* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download osvaldo 3-23-11
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
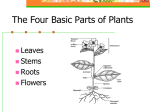
Plant project By Osvaldo Perez Adaptations Stores water to survive Spines help them keep internal heat down and also protects them from being eaten Has a waxy coating that helps reduce evaporation. Have long roots that spread laterally to get water Desert-Cactus Adaptations Has leaves to not get to much water Lives of off decay matter of the rainforest Grows 30cm-30m Rainforest-Bamboo Adaptations Has tough roots that help it get water Has scaly bark that protects them from the elements Has salicylic acid Tundra-Willow tree Function Plant organs that anchors a plant Absorbs water Transports dissolved materials and vascular tissue to and from the stem Roots Function Above average parts of plants that support the leaves and flowers Transport dissolved materials and vascular tissue Stem Function the primary function of leaves is photosynthesis Leaves Characteristics have one seed leaf Monocot Characteristics Have two seed leaves Dicot Transport water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the rest of the plants Xylem Tubular cells at each end Water and dissolved minerals flow through its cell wall Tracheids Transport water throughout the plant Vessel elements Made of tubular cells joined end to end Phloem Are alive at maturity Have no nucleus or ribosomes Have cytoplasm Sieve tube members Nucleated cells that help with the transport of sugars and other organic compounds through the sieve tubes of the phloem Companion cells Pictures