hosts.deny • Other commands: – chmod, chown, chgrp, useradd, passwd • Pluggable Authentication Modules (PAM). © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Hardening Linux • Fedora Add/Remove Software utility © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Hardening Linux (continued) • Fedora User Manager © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Hardening Linux (continued) • Fedora Firewall Configuration GUI © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Hardening Mac OS X • Apple’s operating system is essentially a new variant of the UNIX operating system. • The same rough guidelines for all UNIX systems apply to Mac OS X. – – – – – – © 2010 Mandatory access controls for system resources Tagged downloads Execute disable Library randomization FileVault Application-aware firewall Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Hardening Mac OS X (continued) • Firewall utility in Mac OS X 10.5 © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Hardening Mac OS X (continued) • Setting file permissions in Mac OS X © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Updates • Hotfix – Small software update to address a specific problem • Patch – More formal larger update – Addresses several problems – Developed over longer period of time • Service pack – Collection of patches and hotfixes in on large package © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition XP Automatic Updates © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Windows Update Utility in Vista © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Fedora Software Package Update Utility © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Network Hardening • Securing network infrastructure components typically involves the following activities: ‐ Software updates ‐ Device configuration © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Software Updates • Maintaining current vendor patch levels for your infrastructure is one of the most important things you can do to maintain security. • The different vendors for the different software and hardware must be tracked. • Software and firmware for each device must be kept current. © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Device Configuration • Properly configured network devices are an important part of network hardening: – Routers, switches, firewalls, servers, proxies, etc • Some general steps: – – – – © 2010 Limit access. Choose good passwords. Turn off unnecessary services. Change SNMP community strings. Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Application Hardening • Securing an application against local and Internet-based attacks • Securing applications typically involves the following activities: ‐ Application patches ‐ Hotfixes, patches, upgrades ‐ Patch management © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Patch Management • A disciplined approach to the acquisition, testing, and implementation of patches. • Ability to inventory applications and operating systems in use – – – – – – © 2010 Notification of patches Continual scanning of systems patch status Select which patches to apply Push patches to systems Ability to report patch success or failure Ability to report patch status on any or all systems in the environment Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Windows Update Utility in Vista © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Patch Management • Windows Server Update Services © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Group Policies • • • • Group policy Group policy object (GPO) Globally unique identifier (GUID) Microsoft’s new group policy capabilities: – – – – – – © 2010 Network location awareness Ability to process without ICMP VPN compatibility Power management Device access blocking Location-based printing Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Group Policy Object Editor © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Security Templates • A collection of security settings that can be applied to a system. • They configure the following areas: • • • • • • • © 2010 Account policies Event log settings File permissions Registry permissions Restricted groups System services User rights Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition The MMC with Security Templates Snap-in © 2010 Principles of Computer Security: CompTIA Security+® and Beyond, Second Edition Chapter Summary • Harden operating systems and network operating systems. • Harden applications. • Establish group policies. © 2010