* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
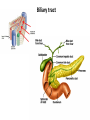
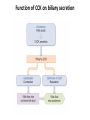
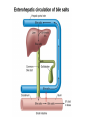
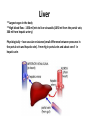
Facts about bile • Bile is produced in the liver • Bile is stored in the gallbladder. • Bile is secreted into the small intestine. • Bile salts are absorbed in the small intestine and recycled. Biliary tract Biliary tract has 4 components Function of CCK on biliary secretion Neurohormonal control of gallbladder contraction and biliary secretion Liver **Largest organ in the body **High blood flow - 1350 ml/min to liver sinusoids (1050 ml from the portal vein, 300 ml from hepatic artery) Physiologically – low vascular resistance (small difference between pressures in the portal vein and hepatic vein). 9 mm Hg in portal vein and about zero!! in hepatic vein Functions of the amazing liver 1. Formation and secretion of bile 2. Excretion of bilirubin 3. Detoxication of various substances • Metabolic products of intestine microbes: • Exogenous toxins (drugs, alcohol, poisons) • Hormones (thyroxine, estrogen, cortisol, aldosterone) 4. Synthesis of plasma proteins: 1. Albumin 2. Clotting factors (synthesis of most of the coagulating factors) 3. Hormone-binding proteins Functions of the liver (cont.) 5. Blood reservoir – filtration and storage of blood (450 ml = almost 10 % of the body’s total blood volume). This increases in cardiac failure. 6. Immunity (Kupffer cells = macrophages). Kupffer cells remove aged RBCs, bacteria, viruses, antigen-antibody complexes and endotoxin. They produce inflammatory mediators for local and systemic use. Functions of the liver (cont.) 7. Vitamins - metabolism and storage of vitamins A, D and B12 8. Relation to blood formation • storage of vitamin B12 • metabolism of iron and its storage as ferritin (hepatic cell contains apoferritin and when excess of iron in the blood it forms ferritin) = blood iron buffer • participation (to small extent) on production of erythropoietin Liver and protein metabolism ***Deamination of amino acids ***Formation of urea for removal of ammonia from the body fluids *** Formation of plasma proteins (90% of all plasma proteins, up to 50 g of plasma proteins daily) –gamma globulins are not formed by liver. ***Interconversions of the various amino acids and synthesis of other compound from amino acids Liver and carbohydrate metabolism ***Maintaining a normal blood glucose concentration ***Storage of glycogen – removing excess of glucose from blood, storage, fast return when the blood concentration decreases = Glucose buffer function ***Conversion of galactose and fructose to glucose ***Gluconeogenesis ***Formation of many chemical compounds from intermediate products of carbohydrate metabolism Liver and fat metabolism ***Oxidation of fatty acids to supply energy for other body function ***Synthesis of large quantities of cholesterol (80% of cholesterol synthesized in the liver is converted into bile salts), phospholipids, and most lipoproteins ***Inactivation of steroids and their excretion of the body ***Synthesis of fat from proteins and carbohydrates