* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
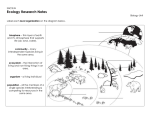
Name:________________________ Date:____________ Period:_____ Unit 1: Scientific Method and Ecology Study Guide Things to study: What is a hypothesis What is the difference between a hypothesis and a theory What’s the definition of a theory What is a controlled experiment What are the steps of the scientific method Definitions of species, population, community, ecosystem, biome, biosphere How does Earth/all living things get their energy? Know how to read a food web and a food chain What are producers and consumers What are autotrophs and heterotrophs Know the difference between herbivores, carnivores, omnivores, decomposers and detritevores Three types of symbiotic relationships: mutualism, commensalisms, parasitism Know how to read an energy pyramid How much energy is transferred between each trophic level Carbon cycle and nitrogen cycle Water cycle 1. The biosphere contains ___________________________________________. 2. The study of interactions among organisms and between organisms is called _______________. 3. One rabbit is an example of a ___________ (species/population/community). 4. A group of the same rabbits living in the same area is called ______________ (species/population/community). 5. A species makes up a ____________ (population/community). A group of different populations makes up a _________ (biome/community). 6. The source for all living things is the ___________. 7. Autotrophs are also known as ___________ (producers/consumers) because they make their own food. Heterotrophs are also known as __________ (producers/consumers) because they have to find their food. 8. What are the two ways autotrophs make their food? _______________ and _________________ 9. A herbivore is a consumer that only eats ______________. 10. A carnivore is a consumer that only eats ______________. 11. An omnivore is a consumer that eats ________________. 12. A decomposer is a consumer that _____________________. 13. Plants are known as ______________ (producers/consumers) 14. Algae found at the bottom of the ocean is a ________________ (producer/consumer) 15. An organism that uses energy from the environment to produce it’s own food is called a(an) ___________ (heterotroph/autotroph). 16. Define a primary consumer. What do they normally eat? ___________________________________________. 17. A snake that eats a mouse that has eaten a bug that fed on grass is know as what type of consumer __________________________ (primary/secondary/tertiary). 18. How much energy is passed on or transferred at each trophic level of an energy pyramid? _________________ 19. What happens to the rest of the energy?______________________________________________________ 20. What to plants and animals use their energy for? ____________________________________________ 21. The repeated movement between water and Earth’s surface and atmosphere is called the _____________ cycle. 22. Define transpiration. ______________________________________________. 23. Define evaporation. ________________________________________________ 24. Define condensation __________________________________________________ 25. Define precipitation ____________________________________________________ 26. How is carbon stored in the atmosphere? _____________________________ 27. What are the key players in the nitrogen cycle? ________________________ 28. Define commensalism and give one example. _______________________________________________ 29. Define mutualism and give one example. __________________________________________________ 30. Define parasitism and give one example _________________________________________________________ 31. You suggest that leaving your trashcan outside might cause maggots to appear. This is a _______________ (conclusion/hypothesis/procedure/result) 32. A hypothesis is always _________________________ (correct/wrong/testable) 33. Define a controlled experiment. ______________________________________ 34. Define a theory ________________________________________________________ 35. How is a theory different from a hypothesis? ____________________________________________________ 36. What are 3 abiotic factors in an ecosystem? _____________________________________________________ 37. What are 3 biotic factors in an ecosystem?_______________________________________________________ 38. If an animal leaves its usual habitat to find food because of sudden rainfall, this would be a result of a(an) ___________________ (abiotic/biotic) factor. 39. An animal leaves its usual habitat because its home has been invaded by another species. This is a result of a(an) _______________ (abiotic/biotic) factor.