* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit1 Studyguide ANSWERS
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Reception of Islam in Early Modern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Spread of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Romania wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Study Guide for Unit 1 Test
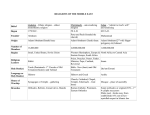
SS7H4: The student will describe the development of the three major religions that originated in Southwest Asia (Middle East)
Person responsible for its
creation
When?
Holy text
Place of worship
Name of followers
Place of Origin
Moral Guides
Religious Leaders
Name of Deity
Judaism
Abraham
Christianity
Jesus
Islam
Muhammad
About 1900 B.C.E.
Torah
Synagogue
Jews
City of Ur in modern day Iraq,
later grew in region of Canaan,
modern day Israel
10 Commandments
Rabbi
Yahweh or Adonai
7 B.C.E to 30 C.E.
Bible
Church
Christians
Palestine, modern day Israel in
city of Jerusalem
622 C.E.
Qu’ran / Koran
Mosque
Muslims
Mecca, Saudi Arabia
and city of Medina
10 Commandments
Priest
God
5 Pillars of Faith
Imam
Allah
1. What group led the crusades and what was their main purpose? During the 11th century, Christian leaders from Europe sent armies of
Christian crusaders to regain the holy city of Jerusalem from Muslim control.
•
Indiscriminate massive killings and death resulted, mostly by the Christians, with nothing really changing. As of 1250, Muslims still
controlled Palestine.
•
The impression left on the Muslims was that of ruthless barbarism, a view that still influences Muslim understanding of the West today.
2. What are the 5 Pillars of Islam?
Faith- believe in 1 God, Muhammad was his messenger
Prayer- 5 times each day in the direction of Mecca
Charity-donate 2.5% of wealth for charitable purposes
Fastno food or water from sunrise to sunset during the month of Ramadan
Hajjpilgrimage to Mecca at least once in a lifetime (if able)
3. The exile of the Jewish people from their homeland/holy land is called what? Diaspora. Throughout their history the Hebrew people have
endured hardships to include a drought that caused them to migrate to Egypt, only to be enslaved. After being led back to Canaan by Moses they
were eventually conquered by the Assyrian and Babylonian empires. When the Persian Empire controlled the Middle East the Jews returned to
their homeland of Israel only to later be conquered by the Greeks and later by the Egyptians. The Roman Empire controlled the area and many
Jews were forced to migrate to various parts of Europe. Those who stayed were enslaved. Centuries later during WWII many Jews were killed
during the Holocaust in Germany and Poland. This led to the creation of Israel as a nation in 1948 and allowed the return of Jews to their
homeland, however, since that time Jews have been involved with violent clashes between neighboring Arab nations over the claim to the holy
lands of Israel.
4. What title was given to the ruler of the Muslim community from 632 CE to 1924 CE.? Caliph means “successor,” the title given to those who
took over leadership of the Umma (the Muslim community) after the death of Muhammad.
5. What is the Muslim word for the pilgrimage to the holy city of Mecca? Hajj
6. Why is Jerusalem a holy city to Jews, Christians, and Muslims? According to the Israel Ministry of Foreign Affairs, “For three
millennia, Jerusalem has been the center of the Jewish faith. The many Jews who had been exiled after the Roman conquest and
scattered throughout the world never forgot Jerusalem. Jerusalem became the symbol off the desire of Jews everywhere to return to
their land. Mount Moriah, where the Temple once stood; the Western Wall, the only remnant of the Temple, which has been the
focus of prayer and longing of Jews for nineteen centuries; the Tomb of David on Mount Zion; and the ancient cemetery on the
Mount of Olives where Jews have been buried for centuries - all these are indelibly etched on Jewish consciousness.
For Christians, Jerusalem is the place where Jesus lived, preached, died, and was resurrected. Among these sites are the Church of
the Holy Sepulcher, the Garden of Gethsemane, the Site of the Last Supper, and the Via Dolorosa with the fourteen stations of the
Cross.
According to Islam, the prophet Mohammed was miraculously transported from Mecca to Jerusalem, and it was from there that he
made his ascent to heaven. The Dome of the Rock and the Al-Aksa ("the remote") Mosque, both built in the seventh century, made
definitive the identification of Jerusalem as the "Remote Place" that is mentioned in the Koran, and thus a holy place after Mecca
and Medina.”
7. What is the term for the belief in one God? Monotheism. Judaism, Christianity, and Islam are all monotheistic religions that originated in the
Middle East.
