* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Principles of Marketing
Marketing research wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Viral marketing wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Competition (companies) wikipedia , lookup
Darknet market wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Product planning wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
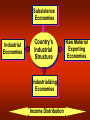
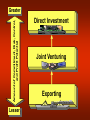
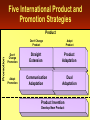
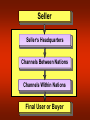
Principles of Marketing Lecture-41 Summary of Lecture-40 Creating Competitive Advantage Competitor Analysis Steps Identifying Competitors Assessing Competitors Selecting Competitors to Attack or Avoid Competitive Strategies Competitive Positions Market Leader Market Challenger Market Follower Market Nicher Global Marketplace Today’s Topics Global Marketing Reasons for Global Marketing Growth –Access to new markets –Access to resources Survival –Against competitors with lower costs (due to increased access to resources) Global competitors attacking the domestic market, Foreign markets might offer higher profit opportunities, Domestic markets might be shrinking, Need an enlarged customer base to achieve economies of scale, Reduce dependency on any one market, Customers might be expanding abroad. Getting involved in international marketing: A five step process DO WE GET INVOLVED IN INTERNATINAL MARKETING? IF YES, WHICH MARKETS? IMPACT ON DOMESTICBASED MARKETING? HOW MUCH COMMITMENT IN EACH MARKET? HOW SHOULD WE REORGANIZE OUR OPERATIONS? Global Marketplace Global competition is intensifying and few industries are now safe from foreign competition. To compete, many companies are continuously improving their products, expanding into foreign markets and becoming Global Firms. Global firms face several major problems: – Variable exchange rates, – Unstable governments, – Protectionist tariffs and trade barriers, – Corruption. Global Vision Recognizing and reacting to international marketing opportunities; Being aware of threats from foreign competitors in all markets; Effectively using international marketing mix opportunities Decisions in International/Global Marketing Looking at the global marketing environment Deciding whether to go international Deciding which markets to enter Deciding how to enter the market Deciding on the global marketing program Deciding on the global marketing organization Looking at the Global Marketing Environment The International Trade System The World Trade Organization and GATT Regional Free Trade Zones The International Trade System – Tariffs, quotas, embargos, exchange controls, nontariff trade barriers – World Trade Organization and GATT – Regional free trade zones • European Union • North American Free Trade Agreement • Other free trade areas Just a reminder…. Infrastructure A nation’s basic conditions in transportation networks, communication systems, ad energy facilities. Exchange Rate The price of one nation’s currency in terms of another country’s currency. Tariff A tax levied on imported goods. Import Quota An administrative trade restriction that limits the number of units of a certain good that can enter a country for resale. Embargo An administrative trade restriction that imposes a complete ban on imports of a specified product. Dumping The controversial trade practice of selling a product in a foreign market at a lower price than it commands in the producer’s domestic market. General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) An international trade accord that has helped to reduce worldwide tariffs. World Trade Organization (WTO) A 125-member organization that succeeds GATT in overseeing trade agreements, mediating disputes, and reducing trade barriers, unlike GATT provisions, WTO decisions are binding. North American Free-Trade Agreement (NAFTA) An accord to remove trade barriers among Canada, Mexico, and the United States. Looking at the Global Marketing Environment Economic Environmental Factors Subsistence Economies Industrial Economies Country’s Industrial Structure Industrializing Economies Income Distribution Raw Material Exporting Economies Political-Legal Environmental Factors Attitudes Toward International Buying Government Bureaucracy Monetary Regulations Political Stability Cultural Environmental Factors How Customers Think About and Use Products Cultural Traditions, Preferences, and Behaviors Business Norms and Behavior Deciding Which Markets to Enter • Consistent with objectives and culture of firm • Demographic Characteristics • Economic Factors • Sociocultural factors • Technological factors Define Organization’s Marketing Objectives and Policies What Volume of Foreign Sales is Desired? How Many Countries Should the Firm Go Into? What Types of Countries Should be Entered? Rank by Market Size & Growth, Cost of Doing Business, Competitive Advantage, & Risk Level. Deciding How to Enter the Market Amount of Commitment, Risk, Control, and Profit Potential Greater Lesser Direct Investment Joint Venturing Exporting • 1st level: Exporting • 2nd level: Joint Venturing – Franchising – Licensing – Contract manufacturing – Joint ownership • 3rd level: Direct Investment Deciding on the Global Marketing Program Five International Product and Promotion Strategies Promotion Product Don’t Change Promotion Adapt Promotion Don’t Change Product Adapt Product Straight Extension Product Adaptation Communication Adaptation Dual Adaptation Product Invention Develop New Product Straight product expansion • Marketing the product with no changes Product adaptation • Altering the product to meet local conditions or the wants of the foreign market Product invention • Creating new products or services for foreign markets Global Pricing Strategies Companies face many problems • Price escalation • Pricing to foreign subsidiaries • Recent economic and technological forces • The Internet Possibilities in setting prices include: – Charge a uniform price all around the world. – Charge what consumers in each country could pay. – Use a standard markup of its costs everywhere. Whole-Channel Concept for Distribution Seller Seller’s Headquarters Channels Between Nations Channels Within Nations Final User or Buyer Global Promotion Strategies Standardized global communication • Advertising themes are standardized from country to country with slight modifications Communication adaptation • Advertising messages are fully adapted to local markets Managing International Marketing Activities Step 1: Organize export department Step 2: Create an international division Step 3: Become a global organization Think Globally Act Locally Enough for today. . . Summary Global Marketing Global Marketplace Looking at the global marketing environment Deciding whether to go international Deciding which markets to enter Deciding how to enter the market Deciding on the global marketing program Deciding on the global marketing organization Think Globally Act Locally Next…. e-Marketing Principles of Marketing Lecture-41