* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Factor Xa inhibitors
Discovery and development of angiotensin receptor blockers wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacokinetics wikipedia , lookup
NK1 receptor antagonist wikipedia , lookup
Adherence (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of integrase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Neuropharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of neuraminidase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotease inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of ACE inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Theralizumab wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Dydrogesterone wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of direct Xa inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of direct thrombin inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
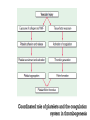
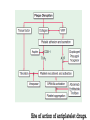
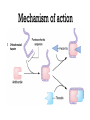
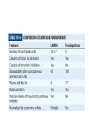
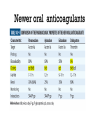
Dr.Hardik Patel Arterial thrombus Rich in platelets Venous thrombus Rich in fibrin and RBC Aspirin produces its antithrombotic effect by irreversibly acetylating and inhibiting platelet COX -1, a critical enzyme in the biosynthesis of thromboxane A2 Aspirin is widely used for secondary prevention of cardiovascular events in patients with coronary artery, cerebrovascular,or peripheral vascular disease. Dosage: 75-325 mg/day Higher dose not more effective than lower dose Side effects: Gastritis, peptic ulcer Bleeding Aspirin resistance Poor absorption, drug interaction, overexpression of cox-2 Theinopyridine (Clopidogrel & Prasugrel) They selectively inhibit ADP-induced platelet aggregation by irreversibly blocking P2Y12 Clopidogrel and prasugrel are prodrugs that require metabolic activation by the hepatic cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzyme system Clopidogrel is more effective than aspirin in patients with recent ischemic stroke, recent MI, or a history of peripheral arterial disease Clopidogrel and aspirin are combined to capitalize on their capacity to block complementary pathways of platelet activation in certain situations The combination of clopidogrel and aspirin should only be used when there is a clear benefit Prasugrel has better role in treatment of MI and prevention of stent rethrombosis , but at the cost of high bleeding tendency The drug is generally avoided in patients with age > 75 years and contraindicated in those patient with history of CVD Clopidogrel Loading 300mg f/b 75mg OD Prasugrel Loading dose of 60 mg f/b 10mg OD Side effects Bleeding , more common with prasugrel than clopidogrel Thienopyridine Resistance The ability of Clopidogrel to inhibit ADP activity varies among individuals This is mainly due to genetic polymorphism of CYP (mainly CYP2C19) enzyme involved the metabolic activation of Clopidogrel. PPI are inhibitors of CYP2C19 enzymes This CYP polymorphism is less significant with Prasugrel activation Orally active inhibitor of P2Y12 Not a prodrug and its produces reversible inhibition of ADP receptor Rapid onset and offset of action Studies have found Ticagrelor superior clopidogrel for MI Dosage : Loading 180 mg, f/b 90mg BD to Dipyridamole is a relatively weak antiplatelet agent on its own An extended-release formulation of dipyridamole combined with low dose aspirin (Aggrenox), is used for prevention of stroke in patients with TIA Abciximab, Eptifibatide and Tirofiban All target GpIIb/IIIa receptor Mainly used in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary interventions and in high-risk patients with unstable angina. Dosing All drugs given as IV bolus f/b infusion Drug Bolus (ugm/kg) Infusion (Ugm/kg/min) Abciximab 0.25 0.125 Eptifibatide 180 +180 2 Tirofiban 0.4 for 30 min 0.1 Side effects Bleeding, thrombocytopenia (immune mediated) New agents in advanced stages of development include Cangrelor, a parenteral, rapidly acting, reversible inhibitor of P2Y12 Vorapaxar, an orally active inhibitor of protease-activated receptor 1 (PAR-1), the major thrombin receptor on platelets Parenteral anticoagulants Heparin, LMWH Fondaparinux Lepirudin, Desirudin, Bivalirudin, Argatroban. Oral anticoagulants Warfarin Oral thrombin inhibitor - Dabigatran etexilate) Oral factor Xa