* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
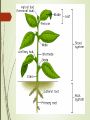
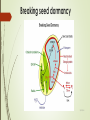
First 10 minutes Sort folders Core Practicals Marked and self assessed work Independent study Complete any unfinished booklets (its says this on the front the booklet) If everything is completed then you should complete Qs… from the I A-level paper. Due Wednesday 23rd November 18/10/2016 Exercise books WWW Notes are excellent Majority of students are making additional annotations EBI More annotations needed during lesson (see Louise and Molly’s book) Highlight key terms and words Make synoptic links where possible Date, title work Specifics from last few lessons Dynamic equilibrium – values may vary within a narrow range but overall kept constant Indicate the example of peptide and steroid hormone Answer quick questions from Topic 9 – in purple pen. 18/10/2016 C/W 18/10/2016 Chemical Control in Plants • Understand that chemical control in plants is brought about by plant growth substances such as auxins, cytokinins and gibberellins. • Know that auxin has several effects, including cell elongation, suppression of lateral buds (apical dominance) and promoting root growth. • Understand that plant growth substances often interact with each other as shown by the antagonistic actions of cytokinin and auxin on apical dominance. Engage – Discuss with your partner and make a list of the stimuli that you think plants are sensitive to and respond to • Understand the principles of mammalian hormone production by endocrine glands and their mode of action involving receptors on target cells. Chemical control in plants Plants are sensitive to Light – direction, intensity Temperature Gravity Water Touch Chemicals Directional growth responses are known as tropisms! 18/10/2016 18/10/2016 How plants grow Do we know what assimilation means? Growth is a permanent increase in the size of an organism or some part of it. Cell division and the assimilation of new material within the cells that result from the division, followed by expansion. Main areas of cell division in plants are known as the meristems – where might key areas of growth be? Regions of cell division and cell elongation are particularly sensitive to ???. 18/10/2016 C/W 18/10/2016 Checkpoint • Understand that chemical control in plants is brought about by plant growth substances such as auxins, cytokinins and gibberellins. • Know that auxin has several effects, including cell elongation, suppression of lateral buds (apical dominance) and promoting root growth. • Understand that plant growth substances often interact with each other as shown by the antagonistic actions of cytokinin and auxin on apical dominance. • Understand that chemical control in plants is brought about by plant growth substances such as auxins, cytokinins and gibberellins. Auxins – indoleacetic acid (IAA) Effective in very low concentrations Movement involves active transport and calcium ions Involved in apical dominance – supress growth of lateral shoots Low concentrations promote root growth Response to auxin depends on concentration and region on plant 18/10/2016 Your task – In your own words, using labelled diagrams describe how auxin causes growth in shoot when responding to light IAA made in tip of shoot Diffuses into zone of elongation IAA binds to receptors and causes H+ to be pumped in cell wall spaces. Causes cellulose to become more flexible Water moves in via osmosis Cells stretch and expand Enzyme is eventually inhibited and cellulose becomes more rigid 18/10/2016 Know that auxin has several effects, including cell elongation, suppression of lateral buds (apical dominance) and promoting root growth. Auxin and root growth At higher concentrations, auxin actually inhibits growth. Explain in your own words how Auxin acts at the root? This is an example of positive gravitotropism. 18/10/2016 Seed Germination – Seeds might save the world!!! 18/10/2016 Giberellins Elongation of growing cells Growth of fruit Breaking dormancy in seeds 18/10/2016 C/W 18/10/2016 Checkpoint • Understand that chemical control in plants is brought about by plant growth substances such as auxins, cytokinins and gibberellins. • Know that auxin has several effects, including cell elongation, suppression of lateral buds (apical dominance) and promoting root growth. • Understand that plant growth substances often interact with each other as shown by the antagonistic actions of cytokinin and auxin on apical dominance. Giberellin and seeds A. In the presence of water, it stimulates the production of amylase (converts starch into maltose), allowing for the formation of ATP (via glucose) B. Gibberellin (or gibberellic acid) is necessary for seed germination C. The energy produced in the embryo - as a result of the action of gibberellin - is used to facilitate germination D. Gibberellin also causes stem elongation by promoting both cell elongation and cell division E. The glucose produced may also be used to synthesis cellulose for cell wall formation Put the statements in order on your white boards 18/10/2016 • Understand that chemical control in plants is brought about by plant growth substances such as auxins, cytokinins and gibberellins. Giberellin and seeds B.Gibberellin (or gibberellic acid) is necessary for seed germination A. In the presence of water, it stimulates the production of amylase (converts starch into maltose), allowing for the formation of ATP (via glucose) C. The energy produced in the embryo - as a result of the action of gibberellin - is used to facilitate germination E. The glucose produced may also be used to synthesis cellulose - for cell wall formation D. Gibberellin also causes stem elongation by promoting both cell elongation and cell division 18/10/2016 Breaking seed dormancy 18/10/2016 Cytokinins Understand that plant growth substances often interact with each other as shown by the antagonistic actions of cytokinin and auxin on apical dominance. Growth regulators that promote cell division in the apical meristems and the cambium through interactions with auxins. (Synergy) They promote lateral bud development, which can overcome apical dominance if the leading shoot is removed or damaged. (Antagonistic) Cytokinins work synergistically with ethene in abscission of leaves, flowers and fruits. 18/10/2016 C/W 18/10/2016 Checkpoint • Understand that chemical control in plants is brought about by plant growth substances such as auxins, cytokinins and gibberellins. • Know that auxin has several effects, including cell elongation, suppression of lateral buds (apical dominance) and promoting root growth. • Understand that plant growth substances often interact with each other as shown by the antagonistic actions of cytokinin and auxin on apical dominance. Questions 1.List as many of the different environmental stimuli that elicit a response in plants as you can. For each, try to explain why it is important for the plant to respond to that stimulus. 2.Growth in animals usually stops at a certain stage. The meristems of plants, where growth occurs, remain active throughout the life of the plant. Explain why this difference is important in the way the organisms respond to stimuli. 18/10/2016 Key Terms Tropisms – Plant growth responses to environmental cues. Auxins – Plant hormones that act as a powerful growth stimulants and are involved in apical dominance, stem and root growth, and tropic responses to unilateral light. Giberellins – Plant hormones that act as growth regulators, particularly in the internodes of stems by stimulating elongation of the growing cells; they also promote the growth of fruit and are involved in breaking dormancy in seeds and in germination. Cytokinins – Plant hormones that promote cell division in the apical meristems and the cambium through interactions with auxins. They promote lateral bud development, which can overcome apical dominance, they work synergistically with ethene in the abscission of leaves, flowers and fruits. 18/10/2016 Now complete the Giberellin Exam Question 18/10/2016 Mark Scheme 18/10/2016 Mark scheme 18/10/2016 Mark scheme 18/10/2016 This relates to the following specification point: 18/10/2016