* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Environmental Changes2
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Reforestation wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Biological Dynamics of Forest Fragments Project wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Human impact on the nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Coevolution wikipedia , lookup
Ecological succession wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Natural environment wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
Nitrogen cycle wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
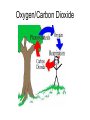
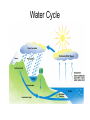
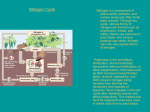
Environmental Changes Ecological SuccessionThe natural process where a habitat changes over time Succession • Bedrock- lichens- mosses- grass- trees and shrubs- forest • Gradual changes result in a stable community • Climate changes, natural disasters, animal plant and human activity can alter the stable environment • Example: lake to forest- lake-sedimentsplant debris build up- lake fills in- swampforest Succession Lake Succession Relationships Symbiosis- organisms live together Symbiotic Relationships • Commensalism- one organism benefits and the other is not benefited or harmed. EX. Barnacle on whale • Mutualism- both organisms benefit EX. Nitrogen fixing bacteria- fix nitrogen for use by plants, protozoa in termites • Parasitism- one organism benefits, the other is harmed EX. Tapeworm or fleas in dogs The anemonefish lives among the forest of tentacles of an anemone and is protected from potential predators not immune to the sting of the anemone. The anemonefish is protected from the sting of the anomone tentacles by a substance contained in the mucous on its skin. The exact nature of this protective substance is not known, but is believed to be a combination of a partial natural secretion and chemicals the fish harvests by rubbing up against the anemone's tentacles. What ever the case may be, the anemone treats the fish as part of itself and does not sting it. Commensalism Mutualism Bees and many species of flowering plants interact with each other in a mutualistic fashion. In this interaction, the flower becomes pollinated by the insect, while the bee receives food in the form of pollen and nectar. Parasitism Mosquito: Females ingest blood for the protein. Male mosquitos ingest plant juices. Very few animals have a diet that is restricted only a single food source, so the concept of a linear food chain is extremely simplistic. In reality, trophic relationships within a community are more like a food web in which dozens of plant species support a wide variety of herbivores which in turn are consumed by numerous predators and parasites. If one species within a food chain becomes scarce (perhaps due to bad weather or over-exploitation), there will be serious repercussions on all other species in the chain. But in a complex food web, changes in individual populations are likely to have a smaller impact because they are buffered by the availability of an alternative prey or host species. Material Cycles The recycling of Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide, and Hydrogen in an ecosystem from living organisms to soil and back to living organisms Cycles • Photosynthesis- O2- Respiration- CO2photosynthesis • Water- evaporation- water- condensation • Nitrogen in air- converted to nitrates in soil for use by plants by nitrogen fixing bacteria • Nitrates in soil converted to protein by plants • Nitrogenous waste and dead organisms release ammonia when decomposed Nitrogen cycle Oxygen/Carbon Dioxide Water Cycle