* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Assessment of the Abdomen
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
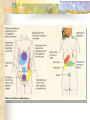
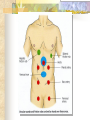
Assessment of the Abdomen By Freida Fuller-Jonap fulerjonap_f 678-547-6742 The Abdominal Assessment Includes the lower end of the esophagus stomach kidneys edge of the urinary bladder spleen liver gallbladder uterus large and small intestines peritoneum Health History Data Should Include Diet nutrition level of stress alcohol/cigarette smoking medications stood urinary exposure to infectious disease possibility of pregnancy family history previous GI or GU trauma specific problems related to GI tract and GU system Assessment should occur in a particular order Inspection Ausculatation Percussion Palpation Inspection Skin: color, texture, scars, lesions, striae, rashes, wounds, incisions, ostomies, etc Color: Grey Turner Sign jaundice ascites Vascularity Striae Inspect the Umbilicus Cullen’s sign Contour: flat, rounded, concave, protuberant Assymetry Masses Movement Pulsations of the aorta Peristalsis of intestines Auscultation Bowel sounds hyperactive hypoactive Absent Vascular Sounds Bruits aorta renal arteries iliac arteries Friction Rubs Percussion Tympany Liver Span: normal span 6-12 cm. Liver enlargement, hepatomegaly is characterist of liver tumors, cirrhosis, abscess, and vascular engorgement Fist Percussion of CVA Palpation Light palpation Deep palpation Palpation of the Liver Palpation of the spleen Palpating kidneys Palpating the urinary bladder Special Abdominal Tests Ascites Fluid Wave Fluid Shift Special Abdominal Tests (continued) Ballottement Technique Appendicitis Rebound tenderness (Blumberg’s sign Rovsing’s Referred rebound tenderness Psoas Oburator sign Acute cholecystitis Murphy’s sign Diagnostic Testing Ultrasound of the Abdomen: visualize abdominal aorta, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, bile ducts, spleen kidneys, ureters, and bladder CT of the Abdomen MRI: less accurate that CT for most abdominal diseases, maybe better for liver and pelvis that CT Tests for Gallbladder Diseases Bilirubin Direct Indirect Diagnostic Study for the Pancreas Serum Amylase Liver Studies Ammonia: hepatitis, cirrhosis, hepatic encephalopathy Prothrombin Time: cirrhosis, hepatitis, bile duct obstruction, ALT (alanine aminotransferase: hepatitis, liver necrosis, cirrhosis, cholestasis, tumor and hepatotoxic drugs AST (aspartate aminotransferase) Used to be SGOT. Hepatitis, gallstone, cirrhosis AST/ALT ratio: cirrhosis, liver congestion, tumors ALP (alkaline phosphatase): cirrhosis, biliary obstruction, liver tumor Diagnostic Tests for Kidney Disorders BUN: metabolic function of the liver and excretory function of the kidney Increased: renal disease/failure, nephrotoxic drugs GI bleeding, excessive protein ingestion Decreased: Liver failure, overhydration, malnutrition, malabsorption, nephrotic syndrome Creatinine Potassium Urinalysis Protein Leukocyte esterase Nitrates Urine for C & S IVP: intravenous pyelogram KUB: Kidneys, ureters, bladder Diagnostic Tests for Gastrointestinal System EGD (esophagogastroduodenoscopy): tumors, esophageal diverticula, hiatal hernia, esophagitis, gastritis… Barium enema Barium Swallow Colonoscopy Sigmoidoscopy