* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name: Period: ______ Grammar Unit 2: Verbs Study Guide A verb is
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Germanic weak verb wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Navajo grammar wikipedia , lookup
Chichewa tenses wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Udmurt grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Germanic strong verb wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Hungarian verbs wikipedia , lookup
Polish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek verbs wikipedia , lookup
Grammatical tense wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ukrainian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Russian grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Kannada grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
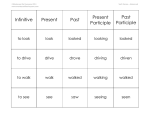
Name: _____________________ Period: ______ Grammar Unit 2: Verbs Study Guide A verb is a word used to express an action, a condition, or a state of being. Example sentence: The roller coaster climbs up a hill. An action verb tells what a subject does. The action it expresses may be either physical or mental. Example sentence: Some people hate amusement parks. A linking verb links its subject to a word in the predicate. The most common linking verbs are forms of the verb be. Linking Verbs Forms of be Verbs that express condition Helping verbs help main verbs express precise shades of meaning. The combination of one or more helping verbs with a main verb is called a verb phrase. Common Helping Verbs Forms of be Forms of do Forms of have Others University of Detroit Jesuit High School & Academy/Grammar Unit 2:Study Guide/8th Grade/2016-2017/mts 1 Action verbs are often accompanied by words that complete their meaning. These complements are direct objects and indirect objects. A direct object is a noun or pronoun that names the receiver of a verb’s action; answers the question what or whom. An action verb that has a direct object is called a transitive verb; circle the transitive verb in your diagram. Example sentence: He performed dangerous stunts on a motorcycle. An indirect object tells to what or whom or for what or whom an action is done. Example sentence: Knievel taught his son some stunts. An action verb that does not have a direct object is called an intransitive verb. The word that a linking verb connects its subject to is called a subject complement. The subject complement identifies or describes the subject. Some common linking verbs are is, feel, seem, and look. A subject complement can be a predicate noun or a predicate adjective. A predicate noun is a noun that follows a linking verb and identifies, renames, or defines the subject. Example sentence: Brown Beauty was the mare’s name. Example sentence: Saddle horses are powerful. A predicate adjective is an adjective that follows a linking verb and modifies the subject. University of Detroit Jesuit High School & Academy/Grammar Unit 2:Study Guide/8th Grade/2016-2017/mts 2 Every verb has four basic forms called its principal parts: the present, the present participle, the past, and the past participle. The Four Principal Parts of a Verb Present Present Participle Past Past Participle *Notice that helping verbs are used with the present participle and past participle. A regular verb is a verb whose past and past participle are formed by adding –ed or –d to the present. Present Present Participle Past Past Participle Irregular verbs are verbs whose past and past participle forms are not made by adding –ed or –d to the present. Common Irregular Verbs Present Past Past Participle Group 1 The forms of the present, the past, and the past participle are all the same. Group 2 The forms of the past and the past participle are the same. Group 3 The past participle is formed by adding –n or – en to the past. Group 4 The past participle is formed from the present, often by adding –n or –en. Group 5 The last vowel changes from i in the present to a in the past, to u in the past participle. University of Detroit Jesuit High School & Academy/Grammar Unit 2:Study Guide/8th Grade/2016-2017/mts 3 The Irregular Verb Be Present Past Past Participle The past and past participle do not follow any pattern. A tense is a verb form that shows the time of an action or condition. The present tense shows that an action or condition occurs now. Example sentence: __________________________________________________________________ The past tense shows that an action or condition was completed in the past. Example sentence: __________________________________________________________________ The future tense shows that an action or condition will occur in the future. Example sentence: __________________________________________________________________ A progressive form of a verb expresses an action or condition in progress. The progressive forms of the three simple tenses are used to show that actions or conditions were, are, or will be in progress. Forming Simple Tenses Singular Plural Present (present principal part) Past (past principal part) Future (will + present part) To make the progressive form of one of these tenses, add the present, past, or future form of be to the present participle. Present Progressive: _________________________________________________________________ Past Progressive: ____________________________________________________________________ Future Progressive: __________________________________________________________________ The present perfect tense places an action or condition in a stretch of time leading up to the present. To form the present, past, or future form of have to the past participle. Forming Perfect Tenses Singular Plural Present Perfect (has or have + past participle) Past Perfect (had + past participle) Future Perfect University of Detroit Jesuit High School & Academy/Grammar Unit 2:Study Guide/8th Grade/2016-2017/mts 4 (will + have + past participle) The present tenses convey actions and conditions that occur in the present. The present tense places the actions in the present. Example sentence: __________________________________________________________________ The present perfect tense shows places the actions in a period of time leading up to the present. Example sentence: __________________________________________________________________ The present progressive tense shows the actions in progress now. Example sentence: __________________________________________________________________ The past tenses convey actions and conditions that came to an end in the past. The past tense shows actions that began and were completed in the past. Example sentence: __________________________________________________________________ The past perfect tense places the actions before other past actions. Example sentence: __________________________________________________________________ The past progressive forms show that the actions were in progress in the past. Example sentence: __________________________________________________________________ The future tenses convey actions and conditions that are yet to come. By using the different future verb forms, you can show how future events are related in time. The future tense shows that the actions have not yet occurred. Example sentence: __________________________________________________________________ The future perfect tense places the actions before other future actions. Example sentence: __________________________________________________________________ The future progressive forms show that the actions will be continuing in the future. Example sentence: __________________________________________________________________ University of Detroit Jesuit High School & Academy/Grammar Unit 2:Study Guide/8th Grade/2016-2017/mts 5 Troublesome Verb Pairs Lie means “to rest in a flat position.” It does not take an object. Lay means “to put or place.” It does take an object. Lie and Lay Present Past lie Past Participle lay Sit means “to be seated.” It does not take an object. Set means “to put or place.” It does take an object. Sit and Set Present Past sit Past Participle set Rise means “to move upward” or “get out of bed.” It does not take an object. Raise means “to lift” or “to care for or bring up.” It does take an object. Rise and Raise Present Past Past Participle rise raise Let means “to allow” or “to permit.” Leave means “to allow something to remain where it is.” Both let and leave may take an object. Let and Leave Present Past let Past Participle leave ***Terms to know (matching portion on test): action verb intransitive verb linking verb regular verb helping verb irregular verb direct object progressive indirect object tense predicate adjective verb phrase predicate noun complement transitive verb subject complement University of Detroit Jesuit High School & Academy/Grammar Unit 2:Study Guide/8th Grade/2016-2017/mts 6