inhibitors- Rivaroxaban, Apixaban, Edoxaban Heparin A sulphated polysachharide, isolated from mast cells Heparin acts by activating antithrombin and accelerating the rate at which antithrombin inhibits clotting enzymes, particularly thrombin and factor Xa. Heparin has equal capacity to promote the inhibition of thrombin and factor Xa anti-factor Xa to anti-factor IIa ratio of 1:1 In the circulation, heparin binds to the endothelium and to plasma proteins other than antithrombin Heparin binding to endothelial cells explains its dose-dependent clearance Clearance is mainly extrarenal; heparin binds to macrophages,which internalize and depolymerize the long heparin chains and secrete shorter chains back into the circulation. Because of its dose-dependent clearance mechanism, the plasma half-life of heparin ranges from 30 to 60 min with bolus IV doses of 25 and 100 units/kg, respectively Activated platelets also release PF4, a highly cationic protein that binds heparin with high affinity. The large amounts of PF4 found in the vicinity of platelet-rich arterial thrombi can neutralize the anticoagulant activity of heparin. This phenomenon may attenuate heparin’s capacity to suppress thrombus growth. Monitored using the aPTT or anti-factor Xa level Therapeutic heparin levels are achieved with a two- to three fold prolongation of the aPTT For prophylaxis : 5000 units SC two or three times daily Coagulation monitoring is not necessary Therapeutic dose Coronary disease : IV heparin bolus of 5000 units or 70 units/kg, a heparin infusion rate of 12–15 U/kg per/hr PTE: Initial bolus of 5000 units or 80 units/kg, followed by an infusion of 18 units/kg per h. Bleeding Thrombocytopenia Osteoprosis Elevated transaminases Small fragments of heparin, mean molecular weight 1/3 of UH Acts by activating antithrombin, but more affinity towards Xa than thrombin Longer and predictable half life, doesn't need coagulation monitoring Dosing For prophylaxis: OD SC doses of 4000–5000U Venous thromboembolism:100U/kg BD Unstable angina: 100-120U/kg BD Monitoring Anti factor Xa monitoring required in certain situations Aa synthetic analogue of the antithrombin- binding pentasaccharide sequence Acts by inhibiting factor Xa , no activity against thrombin Dosage : 2.5 mg OD for prophylaxis and ACS 7.5 mg OD for VTE Approved parenteral direct thrombin inhibitors include recombinant hirudins (lepirudin and desirudin), argatroban, and bivalirudin Mainly used in patients with HIT. Usually given as IV infusion Monitoring done using aPTT Vit K Antagonists Warfarin Thrombin inhibitors Dabigatran Factor Xa inhibitors Rivoroximab, Apixaban, Edoxaban Warfarin interferes with the synthesis of the vitamin K–dependent clotting proteins, which include prothrombin (factor II) and factors VII, IX, and X. The synthesis of the vitamin K–dependent anticoagulant proteins, proteins C and S are also reduced Warfarin is a racemic mixture of R and S isomers CYP polymorphism alters metabolism of warfarin Because of the variability in the anticoagulant response to warfarin,coagulation monitoring is essential to ensure that a therapeutic response is obtained For most indications, warfarin is administered in doses that produce a target INR of 2.0–3.0 Warfarin is usually started at a dose of 5-10mg A minimum 5-day course of parenteral anticoagulation is recommended to ensure that the levels of factor Xa and prothrombin have been reduced into the therapeutic range with warfarin Bleeding : Narrow therapeutic range Skin necrosis : Occurs 2-5 days after start of treatment Contraindicated To during pregnancy be stopped 5 days before elective surgery Dabigatran, rivaroxaban, and apixaban are licensed as alternatives to warfarin for stroke prevention in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation Rivaroxaban, and apixaban have been approved for use in elective hip or knee arthroplasty. Rivaroxaban and dabigatran are also licensed for treatment of DVT or PE In Europe Rivaroxaban along with dual antiplatelets for ACS For stoke prevention Rivaroxaban ; 20mg OD Dabigatran : 150mg BD Apixaban : 5mg BD For treatment of DVT or PTE Rivaroxaban 15mg BD for 3 weeks f/b 20mg OD Post surgical prophylaxis Rivaroxaban 10mg OD Apixaban 2.5mg BD Not routinely required For Xa inhibitors: aPTT Dabigatran : PT Bleeding Reduced incidence compared to Warfarin GI bledding common Contraindicated during pregnancy Thank you