* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download unit 1 human body orientation ppt teacher
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
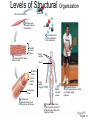
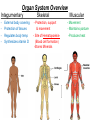
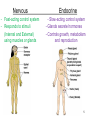
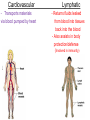
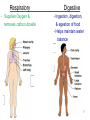
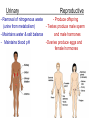
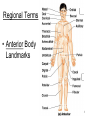
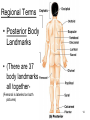
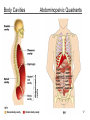
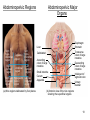
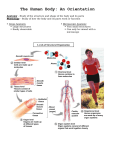
Chapter 1 The Human Body: An Orientation 1 • Anatomy – study of the structures and shape of the body • Physiology – study of how the body and its parts work or function • Gross Anatomy - large structures or Organs seen with the eyes • Microscopic Anatomy – small structures 2 Levels of Structural Organization Molecules Smooth muscle cell 2 Cellular level Cells are made up of molecules. Atoms 1 Chemical level Atoms combine to form molecules. 3 Tissue level Tissues consist of similar types of cells. Smooth muscle tissue Blood vessels Heart Epithelial tissue Smooth muscle tissue Connective tissue 4 Organ level Organs are made up of different types of tissues. Blood vessel (organ) Cardio– vascular system 5 Organ system level Organ systems consist of different organs that work together closely. 6 Organismal level Human organisms are made up of many organ systems. 3 Figure 1.1 Figure 1.1 Organ System Overview Integumentary - External body covering Protection of tissues Regulates body temp Synthesizes vitamin D Skeletal - Protection, support & movement - Site of Hematopoeisis(Blood cell formation) -Stores Minerals Muscular - Movement - Maintains posture -Produces heat 4 Nervous - Fast-acting control system - Responds to stimuli (Internal and External) using muscles or glands Endocrine - Slow-acting control system - Glands secrete hormones - Controls growth, metabolism and reproduction & reproduction 5 Cardiovascular - Transports materials via blood pumped by heart - WBC’s have role in body protection/defense Lymphatic - Returns fluids leaked from blood into tissues back into the blood - Also assists in body protection/defense (Involved in immunity) 6 Respiratory - Supplies Oxygen & removes carbon dioxide Digestive - Ingestion, digestion, & egestion of food - Helps maintain water balance 7 Urinary Reproductive - Removal of nitrogenous waste - Produce offspring (urine from metabolism) - Testes produce male sperm - Maintains water & salt balance and male hormones - Maintains blood pH -Ovaries produce eggs and female hormones 8 Homeostasis **All systems work together to maintain the homeostasis of the body.** • Maintenance of a stable internal environment = a dynamic state of equilibrium. • Homeostasis must be maintained for normal body functioning and to sustain life. • Homeostatic imbalance – a disturbance in homeostasis resulting in disease. 9 The Language of Anatomy • Special terminology is used to prevent misunderstanding • Exact terms are used for: – Position -Direction – Regions -Structures Orientation and Directional Terms Distal – farther from the origin of body part or trunk ex. The wrist is distal to the shoulder. Superficial (external) – toward or at the body surface ex. The skin is superficial to the skeleton. Deep – (internal) away from the body surface ex. The lungs are deep to the sternum. 10 Orientation and Directional Terms 11 Orientation and Directional Terms Table 1.112 (cont) Regional Terms • Anterior Body Landmarks 13 Regional Terms • Posterior Body Landmarks • (There are 37 body landmarks all together(Femoral is labeled on both pictures) 14 B o d y P l a n e s 15 Body Planes and Sections • A median, or midsagittal, section divides the body (or organ) into equal left and right parts. • A frontal, or coronal, section divides the body (or organ) into anterior and posterior parts. • A transverse, or cross, section divides the body (or organ) into superior and inferior parts. Body Cavities Abdominopelvic Quadrants 17 Body Cavities • Dorsal body cavity – Cranial cavity houses the brain – Spinal cavity houses the spinal cord • Ventral body cavity – Thoracic cavity houses heart, lungs, and others – Abdominopelvic cavity houses digestive system and most urinary system organs Abdominopelvic Regions Abdominopelvic Major Organs Diaphragm Stomach Liver Right hypochondriac region Right lumbar region Epigastric region Left hypochondriac region Umbilical region Left lumbar region Right iliac Hypogastric Left iliac (inguinal) (pubic) (inguinal) region region region (a) Nine regions delineated by four planes Gallbladder Ascending colon of large intestine Small intestine Cecum Appendix Transverse colon of large intestine Descending colon of large intestine Initial part of sigmoid colon Urinary bladder (b) Anterior view of the nine regions showing the superficial organs 19