* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Heart - WordPress.com
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
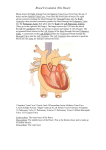
The Heart Unit 3 What is the purpose of the heart? • The heart is a hollow muscle that pumps blood throughout the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions. Facts about the human heart • The human heart pumps around 70 times per minute, every minute of every day until we die! • It must pump fluid through 160 000 km of vessels. • It must pump in two directions at once, without mixing the fluid travelling in the two directions. Video: A real heart beating http://www.youtube.com/watch?v =Gnv54V8Jj1U Video: How the heart works http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oHMmtqKgs50 Structure of the Heart • The heart of a mammal is divided into four chambers. 1. 2. 3. 4. Right Atrium Right Ventricle Left Atrium Left Ventricle Parts of the Heart • Aorta: This is the largest blood vessel in the body and leads directly from the heart. It mostly carries oxygenated blood • Pulmonary Artery: carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs to be oxygenated • Pulmonary Vein: returns oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart to be pumped to the rest of the body • Pulmonary circulation • Atria: where blood enters the heart (located on the top of the heart) • Ventricle: where blood exits the heart (located on the bottom of the heart) • Septum: a wall that separates the left and right sides of the heart • Vena Cava: This is the largest vein in the body that carries deoxygenated blood back to the heart. It is divided into two parts: • Superior Vena Cava: Returns blood from the upper portions of the body. • Inferior Vena Cava: Returns blood from the lower portions of the body. • Bicuspid Valve: prevents blood from flowing the wrong way in the heart. It is found between the left atrium and left ventricle. It has 2 cusps (parts). • Tricuspid Valve: prevents blood from flowing the wrong way in the heart. It is found between the right atrium and right ventricle. It has 3 cusps. Both of these valves are called atrioventricular valves (AV valves) because the divide the atria and ventricles • Semilunar valve: prevents blood from being sucked back into the heart. There are two of semilunar valves in the heart. One is located between the aorta and left ventricle the other is between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery When you listen to you heart with a stethoscope, the lub-dup sound you hear are the valves opening and closing How does blood flow through the heart? 1. Blood from the body enters the heart from the vena cava. The super vena cava collects blood from the upper body and the inferior vena cava collects blood from the lower body. 2. The vena cava carry blood to the right atrium. 3. The atria contract, forcing the blood into the right ventricle. 4. The ventricles contract. The blood is forced out of the heart into the pulmonary artery. 5. The pulmonary arteries take the blood to the lungs where it receives oxygen. 6. Upon exiting the lungs, the blood flows back to the heart in the pulmonary veins. 7. The oxygenated blood collects in the left atrium. 8. Again, the atria contract and the blood move into the left ventricle. 9. The ventricles contract and the left ventricle pumps the blood out of the heart through the aorta to reach the body’s tissues. Trace the pathway of blood through the heart Videos: Blood flow through the heart http://www.youtube.com/watch?v= FCimR_P9ID0 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v =Rj_qD0SEGGk