* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Minneapolis Community and Technical College (MCTC): Biology
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
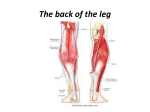
MinneapolisCommunityandTechnicalCollege(MCTC):BiologyDepartment _______________________________________________________________________________ ANATOMY LABORATORY PACKET 1 Histology: The study of Tissues Identify the following tissues, cells & tissue features (indented) on microscope slides. I. Epithelial tissue A. Simple squamous epithelium B. Simple cuboidal epithelium C. Simple columnar epithelium Goblet cell (Cell) D. Pseudostratified columnar epithelium Goblet cell E. Stratified squamous epithelium F. Transitional epithelium II. Connective Tissue (c.t.) A. Areolar connective tissue Fibroblast nucleus Elastic fibers Collagen fibers B. Adipose Adipocyte (Cell) Nucleus C. Reticular connective tissue Reticular fibers D. Dense (Fibrous) regular connective tissue Fibroblast nucleus Collagen fibers E. Dense (Fibrous) irregular connective tissue Fibroblast nucleus Collagen fibers Page 1 of 14 MinneapolisCommunityandTechnicalCollege(MCTC):BiologyDepartment _______________________________________________________________________________ F. Hyaline cartilage Chondrocyte (Cell) Lacuna Extracellular Matrix G. Elastic cartilage Chondrocyte (Cell) Lacuna Elastic fibers H. Fibrocartilage Chondrocyte (Cell) Lacuna Collagen fibers I. Compact bone (Osseous) Tissue Central canal Osteocyte (Cell) Canaliculus (Canaliculi = plural) J. Blood connective tissue Erythrocyte (Cell) Leukocyte (Cell) ` Plasma III. Muscle tissue A. Skeletal muscle tissue Nucleus Striations B. Cardiac muscle tissue Nucleus Intercalated disc Striations C. Smooth muscle tissue Nucleus IV. Nervous tissue Neuron (Cell) Cell body Nucleus Cell processes (1 axon & 1 or more dendrites) Supporting cell (Cell) Nucleus Page 2 of 14 MinneapolisCommunityandTechnicalCollege(MCTC):BiologyDepartment _______________________________________________________________________________ Integumentary System (Skin & associated structures) SKIN MODEL: Epidermis Stratum corneum Stratum lucidum (found ONLY in thick skin) Stratum granulosum Stratum spinosum Stratum basale (germinativum) Dermis Papillary region: top 1/5 of dermis which contains dermal papillae Reticular region: bottom 4/5 of dermis Dermal papillae Arrector pili muscle Mechanoreceptors: Meissner’s (Tactile) corpuscle Pacinian (Lamellar) corpuscle Glands: Sweat glands (Sudoriferous) Eccrine sweat gland (small & numerous) Apocrine sweat gland (large & fewer) Sebaceous gland Hair Hair follicle Hair bulb: expanded bottom of hair in follicle Hair papilla: indentation of hair bulb containing blood vessels and nerve Hair root: hair below surface of epidermis Hair shaft: hair above surface of epidermis Hypodermis (Subcutaneous layer): This layer binds skin to the underlying musculature. Page 3 of 14 MinneapolisCommunityandTechnicalCollege(MCTC):BiologyDepartment _______________________________________________________________________________ MICROSCOPE SLIDES of skin: Skin Layer Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous layer 1. Main Tissue type epithelial tissue dense irregular adipose tissue Thick skin Epidermis: thick in “thick skin” Stratum corneum Stratum lucidum (found ONLY in thick skin) Stratum granulosum Stratum spinosum Stratum basale (germinativum) Dermis: Papillary region Reticular region Dermal papillae Sweat glands Hypodermis: Adipose tissue 2. Thin skin: Scalp/Hair follicles Hair follicles Hair shafts Hair bulbs Sebaceous gland 3. Thin skin Epidermis: thin in “thin skin” Dermis Sweat gland Subcutaneous layer Page 4 of 14 MinneapolisCommunityandTechnicalCollege(MCTC):BiologyDepartment _______________________________________________________________________________ Microscopic Structure of Compact Bone Osteon Model Osteon (also called: Haversian system) Central canal: contains artery, vein, lymph vessel and nerve Concentric lamella (lamellae = plural) Osteocyte Lacuna (lacunae = plural) Canaliculus (canaliculi = plural) The Axial Skeleton Before you begin your study of the skeletal system, first study the definitions of general bone markings. The axial skeleton consists of 80 bones, which lie in or around the midline of the body. It consists of the skull, hyoid bone, sternum, ribs and vertebrae. Be able to identify the following bones, structures, and markings I. A. SKULL Sutures Coronal suture Sagittal suture Squamosal suture Lambdoid (Lambdoidal) suture B. Cranial Bones (8 total) Frontal Supraorbital foramen Parietal Occipital Occipital condyle Foramen magnum (hole) Hypoglossal canal (hole) Page 5 of 14 MinneapolisCommunityandTechnicalCollege(MCTC):BiologyDepartment _______________________________________________________________________________ Temporal Zygomatic process Mastoid process Styloid process External auditory (acoustic) meatus Internal acoustic meatus (hole) Carotid canal (hole) Jugular foramen (hole between occipital and temporal) Sphenoid Greater wings Lesser wings Sella turcica Optic canal (hole) Superior orbital fissure (slit-like hole) Inferior orbital fissure (slit-like hole) Foramen rotundum (hole) Foramen ovale (hole) Foramen spinosum (hole) Foramen lacerum (hole) Ethmoid Crista galli Cribriform plate Olfactory foramina (holes) Middle nasal concha Perpendicular plate Page 6 of 14 MinneapolisCommunityandTechnicalCollege(MCTC):BiologyDepartment _______________________________________________________________________________ C. Facial Bones (14 total) Lacrimal Nasal Zygomatic Temporal process Vomer Inferior nasal concha (conchae=plural) Maxilla Infraorbital foramen Palatine process Palatine Horizontal plate Mandible Body Angle Ramus Mental region Mental foramen (hole) Mandibular condyle Coronoid process Mandibular foramen (hole) D. Paranasal sinuses Frontal sinus Ethmoid sinus Maxillary sinus Sphenoid sinus II. Hyoid bone Page 7 of 14 MinneapolisCommunityandTechnicalCollege(MCTC):BiologyDepartment _______________________________________________________________________________ III. RIBS Head Neck Tubercle Shaft Costal groove Costal cartilage (on articulated thoracic cage) Type of ribs: True ribs (pairs 1-7) False ribs (pairs 8-12) Floating ribs (pairs 11 & 12) Right or Left? *Be able to differentiate between a right and a left rib by doing the following: Locate the costal groove, head and tubercle The costal groove should face inferior and the head & tubercle are posterior. IV. STERNUM Manubrium Body Xiphoid process V. VERTEBRAE (be able to identify on most vertebrae): Body (Centrum) Vertebral arch Lamina (2) Pedicle (2) Vertebral foramen Spinous process Transverse process Superior articular process and facet Inferior articular process and facet Page 8 of 14 MinneapolisCommunityandTechnicalCollege(MCTC):BiologyDepartment _______________________________________________________________________________ - Be able to determine which region of the spine each vertebra is from and identify the following distinguishing characteristics: Cervical (7): C1-C7 Atlas (C1) Transverse foramen Axis (C2) Dens (odontoid) process Transverse foramen Thoracic (12): T1-T12 Superior and inferior costal facets (articulates with head of rib) Transverse costal facet (articulates with tubercle of rib) Lumbar (5): L1-L5 Sacral (5 fused vertebrae forms sacrum): S1-S5 Coccygeal (4 fused vertebrae forms coccyx): Co1-Co4 -On an articulate vertebral column be able to identify: Intervertebral foramen Intervertebral disk The Fetal Skull Identify the six fontanels on a fetal skull Anterior fontanel (1) Posterior fontanel (1) Sphenoidal fontanel (2) Mastoid fontanel (2) Page 9 of 14 MinneapolisCommunityandTechnicalCollege(MCTC):BiologyDepartment _______________________________________________________________________________ The Appendicular Skeleton The appendicular skeleton consists of 126 bones composing two girdles and their attached limbs Girdles: incomplete rings of bone that attach the limbs onto the axial skeleton Be able to identify the following bones