* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sinus_Tachycardia
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
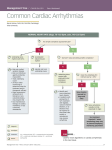
Sinus Tachycardia (tachy - fast) Sinus tachycardia occurs when the sinus rhythm is faster than 100 beats per minute. The rhythm is similar to normal sinus rhythm with the exception that the RR interval is shorter, less than 0.6 seconds. P waves are present and regular and each P-wave is followed by a QRS complex in a ratio of 1:1. At very rapid rates, the P-waves might become superimposed on the preceding T waves such that the P waves are obscured by T waves. The EKG on the top shows normal sinus rhythm. The EKG at the bottom shows sinus tachycardia Sinus tachycardia may be accompanied by a decrease in stroke volume because the ventricles do not have enough time to fill (after atrial systole) before ventricular contraction.. The pulse pressure may decrease due to a lower stroke volume and decreased time for diastolic run-off. Sinus tachycardia results from increased automaticity of the SA node, for instance, due to increased sympathetic stimulation of the heart, fever or cardiac toxicity.