* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lab - TeacherWeb
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
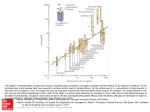
Name: ____________________________________ Lab #: _________ Period: _________ Cell Receptor Activity Background Information: Cell receptors are imbedded in the cell membrane and will attach to specific chemicals. Once this specific chemical fits into the receptor, it will release a message to the cell’s nucleus and instruct it to do something. We call these chemicals chemical messengers and examples are the many different types of antibodies and hormones. Cell receptors are very specific, this means that each receptor will only fit together and receive messages from one chemical messenger. Many chemicals will bind to the cell receptors. Here are some examples: The male hormone testosterone will bind to the cell receptors on muscle cells. The chemical message it delivers tells them to increase the rate of growth, but will not fit into cell receptors on nerve cells. Women who have just given birth to a new baby release the female hormone prolactin. It will fit into cell receptors in the membrane of breast cells and trigger milk production. Mast cells are special immune system cells that contain sacks of histamine. When germs invade your body they attach to the mast cells and cause the release of histamine. Histamine makes your eyes water and your nose run to flush the invading germs out of your body. However, sometimes substances like pollen or bee venom (allergens) will fit into the receptors and the histamines will be released. This causes an allergic reaction. If you can get antibodies from your blood stream to bind to these allergens first, before they reach the mast cells, you will not have allergic reactions. Antihistamines have the same shape as allergens and can be used to block the cell receptors and prevent people from have allergic reactions. T-Lymphocytes are another kind of immune cell that have receptors called CD4. Immune chemical messengers called Interleukin will bond here and tell the cell what to do to get better when sick. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) will also bind at the CD4 site and shut down the immune cell. When HIV blocks most of the CD4 receptors of the T-Lymphocytes in a person, the patient is said to have Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS). Some steroids are artificial hormones. Often they have negative side affects since they trigger increased growth in cells. People taking steroids for muscle growth may induce the cells to grow uncontrollably, this is cancer. Fertility drugs are hormones like Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) that initiates a woman’s ovary to generate more eggs. Unfortunately, it like steroids may cause the ovarian cells to become cancerous. Women that have a history of ovarian cancer in their family are usually advised not to use fertility drugs. Purpose: To understand how cell receptors work. Materials: Lab, scissors, colored pencils and glue. Procedures: 1. On the handouts are different cells and cell receptors. 2. Color and cut out the different chemical messages and glue them into the appropriate site. 3. Under each cell, fill in the name of the cell and what will happen to it. 4. Answer all conclusion questions. Questions: Answer in complete sentences. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. List all the messengers that could not be used. What cell could have received more than one of the chemical messengers shown? Besides pollen, what else could have the same square shape and fit into the mast cell receptor? What is an interleukin? How could you rid someone of some types of allergies? If a woman adopts a newborn baby, how could her doctor initiate the production of milk in her body so she could breast feed? 7. What is histamine? 8. What is cancer? 9. How could steroids and fertility drugs trigger cancer? 10. Which women are at risk of cancer from fertility drugs? Below is a chart showing different pollen levels on different summer days and the histamine levels in the blood of a particular patient. Date 6/30/08 7/4/08 7/19/08 8/15/08 8/30/08 Tree Pollen High High Moderate Low None Grass Pollen Low Moderate High Moderate Low Ragweed Pollen None None None Low High Patient’s histamine levels 0.3 ng/mL 0.5 ng/mL 0.3 ng/mL 1.2 ng/mL 2.5 ng/mL 11. Which type of pollen is the patient most allergic to? 12. If most people had the same allergy as the patient above and you were an unscrupulous (mean and sneaky) pharmacist, when would you raise the price of antihistamine? Cells and Membrane Receptors Cell Name: ______________________________________ Action of Chemical Messenger: _______________________________________ Cell Name: ______________________________________ Action of Chemical Messenger:________________________________________ Cell Name: ______________________________________ Action of Chemical Messenger:________________________________________ Cell Name: ______________________________________ Action of Chemical Messenger:________________________________________ Cell Name: ______________________________________ Action of Chemical Messenger:________________________________________ Hormones & Other Chemical Messengers Pollen Prolactin TSH HIV Testosterone Estrogen Human Growth Hormone FSH Interferon Gamma Interleukin