* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download classification
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
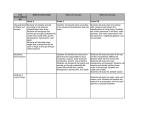
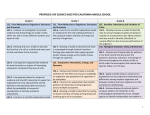
SIXTH GRADE SCIENCE Month DCI Disciplinary Core Ideas (DCI) Learning Activities August/September Lab Skills Lab Safety Demonstrate understanding and use interrelationships among central scientific concepts to revise explanations and to consider alternative explanations Use mathematical, physical and computational tools to build conceptual-based models and to pose theories Understand how scientists use design technology to solve problems Assessment Interdisciplinary connections Teacher Observation LA: RST.6-8 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 WHST 6-8 1.a.b.c.e WHST 6-8 2.a.b.d Class Discussion Explain how to conduct a science experiment Notes and study guides MATH: Understand how to make 6.RP.1; 6NS.1 tables and graphs to make Labs 6.NS.2 sense of data in a science 6.EE.1 experiment Tests .9 6.SP.1 Explain the rules for laboratory Quizzes .2 safety .3 Homework .4 .5.a,b,c,d Technology: 8.2.4.C.1 21st. Century Careers: 9.1.8.B.2 WORLD LA: 7.1.NH.A.1 7.1.NH.A.4 September/October Cell Theory and Structure MS-LS1-1 Conduct an investigation to provide evidence that living things are made of cells; either one cell or many different number and types of cells MSLS1.A *Within cells, special structures are responsible for particular functions, and that the cell membrane forms the boundary that controls what enters and leaves the cell. *In multicellular organism, the body is a system of multiple subsystems. Explain the parts of cell theory Identify the parts of the compound microscope Diagram and build different models of both the plant and animal cell Recognize that cells differ in size, shape, function, and organization Teacher Observation Class Discussions Notes and Study Guides Labs Quizzes Identify the parts of a cell and explain the function of each part Tests LA: RST.6-8 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 WHST 6-8 1.a.b.c.e WHST 6-8 2.a.b.d MATH: 6.RP.1; 6NS.1 6.NS.2 6.EE.1 .9 6.SP.1 .2 .3 .4 .5.a,b,c,d Homework MS-LS1-2 Develop and use a model to describe the function of a cell as a whole and ways parts of a cell contribute to its function. Explain how cells of onecelled organisms differ from many celled organisms Internet Explain differences among tissues, organs, and organ systems. MS-LS1-3 Use argument supported by evidence for how the body is a system of interacting subsystems composed of cells. Videos Technology: 8.1.4.A.5 21st Century Life and Careers: 9.1.8.A.1 MS-PS1-1 Develop models to describe the atomic composition of simple molecules and extended structures. PS1-A Substances are made from different types of atoms, which combine with one another in various ways. Atoms form molecules that range in size from tow to thousands of atoms. Identify what elements and compounds are Explain the organic molecules in living things November/December/ January Photosynthesis Ecosystems/Biomes Food Webs MS-LS1-6 Construct a scientific explanation based on evidence for the role of photosynthesis in the cycling of matter and flow of energy into and out of organisms. MS-LS1-7 Develop a model to describe how food is arranged through chemical reactions forming new molecules that support growth and/or release energy as this matter moves through an organism. LS1.C Plants, algae (including phytoplankton) and many other microorganisms use the energy from light to make sugars (food) from carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and water through the process of photosynthesis. Sugars can be used immediately or stored for growth or later use. Describe the process of photosynthesis and its relationship to respiration Teacher Observation Class discussions Describe the process of photosynthesis and its relationship to respiration. LA: RST.6-8 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 WHST 6-8 1.a.b.c.e WHST 6-8 2.a.b.d Notes and MATH: study guides 6.RP.1; 6NS.1 6.NS.2 Labs 6.EE.1 .9 Quizzes 6.SP.1 .2 Tests .3 .4 .5.a,b,c,d Technology: 8.2.8.A.1 Social Studies: 6.1.8.C.4.b WORLD LA: 7.1.NH.A.1 7.1.NH.A.4 PS3.D The chemical reaction by Relate visible light to pigments which plants produce complex in plants that are necessary for food molecules requires an photosynthesis. energy input (the sun) to occur. MS-LS2-1 Analyze and interpret data to provide evidence for the effects of resource availability on organisms and populations of organisms in an ecosystem. LS2.A *Organisms and populations of organisms are dependents on their environmental interactions both with other living things and with nonliving factors. *In any ecosystem organisms and populations with similar requirements for food, water, oxygen or other resources must compete with each other for limited resources, which may limit their growth and reproduction. MS-LS2-2 Construct an explanation that predicts patterns of interactions Through a variety of ways discuss and predict how predators will reduce certain populations in an ecosystem. Analyze how mutually beneficial relationships