* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Presenter : Min-Jung Bae1,2 1Department of Applied Biological
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
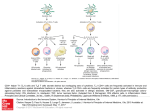
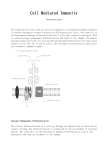
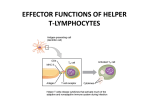
Presenter : Min-Jung Bae1,2 1 Department of Applied Biological Chemistry, The University of Tokyo, 1-1-1 Yayoi, Bunkyo-ku, Tokyo 113-8657, Japan 2 Functional Materials Research Group, Division of Metabolism & Functionality Research Korea Food Research Institute, 1201-62, Anyangpangyo-ro, Bundang-gu, Seognam-si, Kyeonggi-do 463746, Republic of Korea Part 1. Daidzein promotes type 1 helper T-cell differentiation independently of estrogen receptormediated signaling Th1/Th2 balance is critical to immune regulation. We examined the effect of isoflavones––daidzein, genistein, and glycitein––on Th1/Th2 differentiation of naive CD4+ T cells derived from DO11.10 and BALB/c mice. CD4+ T cells activated in the presence of daidzein demonstrated significantly increased interferon- secretion and Th1-specific transcription factor T-bet mRNA expression upon restimulation. Daidzein enhanced STAT1 phosphorylation in naive CD4+ T cells during their primary stimulation. The effect of daidzein was preserved in the absence of antigen-presenting cells and the presence of an estrogen receptor (ER) antagonist. These results indicate that daidzein directly affects naïve CD4+ T cells to enhance Th1 differentiation independent of ER signaling. Part 2. Naringenin, citrus fruits flavanone, regulates the differentiation of interleukine 17-poducingT helper cells. Interleukin 17 (IL-17)-producing helper T cells (Th17 cells) takes a crucial part in the induction of autoimmune diseases such as colitis. Naringenin is a naturally occurring polyphenolic phytochemical isolated from citrus fruits. It has been investigated biological activities, but the mechanism on regulating Th cells differentiation is not yet fully unknown. This study examined the effect of naringenin on Th17 differentiation of naive CD4+ T cells using DO11.10 mice. Activated CD4+ T cells with naringenin produced IL-17 in a dose-dependent manner. Moreover, naringenin significantly increased the mRNA expression of IL-17, RORγt and AhR in CD4+ T cells, and enhanced AhR transcription activity. The promotive effect of naringenin on Th17 differentiation was showed by IL-6 and TGF-β mRNA expression from dendritic cells (DCs) as well as IL-6 transcription activity. Naïve CD4+ T cells cultured with DCs in the present of naringenin also enhanced CD4+IL-17A+ T cell proportions and IL-17 secretions. These results indicate that naringenin can skew naïve CD4+ T cells toward Th17 cells via AhR-mediated and DCs-dependent pathway. Our results provide beneficial information for the safety of phytochemicals related to Th17-skewing response shown augmentation of inflammation.