* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Score Booster Project
Probability amplitude wikipedia , lookup
Tight binding wikipedia , lookup
Path integral formulation wikipedia , lookup
Copenhagen interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization wikipedia , lookup
Renormalization group wikipedia , lookup
Quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Ferromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Coherent states wikipedia , lookup
Spin (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Wave–particle duality wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital wikipedia , lookup
Quantum entanglement wikipedia , lookup
Many-worlds interpretation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum dot wikipedia , lookup
Quantum fiction wikipedia , lookup
Bell's theorem wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Orchestrated objective reduction wikipedia , lookup
Quantum computing wikipedia , lookup
Particle in a box wikipedia , lookup
Quantum electrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Interpretations of quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Quantum teleportation wikipedia , lookup
Quantum machine learning wikipedia , lookup
Quantum key distribution wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Quantum group wikipedia , lookup
EPR paradox wikipedia , lookup
Canonical quantization wikipedia , lookup
Hidden variable theory wikipedia , lookup
Symmetry in quantum mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Quantum state wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen atom wikipedia , lookup
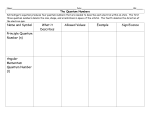
Students ScoreBooster Series Videos WAEC, SSCE, GCE, JAMB (UTME), NECO and NABTEB www.scoreboosterproject.com 1 Chemistry Atomic Structure cont’d Presented by A.A.S Lateef (Feb., 2016) www.scoreboosterproject.com 2 THE ELECTRON • Learning objectives, at the end of this lecture, students should be able to describe the four quantum numbers Be able to name and draw the shapes of the four quantum numbers Have insights into writing the electronic configurations of the elements www.scoreboosterproject.com 3 Structure of Atom www.scoreboosterproject.com 4 Locating the Electron • Locating the electrons now uses quantum mechanical model of the atom • It is a highly mathematical model • It states that the position and the momentum of electrons can be determined at the same time • Scientists developed the concept of orbitals- the volume of space where electrons are found, to describe the position of electrons www.scoreboosterproject.com 5 Four Quantum Numbers • Scientists introduced four quantum numbers to describe the characteristics of electrons and their orbitals • These are; Principal quantum number, n Angular momentum (or azimuthal) quantum number, l Magnetic quantum number, m Spin quantum number, s www.scoreboosterproject.com 6 Four Quantum Numbers (cont’d) Table 1.1 The four quantum numbers and their descriptions Name Symbol Description Allowed Values Principal n Orbital energy Positive integers (1,2,3,….) Angular momentum l Orbital shape Integers from 0 to n-1 Magnetic m Orientation Integers from –l to +l Spin s Electron spin +1/2 or -1/2 www.scoreboosterproject.com 7 Principal Quantum Number (n) • This describes the average distance of orbitals from the nucleus • It also describes the energy of the electron in an atom • The higher the value of n, the higher the energy and the larger the orbital • It can only have positive integer i.e. n = 1,2,3,4,5,… • The value of n can not be negative www.scoreboosterproject.com 8 Angular momentum Quantum Number (l) • • • • • • This is also called Azimuthal quantum number It describes the shape of the orbital. The value is limited by the value of n It can only have positive integer i.e. n = 0 to n-1 E.g. if n =2, l = 0 and 1 NB: value of l defines the shape of the orbital and n defines the size • Orbitals that have the same value of n but different l values are called subshells- these are given letters for easy recognition. www.scoreboosterproject.com 9 Angular momentum Quantum Number (l) Table 1.2 Letter designation of the subshells l value Letter 0 s 1 P 2 d 3 f 4 g NB: Complete shell specification is done by specifying the values of n and l e.g. 2s, 3p www.scoreboosterproject.com 10 Magnetic Quantum Number (m) • Orientation of the orbitals in space is described by this quantum number • The value of m depends on the value of l (m = -I to +l) • E.g. if l =1, m = -1, 0, +1 • This means that there are 3 different p-subshells for a particular orbital. These subshells have the same energy but different orientations in space. www.scoreboosterproject.com 11 Spin Quantum Number (s) • It describes the direction of spin of electron in a magnetic field---- clockwise or anticlockwise • Only two values are allowed which are +1/2 and -1/2 • NB: for each subshell, there can only be maximum of 2 electrons (one with +1/2 and the other with -1/2). Table 1.3 Quantum Numbers for the first two energy levels www.scoreboosterproject.com 12 In summary, • There are four quantum numbers • They are collectively used to specify the position and energy of a shell as well as the shape of the orbitals • There letters that are used to specify the orbitals are s, p, d, f etc n l(0 to n-1) m(-l ..0..+l) Orbitals allowed s 1 0 0 s +1/2, -1/2 2 0,1 -1, 0, +1 s, p +1/2, -1/2 3 0, 1, 2 -2, -1, 0, +1, +2 s, p, d +1/2, -1/2 www.scoreboosterproject.com 13 Exercises 1. Using the Table 1.1, determine the four quantum numbers for an atom with energy levels n = 3 and 4, then find the maximum number of electrons each of the shells can contain. 2. Write the name of the shapes of s, p and d orbitals. www.scoreboosterproject.com 14 Solution 1. • For n =3, • l = 0,1,2 (s, p, d) • m = -2, -1, 0, 1, 2 • • • • • 2. Maximum number of electron = 18 (i.e 2x 9subshells) For n =4, l = 0,1,2,3 (s, p, d, f) m = -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2,3 Maximum number of electron = 32 (i.e 2x 16subshells) s= spherical p = dumb-bell d = double dumb-bell www.scoreboosterproject.com 15 Curriculum Vitae Full name: Saheed Adewale, LATEEF Email: [email protected] Educational Background Kwara State Polytechnic, Ilorin (2005-2007), [ND, Science Technology]. Federal University of Technology, Minna (2008-2012), [B.Eng. Chemical Engineering]. King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals, Saudi Arabia (2014-2016), [MSc, Chemical Engineering]. Awards won Best Polytechnic graduating student (Kwara Polytechnic, 2007). Best Undergraduate Design Project (FUTMinna, 2012). www.scoreboosterproject.com 16 Please like and share this video www.scoreboosterproject.com 17