within an ecosystem, impacts that ecosystem. Dissection of an owl pellet to investigate animals in a specific food web among organisms across multiple ecosystems. MS-LS2-3 Develop a model to describe the cycling of matter and flow of energy among living and nonliving parts of an ecosystem. LS2-B Food webs are models that demonstrate how matter and energy is transferred between producers, consumers and decomposers as the three groups interact within an ecosystem. MS-ESS3- Apply scientific principles to 3 design a method for monitoring and minimizing a human impact on the environment. Build and evaluate models of Food webs in different biomes. (Including marine) using different and varied activities. Discuss and analyze the impact that global warming has had on different biomes and the organisms in that biome. Relate seasonal changes in ecosystems to the movement of Earth around the Sun. Discuss different ways in which humans can affect specific food webs and biomes. January/February CELL GROWTH AND HEREDITY MS-LS3-1 Develop and use a model to describe why structural changes to genes, located on chromosomes, may affect proteins that may result in harmful, beneficial or neutral effects to the structure and function of the organism. LS3.A Describe mitosis and explain the importance Teacher observation Explain the differences between mitosis and its end products Class discussion Name the cells involved in fertilization and explain how fertilization occurs Genes are located in the chromosomes of cells with each chromosome pair Describe the process of DNA containing two variants of each replication of many distinct genes.(Inheritance of Traits) Explain how cancer is related LS3.B to the cell cycle In addition to variations that arise from sexual reproduction, Describe Mendel’s genetic information can be experiments altered because of mutations. Variation of Traits) Explain how probability dictates the results of genetic MS-LS3-2 Develop and use a model to crosses using Punnett squares. describe why asexual reproduction results in Explain and investigate the offspring with identical role that chromosomes play in information and sexual inheritance reproduction results in offspring with genetic Describe the genetic code variation. LA: RST.6-8 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 WHST 6-8 1.a.b.c.e WHST 6-8 2.a.b.d Notes and MATH: study guides 6.RP.1; 6NS.1 6.NS.2 Labs 6.EE.1 Quizzes .9 6.SP.1 Tests .2 .3 .4 .5.a,b,c,d Health: 2.2.6.B.2 2.2.6.D.1 Technology: 8.1.8.E.1 WORLD LA: 7.1.NH.A.1 7.1.NH.A.4 Explain how mutations occur Describe patterns of inheritance in humans MS-LS1-8 Gather and synthesize information that sensory receptors respond to stimuli by sending messages to the brain for immediate behavior or storage as memories Genes determine our ability to taste the chemical PTC and how humans respond to these sensory stimuli. LS1-D Describe the relationship between genes and the science of picky eaters Each sense receptor responds to different inputs (electromagnetic, mechanical, chemical), transmitting them as signals that travel along nerve cells to the brain. The signals are then processed in the brain, resulting in immediate behaviors or memories. Describe the relationship between genes and environment. February/March CLASSIFICATION TAXONOMY MS-LS1-4 Use argument based on empirical evidence and scientific reasoning to support an explanation for how characteristic animal behaviors and specialized plant structures Affect the probability of successful reproduction of animals and plants respectively Describe the characteristics of living things Teacher observation Identify what living things need to survive Class discussion Give examples that show the need for classification systems Notes and MATH: study guides 6.RP.1; 6NS.1 6.NS.2 Labs 6.EE.1 Quizzes .9 6.SP.1 Tests .2 .3 .4 .5.a,b,c,d Describe Aristotle’s system of classification Explain Linnaeus’s system of classification Explain how taxonomic keys are used LS1.B Animals engage in characteristic behaviors that increase the odds of reproduction. Describe the relationship between classification and evolution Name the four kingdoms in Domain Eukarya Identify characters an members of each kingdom List reasons scientific names are more useful to scientists than common names. LA: RST.6-8 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 WHST 6-8 1.a.b.c.e WHST 6-8 2.a.b.d Technology: 8.1.4.A.5 21st. Century Life and Careers: 9.1.8.B.2 WORLD LA: 7.1.NH.A.1 7.1.NH.A.4 March/April EVOLUTION/BIO DIVERSITY MS-LS2-4 Construct an argument supported by empirical evidence that changes to physical or biological component of an ecosystem can lead to shifts in all its populations. MS-LS4-3 Analyze displays of a pictorial data to compare patterns of similarities in the embryological development across multiple species to identify relationships not evident in the fully formed anatomy. Identify how the atmosphere of early earth differs from today and connect the development of modern atmosphere to development of animal species Discuss different theories about how life might have begun and evolved on planet Earth Discuss evolution using