* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download methods
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
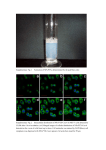
SUPPLEMENTARY ONLINE INFORMATION METHODS Cell culture and Reagents. Human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) and human pulmonary artery endothelial cells (HPAEC) were grown in Endothelial Growth Medium-2-MV (EGM-2-MV) BulletKit (Clonetics, San Diego, CA). At 80-90% confluence, the cells were serum-starved in medium containing EBM-2 and 0.5% fetal bovine serum (FBS) for 16h and subsequently treated with thrombin at the doses and for the times indicated. Microarray analysis. HUVEC were serum-starved overnight (12h) in medium containing EBM-2 and 0.5% FBS, then treated with 1.5 U/ml thrombin for varying periods of time. RNA was harvested and purified with Trizol according to Manufacture’s protocol (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). Preparation of cRNA and hybridization of probe arrays were performed according to the protocols of the manufacturer (Affimetrix, Santa Clara, CA). Briefly, after quality determination on test arrays, the samples were hybridized for 16h at 45oC to Affimetrix human focus array that have 8794 genes. The arrays were washed and then stained with streptavidin-phycoerythrin. Fluorescently stained probe arrays were visualized with GeneArray scanner (Hewlett-Packard). The intensity for each feature of the array was captured with Affimetrix GeneChip software. Pair wise comparisons were made by using probe arrays without thrombin treatment as baseline. Duplicate samples from two independent batches of HUVEC (Clonetics, lot # 6541 and 2F0461) were analyzed for each of the three time points (1, 4 and 18h). FileMaker software was used to examine the qualitative parameters of increase or SUPPLEMENTARY ONLINE INFORMATION decrease. Genes were identified as thrombin-responsive if they met the following criteria: 1) specific hybridization signals consistent with a ‘presence call’ derived from the 20 probe pairs representing each gene by means of a trimmed mean algorithm, and 2) at least 2-fold upregulation or downregulation in both experiments (compared with control untreated). The data were clustered on the basis of similar regulation patterns using Gene cluster (created by Dr. Eizen, Stanford University) and Java Tree View software (created by Alok alok@genome) according to the manual on the default settings. Red and green represent higher and lower expression than the median for that particular gene, respectively. Color intensity is related to the difference with the median (black). Ribonuclease (RNase) protection assays. HPAEC or HUVEC were grown in 6-well plates, serum-starved overnight in EBM-2 medium containing 0.5% FBS and treated with or without thrombin in the presence or absence of inhibitors, as described above. Cells were harvested for RNA by adding RNA-STAT reagent (TEL-TEST Inc., Friendwood, TX) directly into the wells. Total RNA was extracted according to the manufacturer’s instructions. For RNase protection assays, a 440-bp TF, 376-bp PDGFA, 334-bp Egr-1, 283-bp ICAM-1, and 210-bp uPA human RT-PCR fragments were subcloned into the pPCR-Script Amp SK(+) cloning vector using PCR-Script AMP Cloning Kit (Stratagene) and were used as in-vitro transcription templates.. The cDNA inserts were verified by automated sequencing. The cDNA plasmid template for -actin was purchased from Ambion (Austin, TX). [-32P] UTP-labeled riboprobes were synthesized from the Egr-1 and -actin cDNA templates, using T3 RNA polymerase (Ambion) and subsequently gel purified. RNase protection assays were carried out using the RPA IIITM kit (Ambion). SUPPLEMENTARY ONLINE INFORMATION Briefly, the two riboprobes were mixed with 5 µg total cellular RNA in a volume of 10 l and hybridized at 42˚ C overnight in hybridization buffer. The unhybridized RNAs were digested at 37˚ C for 30 min with RNase A /RNase T1 mix. The protected fragments were precipitated by adding the RNase Inactivation/Precipitation III solution and separated on a 4% acrylamide/8M urea gel. The gels were dried and autoradiographed. Immunolocalization studies. HUVEC were plated onto glass cover-slides (Matsunami, Japan) in the 6-well plate at a density of 25,000 cells/slide. The cells were grown in EGM-2 MV medium for 24h and serum starved overnight in medium containing EBM-2 and 0.5% FBS, then treated in the presence or absence of 1U/ml thrombin for 1h, fixed in ice-cold 3.7% paraformaldehyde for 10 min, washed with PBS and subsequently incubated with primary anti-p65 antibody (Santa Cruz, Santa Cruz, CA). Following extensive washes in PBS, the cells were incubated with a rhodamine-labeled secondary antibody (1:200 dilution) (Santa Cruz) for 1h. The slides were washed in PBS, mounted in Crystal/Mount (Biomeda, Foster City, CA) with Hoechst (Sigma) for identification of nuclear localization and examined by fluorescence microscopy. Western blot analyses. Western blot analyses were carried out as previously described 1. The membranes were probed with anti-phospho Ser-256 FKHR (Cell Signaling, Beverly, MA), stripped and reprobed with anti-FKHR to control for loading. SUPPLEMENTARY ONLINE INFORMATION LEGENDS TO ONLINE FIGURES Figure I. Microarray analyses of thrombin treated endothelial cells. The Affymetrix microarray (HG-FOCUS) expression data was clustered on the basis of similar regulation patterns using Gene Tree view. Two independent batches of HUVEC were treated in the absence (control) or presence of thrombin (1.5 U/ml) for 1, 4, 18h. The hierarchical tree show the total cluster of all thrombin responsive genes after data filtering, including only those genes that had ‘presence call’ and at least 2-fold upregulation (A) or 2-fold downregulation (B) in both HUVEC samples compared to control. Fig. II. Thrombin induces the nuclear translocation of p65 in primary endothelial cells. HUVEC were serum-starved overnight in 0.5% FBS and incubated in the absence (Control) or presence 1.5 U/ml thrombin for 1h. The cells were fixed in paraformaldehyde, washed with PBS and subsequently incubated with primary anti-p65 antibody, followed by rhodamine conjugated second antibody. The nuclei were stained with Hoechst. Fig. III. Thrombin induces phosphorylation of FKHR in endothelial cells. Western blot analyses of whole cell extract from HCAEC treated in the absence or presence of 1.5 U/ml thrombin for the times indicated were carried out using phospho-specific antibodies to FKHR Ser-256. The membrane was reprobed for total FKHR. The result is representative of 3 independent experiments. SUPPLEMENTARY ONLINE INFORMATION REFERENCES FOR ONLINE DATA SUPPLEMENT 1. Abid MR, Tsai JC, Spokes KC, Deshpande SS, Irani K, Aird WC. Vascular endothelial growth factor induces manganese-superoxide dismutase expression in endothelial cells by a Rac1-regulated NADPH oxidase-dependent mechanism. Faseb J. 2001;15:2548-2550. SUPPLEMENTARY ONLINE INFORMATION Fig. IA SUPPLEMENTARY ONLINE INFORMATION Fig. IB SUPPLEMENTARY ONLINE INFORMATION Fig. II SUPPLEMENTARY ONLINE INFORMATION Fig. III Time (min) 0 5 15 p256-FKHR FKHR Thrombin 30