* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Transverse Electromagnetic Waves in Free Space
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Diffraction wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatics wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Time in physics wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic radiation wikipedia , lookup
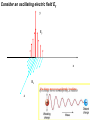
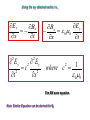
Transverse Electromagnetic Waves in Free Space “Let there be electricity and magnetism and there is light” J.C. Maxwell What we know from previous classes? 1) Oscillating magnetic field generates electric field (Faraday´s law) and vice-versa (modified Ampere´s Law). 2) Reciprocal production of electric and magnetic fields leads to the propogation of EM waves with the speed of light. Question: WAVES?????? How do we show that a wave is obtained? Aim of class today: To derive the EM wave equation Consider an oscillating electric field Ey y Ey x Bz If a charge moves non-uniformly, it radiates z Y This will generate a magnetic field along the z-axis Ey(x) Ey(x+x) C Z x We know that Faraday´s law in the integral form in given as: E.dl B.ds t C s where C is the rectangle in the XY plane of length l width x, and S is the open surface spanning the contour C Faraday´s law on the contour C Bz E y ( x x) E ( x) l l x t this implies... E y Bz x t Keep this is mind... Ampere´s law with displacement current term B.dl E.ds t o C o Y x Ey By(x) x C/ z s By(x+x) Ampere´s law, for the Contour C/ Bz ( x x) Bz ( x)l 0 0 E y t this implies... E y Bz 0 0 x t lx Using the eq. obtained earlier i.e., E y E y Bz 0 0 x t Bz x t Ey 2 t 2 Ey 2 c 2 x 2 where c 2 The EM wave equation Note: Similar Equation can be derived for Bz 1 0 0 Electromagnetic waves for E field for B field In general, electromagnetic waves 1 2 2 c t Where represents E or B 2 2 or their components 1. FEYNMAN LECTURES ON PHYSICS VOL I Author : RICHARD P FEYNMAN, IIT KGP Central Library Class no. 530.4 2. OPTICS Author: EUGENE HECHT IIT KGP Central Library Class no. 535/Hec/O