* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ECG NOTES
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
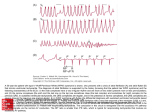
Introduction to ECGs Conduction System Heart Beat Graphic from Boston Scientific International. Start the Heart Now we’re going to look at what you just did. ECG ECG Parts • P – Atrial depolarization (contraction) • QRS – Ventricular depolarization (contraction – BP systole) • T – Ventricular repolarization (rest – BP diastole) • U – Atrial repolarization (rest – BP diastole) R to R interval • The time between the R waves on two consecutive heartbeats. Important “Times” • • • • • 1 small square = 0.04 second 1 large square = 0.2 second Atrial contraction – P-R interval (PRI) = 0.1-0.2 second Ventricular contraction – QRS complex = 0.04-0.11 second Always use 6 second (30 large squares) strip to analyze an ECG waveform • This is what I want you to remember. These squares represent a certain amount of time. This helps us determine the patient’s heart rate and regularity of heartbeat. Now some math! • If your heart beats 75 times per minute, how long is the R to R interval? Answer: 0.8 seconds. Types of heart rhythms Sinus Atrial Ventricular Sinus Rhythms – always have P wave followed by QRS • Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) rate is 60-100 and rhythm is regular Types of sinus rhythms Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) Sinus arrhythmia Sinus bradycardia Sinus tachycardia Sinus arrhythmia – rate is 60-100 and rhythm is irregular Sinus bradycardia – rate is less than 60 and is usually regular Sinus tachycardia – rate is more than 100 and less than 150 is usually regular Atrial Rhythms P wave and/or PR interval are abnormal. QRS may be missing after some P waves. QRS is always normal, if it is present Premature Atrial Contraction (PAC) • Rate is usually normal and may be regular except when the PAC occurs. Some contractions have a shortened PR interval or the P wave may not be identified because it is buried in the T wave. Atrial tachycardia (A Tach) Rate is 150-250 and usually regular. PR interval is shorter than normal and the P wave may move up on the T wave or be buried in it (wet T). Each P wave is followed by a QRS complex. Atrial Flutter (AF) • Rate is 250-400. P waves are usually 0.2 seconds each and occur in clusters of 2, 3, or 4 (look like saw teeth). Each cluster is followed by a QRS complex at regular intervals. Because of this, they are classified as being AF 2:1, 3:1, or 4:1. Atrial fibrilliation (A-Fib) • Atrial rate is too fast to count and individual P waves may be difficult to identify. Normal QRS complexes appear at irregular intervals. There will be many more P waves than QRS complexes. May cause blood clots to form and be sent to the brain, heart or lungs. • Atrial Fibrillation Ventricular Rhythms – rate varies. No P wave in front of abnormally wide QRS complexes (they will be greater than 0.1 second). It may be difficult to identify parts as being QRST. There will be more QRS complexes than P waves in the strip. Premature Ventricular Contraction • Rate is usually normal and may be regular except when PVC occurs. PVC may occur alone at regular intervals (bigeminy, trigeminy) or in clusters (salvos). If 6 or more PVCs occur in 1 minute, the heart is becoming very irritable and ventricular tachycardia can begin at any time. Ventricular tachycardia (V Tach) • Rate is 150-250 and regular (looks like ric rac). No P waves are seen. This is a continuous PVC run. Ventricular fibrillation (V Fib) • Rate is too irregular to count. Cannot identify any par of the waveform. Asystole – Straight line • No heart activity is seen. • Clinical death is present. • Will become biological death if lasts longer than 4-6 minutes. This is all for now • The rest of these slides are about heart disease and we will probably go over them at another time Pathology of MI • Plaque builds up slowly (frequently LAD) • Sudden blockage occurs and muscle and nerve tissue distal begin to malfunction and then die • Abnormal activity and contractions • Leads to V Fib/Asystole • Scar tissue may form during healing and cause disrhythmias. Coronary Vessels Plaque Myocardial Infarction • Heart Attack MI Treatment • • • • • Aimed at restoring coronary blood flow Angioplasty and stent placement Coronary artery by-pass graft (CABG) Anticoagulants: heparin and coumadin Aspirin (ASA): anticoagulant and antiinflammatory agent Pathology of CHF • • • • Congestive heart failure Damaged valves or ventricular muscle Heart cannot completely empty Right failure – blood backs up in legs (pitting edema, 1+ to 4+) • Left failure – blood backs up in lungs (pulmonary edema) • Cardiotonic – lanoxin, digoxin (not if pulse < 60) • Diuretic - lasix CHF • Heart Failure Test Your Knowledge • • • • Label the Parts of Your Heart Label Your Heart's Electrical System Name Your Blood Vessels Define Common Heart Problems