* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 19 EKG – Electrocardiogram
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
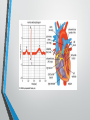
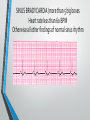
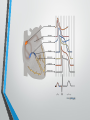
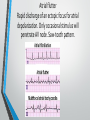
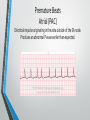
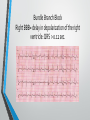
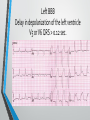
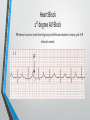
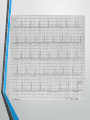
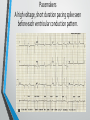
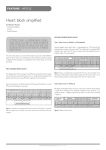
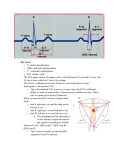
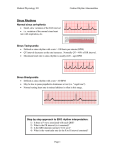
Lecture 19 The Electrocardiogram EKG/ECG Holdorf PhD, MPA, RDMS, RVT Normal complex • P wave-atrial systole • QRS complex – ventricular systole (depolarization) • T wave – Ventricular diastole (repolarization) Hint: • 1 small box = 0.04 seconds • 1 big box = 0.2 seconds • 5 big boxes = 1 second • Normal values: • • • • R-R interval: between 3 to 5 big boxes (60-100 beats/minute QRS complex: less than 3 little boxes (less than .12 seconds PR interval: Less than 1 big box (less than 0.2 seconds) The ECG has which of the following rhythms? • Normal sinus rhythm (via the SA node) Method of analysis Find the P waves (they’re the big ones) Assess at the QRS duration (< little boxes) Assess at R-R interval: between 3 and 5 big boxes Look for P preceding each R wave Check the PR interval (less than I big box) ECG: Common abnormalities • Normal sinus rhythm (R-R interval between 3 and 5 big boxes • • • 60-100 BPM P-wave preceding each QRS PR interval and QRS complex within normal limits SINUS BRADYCARDIA (more than 5 big boxes Heart rate less than 60 BPM Otherwise all other findings of normal sinus rhythm SINUS TACHYCARDIA Less than 3 big boxes Heart rate greater than 100 BPM Otherwise all other findings of normal sinus rhythm If the cardiac electrical impulse is in the bundle branches, where are you on the ECG tracing? The Purkinje fibers The bundle of His? • Answer for all • PR interval ARRHYTHMIAS OVERVIEW • P waves • • Present or absent Relationship to QRS • PR Interval • Normal < 0.20 sec. • QRS Duration • Normal <0.12 sec. Sinus arrhythmia Irregular rhythm related to respiration (increase rate with inspiration; decrease rate with expiration In sinus arrhythmia, the heart rate varies with the phase of respiration. The heart rate typically increases during inspiration and decreases during expiration. Therefore, as observed, the R-R interval is longer during expiration. These changes are mediated through vagal reflexes. Sinus arrhythmia is more common in young healthy athletes. Atrial fibrillation • Rapid discharge of multiple foci in the atria, no discrete P waves, irregularly irregular rhythm. Atrial flutter Rapid discharge of an ectopic focus for atrial depolarization. Only occasional stimulus will penetrate AV node. Saw-tooth pattern. Ventricular Fibrillation Chaotic rhythm in which there are multiple areas exhibiting varying degrees of depolarization and repolarization. Absence of R-waves Premature Beats Atrial (PAC) Electrical impulse originating in the atria outside of the SA node. Produces an abnormal P wave earlier than expected. Ventricular (PVC-premature ventricular contractions) Ectopic ventricular focus (anatomic source) produces an abnormal ventricular complex (usually larger and wider than normal complex). A PVC occurring every other beast is called bigeminy A PVC occurring every 3rd beat is trigeminy Ventricular tachycardia Three or more beast of ventricular origin (PVC) occurring in succession. Bundle Branch Block Right BBB= delay in depolarization of the right ventricle: QRS > 0.12 sec. Left BBB Delay in depolarization of the left ventricle V5 or V6 QRS > 0.12 sec. Heart Block 1st degree AV Block PR interval >0.20 sec. (more than I big box) and of the same duration in every cycle. R-R interval is normal. 2nd degree AV Block PR interval >0.20 sec. and gets progressively longer until a QRS is dropped. In other words, the P moves further away from the QRS. 3rd degree AV block • Complete absence of conduction between the atria and ventricles (also known as complete heart block (CHB). • P-R interval gets progressively shorter. • In other words, the P marches straight into the QRS complex. Pacemakers A high voltage, short duration pacing spike seen before each ventricular conduction pattern. Exercise Stress Testing • • Indications • • • • • To aid in the diagnosis of chest pain To determine the severity and prognosis of CAD To guide post MI rehab To evaluate cardiac arrhythmias To screen high risk professionals or asymptomatic patients Interpretation • • • • Morphology, degree and duration of ST-Segment depression (Mechanical / pressure) ST = segment elevation Duration of exercise Exercise-induced hypotension or arrhythmias