* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earthquakes - Lindbergh Schools
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Seismic inversion wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Seismic communication wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Earthquake engineering wikipedia , lookup
Ring of Fire wikipedia , lookup
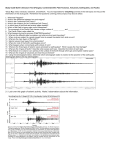
Lesson 1: What are earthquakes and where do they occur Where do Earthquakes Occur? • Earthquakes can occur near the Earth’s surface or far below the surface. • Most earthquakes occur at plate boundaries, but some happen at faults located in the middle of tectonic plates. PLATE BOUNDARIES Earthquake Locations Around the World What Causes Earthquakes? • Earthquakes are caused by movement along faults. • When stress is placed on rocks it deforms, or changes. • Rock is stretched and bent until it can no longer take the stress. • When enough stress builds up in the rock it, it slips and energy is released. • This energy is felt as an earthquake. Earthquakes in St Louis?? Do we live near a plate boundary? Do we live near a fault? The New Madrid Fault If there is no plate boundary in the middle of the United States, why did these earthquakes take place? Geologists are beginning to understand the answer. The New Madrid Fault Zone is part of an ancient plate boundary. In this area, the North American Plate tried to form a divergent plate boundary about 500 million years ago. The splitting stopped before new plates could form. The faults in the New Madrid Zone are remnants of this old event. Earthquakes occur because the North American Plate is still "settling down". The faults in the New Madrid Zone do not reach the Earth’s surface. They are buried beneath thousands of feet of rock and sediment deposited by the Mississippi River. Geologists have located them by looking at the patterns of earthquakes in the zone. Several of the largest earthquakes ever recorded in the United States occurred in the Midwest, far from any plate boundary. These earthquakes took place in an area called the New Madrid Fault Zone, named after the town of New Madrid, Missouri. New Madrid Fault Over a three-month period in the winter of 1811 to 1812, the New Madrid Fault Zone was struck by three huge earthquakes estimated to be greater than magnitude 8.0 The New Madrid Fault is what causes Alabama to experience earthquakes. 3 Types of Faults associated with Earthquakes PLATE MOTION FAULT TYPE Transform Strike –Slip Fault Convergent Reverse Fault Divergent Normal Fault Strike-Slip Fault occurs at a Transform Boundary Reverse Fault occurs at a Convergent Boundary Normal Faults occur at Divergent Boundaries How do Earthquake Waves Travel? Energy released from moving plates and faults travels through the Earth as waves. These waves are called seismic waves. Types of Seismic Waves 1. BODY WAVES: Seismic waves that travel through the Earth. 2. SURFACE WAVES: Seismic waves that travel along the surface. WAVES TRAVEL: 1.At different speeds and 2 In different ways Depending on what kind of material they are moving through. Seismic Wave Arrival • First- P-waves • Second- S-waves • Third- Surface Waves Quiz • • • • • • 1. Most Earthquakes occur along ________________. 2. The first seismic waves to arrive are______________. 3. The second seismic waves to arrive are _____________. 4. The last seismic waves to arrive are_______________. 5. Which seismic waves travel the fastest?___________ 6. Which type of seismic wave can move through a solid, liquid or a gas?________________ • 7. Which seismic wave cannot travel through material that is completely liquid?______________ • 8. Which seismic waves are the slowest and the most destructive?_______________ Seismograph • A seismograph is an instrument used by scientists to measure earthquakes. • Seismologists who study earthquakes can determine when an earthquake started by noting the arrival times of P-waves and Swaves. • A seismograph records vibrations in the Earth and determines the strength and location of an earthquake. Ancient Chinese Seismograph. The ball would drop from the dragon to the frog. It told the people which direction the earthquake come from. Seismograms 0 1 2 3 Time in Minutes 4 5 6 1. How many minutes did it take for the P-Waves to arrive? 2. How many minutes did it take for the S-waves to arrive? 3. How long did the surface waves last? 7 8 Epicenter • The epicenter is the point on the Earth’s surface directly above an earthquake’s starting point. Focus • The focus is the point inside the Earth where the earthquake begins. • The epicenter is located directly above the focus. Volcanoes form around Vents Lava vents that release magma onto the Earth’s surface. Magma chamber The Composition of Magma Determines whether it is explosive or not! High water content • More likely to be High content • More likely to be • Why? !!! !!! Silica has a thick, stiff consistency • Flows slowly • Tends to Harden in the volcano’s vent Quiz Part 2 a. What physical event causes explosive eruptions? b. Would high water content increase the likelihood of having an explosive eruption? c. Would high silica content increase the likelihood of having an explosive eruption? What Erupts from a Volcano? Blocky lava Lava can be thick or thin. Pahoehoe Aa Pillow lava Types of Volcanoes Shield volcano Cinder cone volcano Composite volcano What causes volcanoes? The Formation of Magma • Mantle rock melts when the temperature increases or the pressure decreases. What causes volcanoes? Where Volcanoes Form • Tectonic Plate Boundaries!!! ~75% world’s active volcanoes in Ring of Fire What causes volcanoes? What causes volcanoes? Hot Spots How do volcanologists predict eruptions? Measuring Small Quakes • Before eruption, increase in number & intensity Measuring Slope • Bulges may form with magma (tiltmeter) Measuring Volcanic Gases • Outflow of volcanic gases Sulfur dioxide, carbon dioxide Measuring Temperature from Orbit • Measure changes in temperature over time You should not be a Volcanologist if…. Robert McGimsey USGS A. Ozerov You don’t like hiking, backpacking, rock climbing, etc. You are not interested in experiencing extreme temperatures and heights. If you don’t like to travel to incredible places and see breathtaking views of the world.