8. What is Sharia? Islamic Law that comes from the Koran and the teachings of Muhammad. In some Islamic societies Sharia guides every day
life.
9. What is the Arabic word that means a struggle for what is right and against wrong-doing; often interpreted as a holy war; some use it to
justify terrorist activities? Jihad
10. The ancient Egyptians and Sumerians had many gods. What is this practice called? Polytheism
11. Why is Mecca a holy city to Muslims? According to library.thinkquest.com, “Mecca is the birthplace of Muhammad, founder of Islam, and is
the most sacred of city in Islam. According to Islamic tradition, Muslims around the world must face Mecca during their daily prayers. Every
year, during the last month of the Islamic calendar, more than one million Muslims make a pilgrimage, or hajj, to Mecca.” According to
Wikipedia, “The Sacred Mosque is a large mosque in the city of Mecca and the largest in the world. The mosque is also commonly known as the
Haram. It surrounds the Kaaba, the place which Muslims turn toward while offering daily prayer. It is considered to be the holiest place on Earth
by devotee Muslims and can accommodate up to 820,000 worshippers during the Hajj period.” Mecca is also the city where the prophet
Muhammad spoke to thousands of Muslims and declared Islam to be the religion of the people.
12. How did Islam spread (give 3 reasons)?
1. At first followers of Muhammad were persecuted (religiously discriminated against) for their beliefs and
left Mecca to worship elsewhere like the city of Medina which was north of Mecca.
2. Over time Muslim dynasties such as the Ummayad and Abbasid and their armies conquered far away lands. Also, the Ottoman
empire spread Islam throughout Southeastern Europe, Southwest Asia, and North Africa.
3. Muslim traders/merchants traveled to far away places such as Northern Africa, Southern and Southeast Asia, eastern coast of
Africa, and Spain.
13. The historic regions of Canaan and Palestine are part of modern-day country? Israel
14. What happens during the Islamic holy month of Ramadan? Muslims observe the Fourth Pillar of Faith by fasting, or not eating or drinking
during daylight hours in order to show their commitment to their faith by making certain sacrifices.
15. What happened around the year 312 CE/AD that led to Christianity becoming the official religion of the Roman Empire? Roman Emperor
Constantine converted to Christianity; making it legal to practice Christianity without being persecuted (discriminated against religiously).
16. What religion began in Ur (Mesopotamia in modern-day Iraq)? Judaism
17. What religion developed out of Judaism? Christianity. Christians recognize important events and people in Hebrew history, while also
following the 10 Commandments and considering Jerusalem to be the holiest place for Christians. However, while Christians believe that Jesus
is the Messiah, which is where the Greek name Christ comes from, Jews do not recognize that Jesus is the Messiah, nor the son of God.
18. How did Christianity spread immediately following the death of Jesus? Disciples of Jesus traveled and spread the word of Jesus… love,
kindness, and forgiveness.
SS7H5: The student will describe the importance of the Ottoman Empire to Southwest Asia (Middle East).
1. Describe the area covered by the Ottoman Empire. Turkey, Southeastern Europe, North Africa, and Southwest Asia
2. List 3 factors in the decline of the Ottoman Empire.
1. The Ottomans constantly fought to maintain control of its vast empire
2. The Ottomans were part of the losing side in World War I, in which they were defeated by the French,
British, and the United States.
3. During the 1600s, European countries could directly trade goods with China and India through trade by
sea by sailing around Africa and no longer needed to buy these goods via the Silk Road that went through
the Ottoman Empire. Also, later in 1800s the Ottomans had difficulty competing in trade with
industrialized Europe.
3. What was the name of the group of young Christian slaves who converted to Islam, trained, and became an elite group of soldiers loyal to the
sultan? Janissaries. Interesting though is that they were disbanded in 1826 after failing in their assassination attempt of the sultan. Over 6,000
were killed for turning against the sultan.
4. Who was the leader of the Ottoman Empire at its peak (during its Golden Age)? Suleiman I “The Magnificent”.
5. The Ottomans conquered this “unconquerable” city and made it their capital. Constantinople
6. Who was The Sick Man of Europe? Turkey (the Ottoman Empire)
7. Name 3 characteristics of life in the Ottoman Empire.
1. Peasants and artisans paid taxes, and the ruling class did not
2. People like Jews and Christians were free to practice the religion of their choice as long as they paid a tax.
3. People wore clothing and head coverings indicating their class and profession