* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 3
DNA repair protein XRCC4 wikipedia , lookup
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
DNA nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
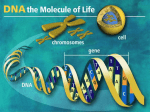
Genetics Instructor: Dr. Jihad Abdallah Lecture 3 Structure of DNA 1 • In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick proposed that DNA is a double-stranded molecule twisted into a helix (the double helix structure) • Each spiraling strand, comprised of a sugarphosphate backbone and attached bases, is connected to a complementary strand by non-covalent hydrogen bonding between paired bases. • These two strands run in opposite directions to each other and are therefore anti-parallel. • The bases are adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C) and guanine (G). • A and G are purines while T and C are pyrimidines • A and T are connected by two hydrogen bonds. G and C are connected by three hydrogen bonds. 2 • In the DNA molecule, the sum of Purines (A and G) is equal to the sum of the Pyrimidines (T and C) • The distance between two base pairs is 3.4 A° (Angistrom). • Each complete turn of the helix is 34 A° (10 base pairs). • In any segment of the molecule, alternating larger (major grooves) and smaller “minor grooves” are apparent along the axis. • The double helix measures 20 A° (2 nm) in diameter. 3 DNA molecule 4 Building units of DNA are called nucleotides 5 (Pyrimidines ) (Purines) The double helix of the DNA is shown along with details of how the bases, sugars and phosphates connect to form the structure of the molecule. 6 3.4 A° 7 Nucleotides • Nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA. Each nucleotide consists of 3 components: - Nitrogen base - Pentose sugar - Phosphate group 8 Nitrogen bases • There are two kinds of nitrogen bases: 1. Purines: double ringed (include Adinine and Guanine) 2. Pyrimidines: single-ringed (include Thymine, Cytosine, and Uracil). Thymine is specific to DNA and Uracil is specific to RNA. 9 Pyrimidines Purines 10 Pentose sugars Found in RNA Found in DNA 11 Polynucleotides • Are formed by the joining of mononucleotides. • The linkage between two mononucleotides consists of a phosphate group linked to two sugars forming a phosphodiester bond • The phosphate groups link the 3’ carbon of one deoxyribose molecule to the 5’ carbon of the next (3’ – 5’ orientation). • Joining of two mononucleotides forms a dinucleotide, joining of three nucleotides forms a trinucleotide and so on. 12 Phosphate group forming 3` - 5` phosphodiester bond 13