and bone markings Pectoral girdle: 2 clavicles, 2 scapulae (plural) Clavicle Sternal (Medial) end – circular Acromial (Lateral) end - flat Scapula 3 borders: Superior, Medial, and Lateral 3 angles: Superior, Inferior, and Lateral Glenoid cavity Spine of scapula Acromion (at the end of spine) Coracoid process Subscapular fossa (anterior surface) Supraspinous fossa (above the spine) Infraspinous fossa (below the spine) Right or Left scapula? Glenoid cavity is always lateral and spine is posterior. Humerus (the only bone in brachial region) Head (proximal and medially) Anatomical neck (crease between head and tubercle) Greater tubercle Lesser tubercle Intertubercular groove Surgical neck (on shaft, just inferior to the head) Page 10 of 14 MinneapolisCommunityandTechnicalCollege(MCTC):BiologyDepartment _______________________________________________________________________________ Humerus (continued) Deltoid tuberosity Trochlea Capitulum Medial epicondyle Lateral epicondyle Olecranon fossa Radial fossa Coronoid fossa Right or Left? Posterior view: head of humerus lies proximal & medial AND the olecranon fossa is distal & posterior. OR Anterior view: The head of humerus lies proximal & medial AND radial & Cornoid fossae are distal & inferior. Ulna (Medial bone of the antebrachial region) Coronoid process Olecranon process Trochlear notch Head (distally) Styloid process Radial notch Radius (Lateral bone of the antebrachial region) Head (Proximal) Radial tuberosity Ulnar notch Styloid process Carpals (know 2 out of 8) Scaphoid Lunate Page 11 of 14 MinneapolisCommunityandTechnicalCollege(MCTC):BiologyDepartment _______________________________________________________________________________ Metacarpals form the palm (Know all 5) I, II , III, IV, V Phalanges (Phalanx singular) All digits except the pollex (thumb) have three phalanges Proximal Middle Distal For example: The “wedding ring” is on Fourth proximal phalanx Pelvis **pelvic girdle (2 coxal bones) + sacrum + coccyx *Be able to determine whether a pelvis is male or female. Pelvic girdle: 2 coxal bones Coxal bones (Each coxal bone is composed of the ilium, ischium & pubis) Acetabulum Obturator foramen Ilium Iliac crest Anterior superior iliac spine Anterior inferior iliac spine Posterior superior iliac spine Posterior inferior iliac spine Greater sciatic notch Iliac fossa Auricular surface Ischium Ischial spine Ischial ramus Lesser sciatic notch Ischial tuberosity Page 12 of 14 MinneapolisCommunityandTechnicalCollege(MCTC):BiologyDepartment _______________________________________________________________________________ Pubis Superior ramus of pubis Pubic body Inferior ramus of pubis Right or Left? Acetabulum has to be lateral and the auricular surface posterior. Femur Head (proximal & projects medial) Neck (area in between head and trochanters) Greater trochanter Lesser trochanter Intertrochanteric groove (intertrochanteric line) Linea Aspera (on posterior side) Lateral epicondyle Medial epicondyle Lateral condyle Medial condyle Intercondylar fossa (distal & posterior) Right or Left? Posterior view: head of femur lies proximal & medial AND the intercondylar fossa is distal & posterior. Patella: The largest sesamoid bone in the body. Tibia Medial condyle Lateral condyle Tibial tuberosity Medial malleolus Page 13 of 14 MinneapolisCommunityandTechnicalCollege(MCTC):BiologyDepartment _______________________________________________________________________________ Fibula Lateral malleolus Head Tarsals (Know 2 out of 7) Calcaneus Talus Metatarsals (Know all 5) I, II , III, IV, V Phalanges (Phalanx singular) Proximal Middle Distal Synovial Joint Learn the following structures on the knee joint model: Lateral (Fibular) collateral ligament Medial (Tibial) collateral ligament Anterior cruciate ligament Posterior cruciate ligament Medial meniscus Lateral meniscus Patellar ligament Quadriceps tendon *Also on the articulated knee joint model be able to identify the bones: Patella, Fibula, Tibia & Femur and the associated bone features Page 14 of 14