* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download UNIT 10
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Ventricular fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
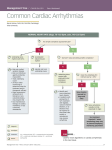
UNIT 10. (27.04.15.-01.05.15) Typical disorder of the cardiovascular system. Cardiac arrhythmias. Questions. 1. Cardiac arrhythmias, definition. Type on the etiology and pathogenesis. Classification. 2. Etiology, pathogenesis, ECG signs of certain types of cardiac arrhythmias. Practical work Work №l Getting sinus tachycardia. Frog narcotize, lock pins on a dissecting table, bare area of the heart, the pericardium open, cut the bridle, to establish record heart rate on a kymograph make the original record of the heart. Count the number of heartbeats. Attach a tube with hot water (70 °) to the sinus area. Make a record of the heart and determine heart rate. Work №2 Getting sinus bradycardia. After restoration of the initial rate attach tube of cold water (0-10 C) to the sinus area. Make a record of the heart and determine heart rate. The conclusions of the works №1 and №2 answer the questions: 1. What kind of sinus tachycardia depending on the mechanism of its development was obtained in? 2. A how systemic hemodynamic changes can cause arrhythmia data? Work № 3 Arrhythmia due to violation of excitability. At the time of diastole put a shot to the heart ventricles. Mark on kymograph appearance beats and following the compensatory pause. The experience can be repeated. The conclusions of the work to answer the questions: 1. How can I call you received a premature experiment? 2. What is the cause of the beats? 3. What are the terms used to produce beats you? 4. How can we explain the emergence of compensatory pauses after ventricular premature beats? Work №4 Arrhythmia due to conduction abnormalities. Getting sinuauricular heart block. For work, you can use the frog from previous experience. Cardiogram record and count the number of heartbeats per 1 minute. Then apply a ligature Staniusa 1 (between the venous sinus and right atrium). Re-record the cardiogram and count the number of heartbeats per 1 minute. Work №5 Getting atrioventricular heart block. Remove the 1st ligature Staniusa by cutting with scissors. To restore the original rhythm of the heart. Apply the 2nd ligature Staniusa (between the atria and ventricles), tighten it. Mark on kymograph and count the number of cuts in 1 minute atria and ventricle. The conclusions of the works number 4 and 5 to answer questions; 1. What types of conduction disturbances got you in these works? 2. Which violations systemic hemodynamics can be caused by a complete atrioventricular block? Work №6. Explore the electrocardiographic signs of different types of arrhythmias. Analyze the ECG in accordance with standard procedure. 1. Assess the regularity of RR intervals in all recorded ECG cycles. (Is equal to each other intervals RR). 2. To determine the incidence of ventricular rhythm, knowing the speed of the belt, and therefore the length of the RR interval by the formula HR = 60 / RR. In this case, one cell is equal to 0.05 seconds. 3. Identify the source of rhythm in relation to the P wave ventricular complexes (sinus rhythm or from another source Supraventricular, ventricular). 4. Assess the function of the conductivity across the width of P wave duration and constancy intervals PQ, wide complex QRS (increase of any of these components may be indicative of the blockade). If any such indication arrhythmias analyze abnormal ECG fragments according to the procedure used when arrhythmias. I. Analysis of the atrial rhythm. 1. Evaluation of the interval P-P. 2. Rating shape and width of P wave II. Analysis of correlation between the rhythm of the atria and ventricles. 1. Evaluation the relationship between P wave complexes and QRS. 2. Rating duration intervals PQ. III. Ventricular rhythm analysis. 1. Evaluation of the interval R-R. 2. Rating shape and width of the complex QRS.