* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download INFLAMMATION
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Atherosclerosis wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
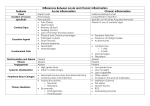
Cellular Response Adaptive Non Adaptive Disturbances of growth Degeneration Inflammation and repair Neoplasia Immune response Dysplasia Necrosis INFLAMMATION Definition -it’s a body response against injury , it’s a first line of defense. -Protective adaptive tissue response to injury. Causes of Inflammation: By injurious agents called irritants. It are different types: 1-Living Irritants: bacteria, virus, parasites. 2-Non Living Irritants: a-Chemical: Acids, alkalis and poisons. b-Physical: Heat, cold, ionizing radiation. c-Mechanical: Trauma, cut. 3-Antigens: cause allergic inflammation. Mechanism: 1. Vascular response 2.Cellular response 1. Vascular Response A-Vasodilatations of arterioles in local blood flow redness and hotness = (hypraemia). B-Increase in capillary permeability leakage of fluid local swelling. C-Release of mediators pain. 1- inflammatory reaction “dilated blood vessels” The widening of blood vessels resulting from relaxation of smooth muscle cells in vessel walls Mechanism: 2. Cellular Response: -Margination of WBCs. -Emigration (Diapedesis). -Chemotaxis . -Phagocytosis. Cellular Response Margination: The polymorphnuclear leucocytes leave the blood and adhesion to the margin of the endothelial lining of the capillaries. Emigration :The polymorphnuclear leucocytes pass between the endothelial cells through the vessels wall by amoeboid movement into damage tissue . Cellular Response Chemotaxis: Is the directed movement of the polymorph-nuclear leucocytes and macrophages in the area of inflammation. Phagocytosis: Is the ingestion and destruction of the foreign particles by the phagocytic inflammatory cells. 2- Margination of WBC’s: PMN move to the peripheral B.V & adherent to endothelium B.V wall ,this process called "Margination of WBC’s 3- Emigration of WBC’s PMN or WBCs migration from vessels lumen into area of tissue damage, this process called" Emigration of WBC’s" Inflammation types: 1- acute . 2- chronic . 3-sub-acute. Inflammation types: 1- Acute inflammation: Sudden onset and short duration. -Cellular response Polymorphnuclear leucocytes, pus cells and macrophages. - Vascular response Numerous, thin walled, dilated blood vessels. 4- Acute inflammatory cells: Mainly we see PMNL & small amount of macrophages. PMNL= WBCs refer to neutrophil ,cytoplasm contain fine violet granules ,several lobes of nucleus , Pus cells= dead PMN lymphocytes or dead neutrophil. Machrophages=usually seen in acute & chronic inflammationl,Function of machrophages:1-phagocytosis &killing of bacteria. 2-phagocytosis of necrotic debris. 3-formation of giant cells. Inflammation types: 2- Chronic Inflammation: Gradual onset and prolonged duration ( connective tissue formation). -Cellular response Lymphocytes, macrophages, plasma cells and giant cells. - Vascular response Few, thick walled, narrow blood vessels. Inflammation types: 3- Sub-acute Inflammation: in between the acute and the chronic 5- chronic inflammatory cells Lymphocytes: WBCs, distinguished by dark blue round nuclei & small amount of cytoplasm. Plasma cells :WBCs, it is mature B-cell ,identified by extensive basophilic cytoplasma & small eccentric nuclei( specific seen in chronic inflammation),it is produce large antibodies Fibroblast: is type of cell synthesizes C.T &plays critical role in wound healing Foreign body giant cell: is fused macrophages which are generated in response to present large foreign body, nuclei are arranged in disorganized manner. Langhans giant cell: is fusion of macrophages & contain arranged in horse shoeshaped pattern in cell periphery, found in granulomatous & tuberculosis conditions. 6- chronic inflammatory cells Mainly we have Plasma cell ,lymphocytes.&Fibroblast cells to form 7- chronic inflammatory cells: Mainly plasma cell ,small amount of lymphocytes ,macrophages & fibroblast cells to form C.T 8- Giant cell ( langerhan’s) specific : Atypical langhans giant cell formed by fusion of macrophages in tuberculosis granuloma ,contain nuclei horse shoe-shaped 9- Giant cell (foreign body) nonspecific: Giant cell,nuclei arranged in disorganization pattern,fibroblast & few lymphocytes. 10- Acluster of giant cells around (foreign body) : A cluster of giant cells around (foreign body )&number of lymphocytes.