Darwin’s finches to explain evolutionary concepts. Discuss how and why animal’s isolated on islands (Galapagos, Madagascar) might have developed independently. LS2.C Ecosystems are dynamic in nature: their characteristics can vary over time. Disruption to any physical or biological component of an ecosystem can lead to shifts in all its populations. MATH: 6.RP.1; 6NS.1 6.NS.2 6.EE.1 .9 6.SP.1 .2 .3 .4 .5.a,b,c,d Discuss concepts and specific examples of how and why these animals have changed and evolved over time. LA: RST.6-8 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 WHST 6-8 1.a.b.c.e WHST 6-8 2.a.b.d MS-LS2-5 Evaluate competing design solutions for maintaining and ecosystems services. LS4.D Discuss ocean diversity using the coral reefs as an example of biodiversity. (Biodiversity and Humans) Changes in biodiversity can influence humans’ resources, such as food, energy, and medicines, as well as ecosystem services that humans rely on- for example, water purification and recycling. Construct an explanation based on evidence that describes how genetic variations of traits in a population increase some MS-LS4-4 individual’s probability of Discuss how animals change surviving and reproducing in a and adapt to their specific environment. environments LS4.B MS.LS4-6 LS4.C Natural selection leads to the predominance or certain traits in a population, and the suppression of others. Use mathematical representations to support explanations of how natural selection may lead to increase and decreases of specific traits in population over time (Adaptation) Adaptation by natural selection acting over generations is one important process by which species change over time in response to changes in environment conditions. Traits that support successful survival and reproduction become more common; those that do not become less common. Thus, the distribution of traits in a population changes. Natural Selection Simulation: different traits are selected and use models to simulate what would happen in different circumstances. Age of Earth MS-ESS1- Construct a scientific 4 explanation based on evidence from rock strata for how the geologic time scale is used to organize Earth’s 4.6billion year old history. ESS1.C The geologic time scale interpreted from rock strata provides a way to organize Earth’s history. Analysis of rock strata and the fossil record provide only relative dates, not an absolute scale. MS-LS4-1 Analyze and interpret data for patterns in the fossil record that document the existence, diversity, extinction and change of life forms throughout the history of life on Earth under the assumption that natural laws operate today as in the past. Fossils MS-LS4-2 Apply scientific ideas to construct an explanation for the anatomical similarities and LS4.A May/June VIRUSES BACTERIA differences among modern Fossils organisms and between modern and fossil organisms to infer evolutionary relationships Discuss the differences Anatomical similarities and between invertebrates and differences between various vertebrates organisms living today and between them and organisms in the fossil record enable the Compare and contrast reconstruction of evolutionary vertebrate skeletons vertebrate history and the inference of skeletons lines of evolutionary descent. MS-LS1-1 Conduct an investigation to provide evidence that living things are made of cells; either one cell or many different numbers and types of cells FUNGI LS1-A KINGDOM PROTISTA All living things are made up of cells, which is the smallest unit that can be said to be alive. An organism may consist of one single cell (unicellular) or many different cells (multicellular) Explain how viruses differ from living things Describe the structure of viruses, and explain how viruses reproduce and cause disease Explain the use of vaccines in viral diseases Describe some helpful viruses Explain how cells of bacteria differ from those of eukayotes Class discussion LA: RST.6-8 1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 Notes and WHST 6-8 1.a.b.c.e study guides WHST 6-8 2.a.b.d Labs Quizzes Tests MATH: 6.RP.1; 6NS.1 6.NS.2 6.EE.1 .9 6.SP.1 .2 .3 .4 .5.a,b,c,d Describe characteristics of bacterial cells MS-LS3-2 Develop and use a model to describe why asexual reproduction results in offspring with identical genetic information and sexual reproduction results in offspring with genetic variation. LS1-B Organisms reproduce either sexually or asexually, and transfer their genetic information to their offspring. Describe the ways that bacteria reproduce (Fission and conjugation) Describe conditions in which bacteria thrive and reproduce Explain how infectious disease spread Describe treatments for bacterial and viral diseases Identify characteristics shared by all protists Describe three groups of protists Compare and contrast protist groups Describe cause and effects of saltwater and freshwater algae blooms and their effects on the environment Visual and Performing Arts: 1.1.5.C.2 Health: 2.2.6.D.2 2.3.6.A.1 WORLD LA: 7.1.NH.A.1 7.1.NH.A.4 Identify characteristics shared by all fungi Classify fungi into groups based on their method of reproductions