* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 23-1 Specialized Tissues in Plants
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
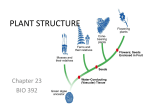
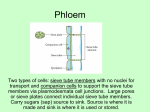
23–1 Specialized ___________________ in Plants I) ________________ Plant Structure A) The three principal ________________ of seed plants are roots, ______________, and leaves. 1) These organs perform functions such as the ____________________ of nutrients, ______________________, and coordination of plant activities. B) ________________: 1) absorb water and dissolved _____________________. 2) ________________ plants in the ground. 3) _________________ the plant from harmful soil bacteria and fungi. C) ________________ provide: 1) a ___________________ system for the plant body. 2) a ___________________ system that carries nutrients. 3) a ___________________ system that protects the plant against predators and disease. D) _______________: 1) are a plant’s main _________________________ systems. 2) increase the amount of sunlight plants ______________________. (a) Adjustable pores conserve water and let oxygen and carbon dioxide enter and exit the leaf. II) Plant _____________________ Systems A) Plants consist of _________________ main tissue systems: 1) ___________________ tissue 2) ___________________ tissue 3) ___________________ tissue B) Dermal _____________________ 1) The outer covering of a plant consists of ______________________ cells. (a) Epidermal cells make up ______________________ tissue. • The outer surfaces of epidermal cells are covered with a thick waxy layer, known as the ________________. PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com • The cuticle _______________ the plant against water loss and injury. • Some epidermal cells have projections called ___________________, that help protect the leaf and also give it a ________________ appearance. 2) In roots, dermal tissue includes root ______________ cells that provide a large amount of surface area and aid in water ________________________. 3) On the underside of leaves, dermal tissue contains _________________ cells, which regulate water loss and gas exchange. C) __________________________ Tissue 1) Vascular tissue forms a ________________________ system that moves water and nutrients throughout the plant. 2) Vascular tissue is made up of __________________, a water-conducting tissue, and _______________________, a food-conducting tissue. 3) Vascular tissue contains several types of specialized cells. • Xylem consists of ____________________ and vessel elements. • Phloem consists of _________________ tube elements and ______________________ cells. (b) Xylem • All seed plants have tracheids. (i) Tracheids are long, narrow cells that are ___________________ to water. They are pierced by openings that connect neighboring cells to one another. • Angiosperms also have ____________________ elements. (i) Vessel elements form a continuous ______________ through which water can move. 4) Phloem (a) Phloem contains sieve tube elements and ______________________ cells. (b) Sieve tube elements are __________________ cells joined end-to-end to form sieve tubes. • The end walls of sieve tube elements have many small _____________. PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com • __________________ and other foods can move through these holes from one adjacent cell to another. 5) Companion cells are phloem cells that surround sieve tube elements. (a) Companion cells ________________ the phloem cells and aid in the movement of substances in and out of the phloem. D) ___________________ Tissue 1) Cells that lie between ______________ and vascular tissues make up the ground __________________. 2) The three kinds of ground tissue are: (i) _________________________ (ii) _________________________ (iii)_________________________ (b) Parenchyma cells have ____________ walls and large central vacuoles surrounded by a thin layer of cytoplasm. (c) Collenchyma cells have strong, ________________ cell walls that help _______________ larger plants. (d) Sclerenchyma cells have extremely _______________, rigid cell walls that make ground tissue _________________ and strong. III) Plant Growth and ____________________ Tissue A) In most plants, new cells are produced at the ____________ of the roots and stems. 1) These cells are produced in ____________________. 2) A meristem is a cluster of ________________ that is responsible for continuing growth throughout a plant's lifetime B) The new cells produced in meristematic tissue are _______________________. 1) As the cells develop into _______________ cells, they differentiate. C) _________________________ is the process in which cells become ____________________ in structure. 1) As the cells differentiate, they produce _______________, ground, and ______________________ tissue. PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com 2) Near the ___________ of each growing stem and root is an _______________ meristem. (a) An apical meristem is a group of ______________________ cells that divide to produce increased length of stems and roots. D) Meristematic tissue is the only plant tissue that produces new cells by ____________________. PDF created with pdfFactory trial version www.pdffactory.com