* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Problémový okruh 5 (Dušnost a bolest na hrudi)
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Echocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Drug-eluting stent wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
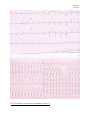
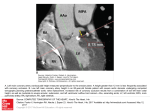
Course 5 Case 25 Kas 5-26E: A man with palpitation and syncope Patient: male, 54 years History of presenting complaint: A 54 years old disabled pensioner, former barber, is brought in from home by emergency. He says he had a sudden feeling of palpitation at rest accompanied with dyspnoea and dull pressure behind the sternum. His wife called an emergency. A few minutes before the emergency arrived, he went unconscious and was resuscitated first by his wife and then, by attending physician. Patient was intubated, ECG monitor showed broad QRS complex tachycardia. Electrical cardioversion proceeded without delay with a short-term restoration of sinus rhythm. In a few seconds, tachycardia returned with fast deterioration to ventricular fibrillation. Defibrillation (300 J) and administration of Amiodarone 1 amp i.v. led to successful recovery of sinus rhythm which remained maintain till admission. At admission, patient is sedated and ventilated. Past history: Since 1995 hypertension, 1998 inferior myocardial infarction 10/2002 anterior myocardial infarction treated with primary PCI+stent in LAD (left anterior descending artery), 3 vessel disease, chronic RCA (right coronary artery) occlusion, diffuse disease of coronary arteries including periphery not amendable to CABG, hence, a conservative treatment was recommended. At the same time, severe left ventricular dysfunction (EF 35%) was diagnosed. In the following months, patient developed symptoms of heart failure (NYHA III) Operation: 0 Chronic medication: Gopten (trandolapril) 1x2mg, furosemid forte 1x1 acidum acetylosalicylicum (Aspirin) 1x200mg, Concor (bisoprolol) 1x2,5mg 1x1/2 tbl. Zocor (simvastatin) 1x20mg, Verospiron (spritolacton) 2x1 Social habits: non-smoker since infarction, till infarction 10 cigarettes a day since his 20. Family history: father died of pulmonary embolization at 78, mother died of breast cancer. He did not have brothers and sisters, 2 healthy children. Physical examination: 180 cm, 100 kg, ventilated, lungs: symmetrical breath sounds, basal crackles. Regular heart rate around 100/min. BP 115/70 mmHg. Holosystolic murmur over the apex radiating towards axillae, (3/6). Otherwise normal. ECG taken after defibrillation (Figure 1) Course 5 Case 25 ECG recorded by an emergency ambulance (Figure 2) Course 5 Case 25 Blood tests: potassium 3,8 mmol/l,. Urea 16,8, mmol/l, otherwise normal including Mg, creatinine, troponin Echocardiography (normal valueus in parentheses): Dilation and dysfunction of the left ventricle, EF 30% (above 55%), akinesis in the a. right coronary artery supplied segments, the rest hypokinetic, Moderate mitral insufficiency due to papillary muscle displacement. Right ventricle 30mm (within 30mm), left ventricle 62mm (within 60mm), left atrium 47 mm (within 43mm). Coronary angiography: No change as compared to 10/2002 Therapy: Amiodarone i.v., betablockers, diuretics Questions: 1. Make a list of admission diagnoses arranged in order by priority. 2. Describe both ECGs 3. Explain pathophysiological and anatomical basis of the case. 4. What is the prognosis of the patient? What is the patient life in danger of? In this regard, what other therapeutic measures do you recommend? 5. This patient has high blood levels of urea with normal level of creatinine. What is possible explanation ? 6. Causes and consequences of heart failure 7. Causes and consequences of atherosclerosis 8. Atherosclerosis – morphology 9. Morphologic changes of organs in consequence of heart failure